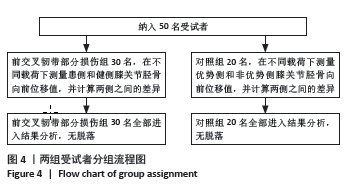
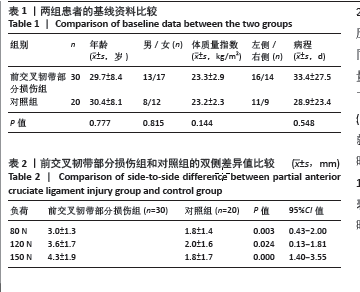
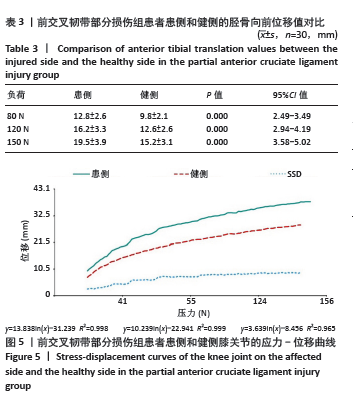
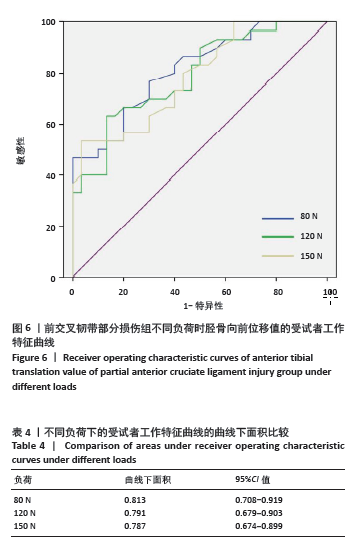
[1] 吴秀霖,徐俊杰,叶梓鹏,等.前交叉韧带损伤合并髌骨不稳研究进展[J].国际骨科学杂志,2024,45(1):11-14,18.
[2] KHAN T, ALVAND A, PRIETO-ALHAMBRA D, et al. ACL and meniscal injuries increase the risk of primary total knee replacement for osteoarthritis: a matched case-control study using the Clinical Practice Research Datalink (CPRD). Br J Sports Med. 2019;53(15):965-968.
[3] STONE AV, MARX S, CONLEY CW, et al. Management of Partial Tears of the Anterior Cruciate Ligament: A Review of the Anatomy, Diagnosis, and Treatment. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2021;29(2):60-70.
[4] DALLO I, CHAHLA J, MITCHELL JJ, et al. Biologic approaches for the treatment of partial tears of the anterior cruciate ligament: A current concepts review. Orthop J Sports Med. 2017;5(1):2325967116681724.
[5] 吕琦,马春辉,王培军,等. 3.0T MRI评估青年人群膝关节前交叉韧带(ACL)损伤的危险相关因素[J]. 复旦学报(医学版),2014, 41(5):667-672.
[6] FILBAY SR, GRINDEM H. Evidence-based recommendations for the management of anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) rupture. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol. 2019;33(1):33-47.
[7] RUNER A, SARSINA TRD, STARKE V, et al. The evaluation of Rolimeter, KLT, KiRA and KT-1000 arthrometer in healthy individuals shows acceptable intra-rater but poor inter-rater reliability in the measurement of anterior tibial knee translation. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2021;29(8):2717-2726.
[8] LI JQ, TANG JX, YAO L, et al. The validity of the Ligs digital arthrometer at different loads to evaluate complete ACL ruptures. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2023;11:1049100.
[9] CHEN Y, CAO S, WANG C, et al. Quantitative analysis with load–displacement ratio measured via digital arthrometer in the diagnostic evaluation of chronic ankle instability: a cross-sectional study. J Orthop Surg Res. 2022;17(1):287.
[10] KAEDING CC, LÉGER-ST-JEAN B, MAGNUSSEN RA. Epidemiology and diagnosis of anterior cruciate ligament injuries. Clin Sports Med. 2017;36:1-8.
[11] WHITTAKER JL, WOODHOUSE LJ, NETTEL-AGUIRRE A, et al. Outcomes associated with early post-traumatic osteoarthritis and other negative health consequences 3–10 years following knee joint injury in youth sport. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2015;23:1122-1129.
[12] JOHNSON VL, ROE JP, SALMON LJ, et al. Does age influence the risk of incident knee osteoarthritis after a traumatic anterior cruciate ligament injury? Am J Sports Med. 2016;44:2399-2405.
[13] FILBAY SR, ACKERMAN IN, RUSSELL TG, et al. Return to sport matters—longer-term quality of life after ACL reconstruction in people with knee difficulties. Scand J Med Sci Sports. 2017;27:514-524.
[14] SANDERS TL, MARADIT KREMERS H, BRYAN AJ, et al. Incidence of anterior cruciate ligament tears and reconstruction. Am J Sports Med. 2016;44:1502-1507.
[15] ARDERN CL, EKÅS G, GRINDEM H, et al. 2018 International Olympic Committee consensus statement on prevention, diagnosis and management of paediatric anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) injuries. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2018;26:989-1010.
[16] MUSAHL V, KARLSSON J. Anterior Cruciate Ligament Tear. N Engl J Med. 2019;380:2341-2348.
[17] MAGNUSSEN RA, PEDROZA AD, DONALDSON CT, et al. Time from ACL injury to reconstruction and the prevalence of additional intra-articular pathology: is patient age an important factor? Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2013;21:2029-2034.
