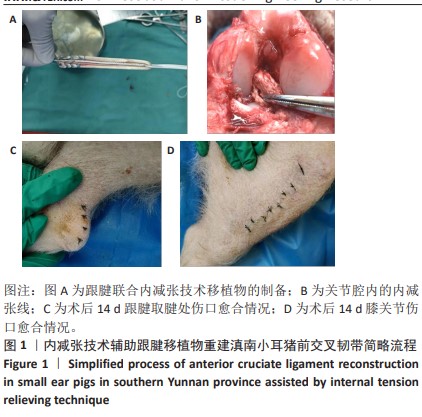
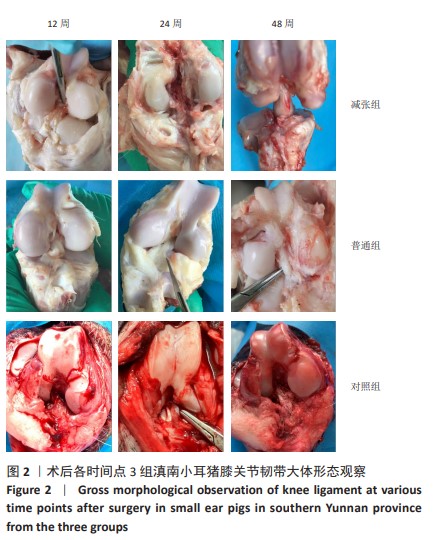
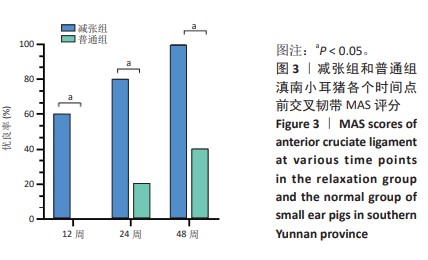
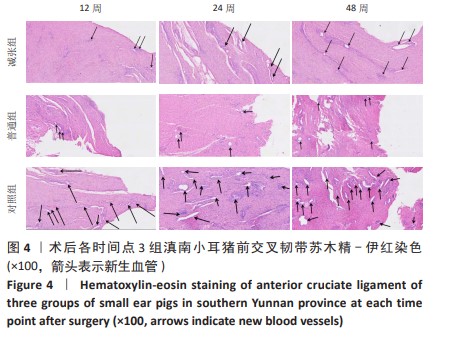
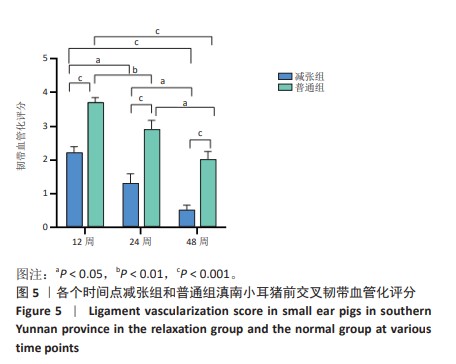
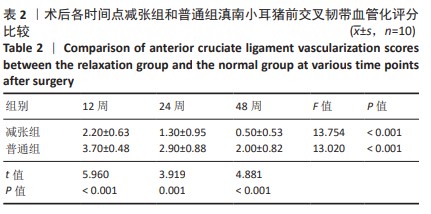
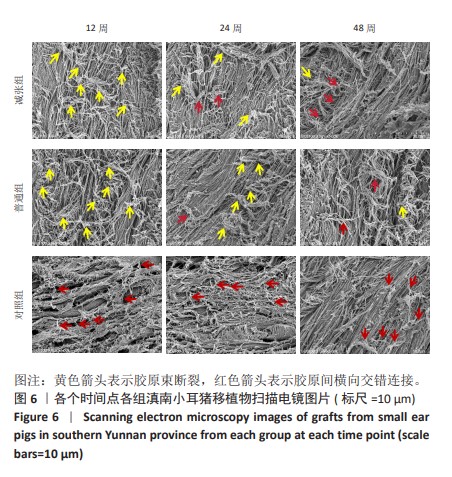
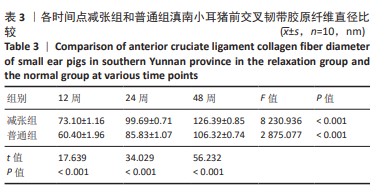
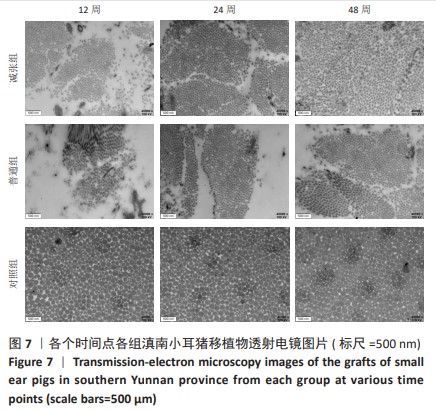
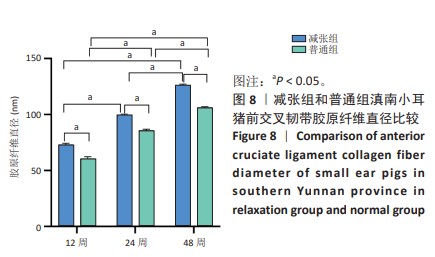
[1] 姜文斌,于胜波,隋鸿锦.前交叉韧带损伤的研究进展[J].中国临床解剖学杂志,2022,40(3):369-371,375.
[2] 李光磊,王宝鹏,张汉宽,等.前交叉韧带解剖学研究进展[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2021,29(16):1491-1495.