[18] SRI-RAM K, SALMON LJ, PINCZEWSKI LA, et al. The incidence of secondary pathology after anterior cruciate ligament rupture in 5086 patients requiring ligament reconstruction. Bone Joint J. 2013;95-B: 59-64.
[19] MULLIGAN EP, MCGUFFIE DQ, COYNER K, et al. The reliability and diagnostic accuracy of assessing the translation endpoint during the Lachman test. Int J Sports Phys Ther. 2015;10:52-61.
[20] LEBLANC MC, KOWALCZUK M, ANDRUSZKIEWICZ N, et al. Diagnostic accuracy of physical examination for anterior knee instability: a systematic review. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2015;23(10): 2805-2813.
[21] SOKAL PA, NORRIS R, MADDOX TW, et al. The diagnostic accuracy of clinical tests for anterior cruciate ligament tears are comparable but the Lachman test has been previously overestimated: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2022; 30(10):3287-3303.
[22] LELLI A, TURI RPD, SPENCINER DB, et al. The “Lever Sign”: A new clinical test for the diagnosis of anterior cruciate ligament rupture. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2016;24(9):2794-2797.
[23] COOPERMAN JM, RIDDLE DL, ROTHSTEIN JM. Reliability and validity of judgments of the integrity of the anterior cruciate ligament of the knee using the Lachman’s test. Phys Ther. 1990;70(4):225-233.
[24] GUNAYDIN B, SAHIN GG, SARI A, et al. Corrigendum to “A new method for diagnosis of anterior cruciate ligament tear: MRI with maximum flexion of knee in the prone position: A case control study” [Int. J. Surg. 68 (2019) 142-147]. Int J Surg. 2020:73:123.
[25] VAN DYCK P, DE SMET E, VERYSER J, et al. Partial tear of the anterior cruciate ligament of the knee: injury patterns on MR imaging. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2012;20(2):256-261.
[26] TORZILLI PA, PANARIELLO RA, FORBES A, et al. Measurement reproducibility of two commercial knee test devices. J Orthop Res. 1991;9:730-737.
[27] BACH BR, WARREN RF, FLYNN WM, et al. Arthrometric evaluation of knees that have a torn anterior cruciate ligament. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1990;72:1299-1306.
[28] BALLANTYNE BT, FRENCH AK, HEIMSOTH SL, et al. Influence of examiner experience and gender on interrater reliability of KT-1000 arthrometer measurements. Phys Ther. 1995;75:898-906.
[29] ROBNETT NJ, RIDDLE DL, KUES JM. Intertester reliability of measurements obtained with the KT-1000 on patients with reconstructed anterior cruciate ligaments. J Orthop Sports Phys Ther. 1995;21(2):113-119.
[30] WIERTSEMA SH, VAN HOOFF HJ, MIGCHELSEN LA, et al. Reliability of the KT1000 arthrometer and the Lachman test in patients with an ACL rupture. Knee. 2008;15(2):107-110.
[31] BOYER P, DJIAN P, CHRISTEL P, et al. Reliability of the KT-1000 arthrometer (Medmetric) for measuring anterior knee laxity: comparison with Telos in 147 knees. Rev Chir Orthopédique Réparatrice Appar Mot. 2004;90(8):757-764.
[32] SERNERT N, HELMERS J, KARTUS C, et al. Knee-laxity measurements examined by a left-hand- and a right-hand-dominant physiotherapist, in patients with anterior cruciate ligament injuries and healthy controls. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2007;15(10): 1181-1186.
[33] PAPANDREOU MG, ANTONOGIANNAKIS E, KARABALIS C, et al. Inter-rater reliability of Rolimeter measurements between anterior cruciate ligament injured and normal contra lateral knees. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2005;13(7):592-597.
[34] HATCHER J, HATCHER A, ARBUTHNOT J, et al. An investigation to examine the inter-tester and intra-tester reliability of the Rolimeter knee tester, and its sensitivity in identifying knee joint laxity. Randomized Controlled Trial. 2005;23(6):1399-1403.
[35] ERICSSON D, ÖSTENBERG AH, ANDERSSON E, et al.Test-retest reliability of repeated knee laxity measurements in the acute phase following a knee trauma using a Rolimeter. J Exerc Rehabil. 2017;13(5):550-558.
[36] ROHMAN EM, MACALENA JA. Anterior cruciate ligament assessment using arthrometry and stress imaging. Curr Rev Musculoskelet Med. 2016;9(2):130-138.
[37] RYU SM, NA HD, SHON OJ, et al. Diagnostic Tools for Acute Anterior Cruciate Ligament Injury: GNRB, Lachman Test, and Telo. Knee Surg Relat Res. 2018;30(2):121-127.
[38] KIM SH, PARK YB, HAM DW, et al. Stress radiography at 30° of knee flexion is a reliable evaluation tool for high-grade rotatory laxity in complete ACL-injured knees. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2020;28(7):2233-2244.
[39] RAGGI F, SARSINA TRD, SIGNORELLI C, et al. Triaxial accelerometer can quantify the Lachman test similarly to standard arthrometers. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2019;27:2698-2703.
[40] MASSEY PK, HARRIS JD, WINSTON LA, et al. Critical Analysis of the Lever Test for Diagnosis of Anterior Cruciate Ligament Insufficiency. Arthroscopy. 2017;33(8):1560-1566.
[41] WU D, WANG DH, HAN YJ, et al. A novel digital arthrometer to measure anterior tibial translation. J Orthop Surg Res. 2023;18(1):101.
|