[3] KOTSIFAKI R, KORAKAKIS V, KING E, et al. Aspetar clinical practice guideline on rehabilitation after anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction. Br J Sports Med. 2023;57(9):500-514.
[4] SAKI F, SHAFIEE H, TAHAYORI B, et al. The effects of core stabilization exercises on the neuromuscular function of athletes with ACL reconstruction. Sci Rep. 2023;13(1):2202.
[5] BUCKTHORPE M, GOKELER A, HERRINGTON L, et al. Optimising the Early-Stage Rehabilitation Process Post-ACL Reconstruction. Sports Med. 2024;54(1):49-72.
[6] HEUSDENS CHW. ACL repair: a game changer or will history repeat itself? A critical appraisal. J Clin Med. 2021;10(5):912.
[7] 韦钊岚,韦朝喜,易伟林,等.“长袖套”保留残迹前交叉韧带重建术[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2021,29(24):2261-2264.
[8] 韦宝堂,韦力,邹亮.关节镜下内减张技术重建膝关节前交叉韧带的效果分析[J].微创医学,2019,14(5):577-579.
[9] WILSON WT, HOPPER GP, BANGER MS, et al. Anterior cruciate ligament repair with internal brace augmentation: A systematic review. Knee. 2022;35:192-200.
[10] 龚熹,余家阔,敖英芳.最大化保留残端结合内减张技术单束重建后交叉韧带临床疗效观察[J].中国运动医学杂志,2013,32(2):101-103,156.
[11] 马勇,崔国庆,敖英芳,等.后内束减张经胫骨骨道双束重建后交叉韧带[J].中国运动医学杂志,2012,31(11):957-961.
[12] 毛健宇,李彦林,王国梁,等.减张技术解剖重建前交叉韧带结合术后快速康复治疗前交叉韧带断裂[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2018, 20(1):38-44.
[13] 刘德健,李彦林,毛健宇,等.内减张技术辅助前交叉韧带重建的运动学分析[J].中华关节外科杂志 (电子版),2020,14(1):17-23.
[14] 李彦林,王国梁,毛健宇,等. 一种用于交叉韧带重建的减张线及其编织方法[P].中国:CN107280809A. 2017-10-24.
[15] 熊波涵,卢晓君,薛文强,等.内减张技术辅助前交叉韧带重建对滇南小耳猪关节软骨的保护作用[J].中国组织工程研究,2024, 28(14):2221-2226.
[16] 熊波涵,余洋,郑礼玲,等.滇南小耳猪自体跟腱移植前交叉韧带重建模型的构建[J].中国组织工程研究,2024,28(20):3157-3163.
[17] 敖英芳.膝关节交叉韧带外科学[M].北京:北京大学医学出版社,2009.
[18] 吴冰,丘志河,李盛,等.自体腘绳肌腱移植重建前交叉韧带后移植物的组织学研究[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2018,32(7):873-879.
[19] YOSHIMIZU R, NAKASE J, OKUDA M, et al. Ligamentization of the reconstructed ACL differs between the intraarticular and intraosseous regions: A quantitative assessment using UTE-T2* mapping. PLoS One. 2022;17(7):e0271935.
[20] ÖZBEK EA, KOCAOĞLU H, KARACA MO,et al. Effect of Soft Tissue Interposition and Postoperative Suspensory Cortical Button Migration on Functional Outcomes and Ligamentization After Single-Bundle ACL Reconstruction. Orthop J Sports Med. 2022;10(9):23259671221122748.
[21] WANG HD, LI Z, HU X, et al. Efficacy of Stem Cell Therapy for Tendon Graft Ligamentization After Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction: A Systematic Review. Orthop J Sports Med. 2022;10(6):23259671221098363.
[22] XU Y, AO YF. Histological and biomechanical studies of inter-strand healing in four-strand autograft anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction in a rabbit model. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2009;17(7):770-777.
[23] XIE X, CAI J, LI D, et al. Multiphasic bone-ligament-bone integrated scaffold enhances ligamentization and graft-bone integration after anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction. Bioact Mater. 2023:31:178-191.
[24] DE ROUSIERS A, ROUGEREAU G, ROUSSELIN B, et al. Adaptation of the Signal Noise Quotient MRI classification for graft ligamentization analysis following ATFL and CFL anatomical reconstruction: Validation of the SNQA. Foot Ankle Surg. 2023;29(3):243-248.
[25] YEO PY, SEAH AMJ, VISVALINGAM V, et al. Anterior cruciate ligament rupture and associated Segond fracture: Incidence and effect on associated ligamentous and meniscal injuries. Asia Pac J Sports Med Arthrosc Rehabil Technol. 2022:30:36-40.
[26] FORSYTHE B, CHAHLA J, KORRAPATI A, et al. Bone Marrow Aspirate Concentrate Augmentation May Accelerate Allograft Ligamentization in Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction:A Double-Blinded Randomized Controlled Trial. Arthroscopy. 2022;38(7):2255-2264.
[27] 徐飞,李彦林,王国梁,等.内减张技术在辅助前交叉韧带重建中的研究进展[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2021,35(12):1630-1636.
[28] 刘德健,李彦林,毛健宇,等.内减张技术辅助前交叉韧带重建的运动学分析[J].中华关节外科杂志(电子版),2020,14(1):17-23.
[29] 余洋,赵正吕,谢冰,等.关节镜下内减张技术辅助解剖单束重建后交叉韧带结合快速康复治疗后交叉韧带断裂的临床疗效[J].中华创伤杂志,2023,39(7):593-602.
[30] WU B, ZHAO Z, LI S, et al. Preservation of remnant attachment improves graft healing in a rabbit model of anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction. Arthroscopy. 2013;29(8):1362-1371.
[31] SNAEBJÖRNSSON T, HAMRIN SENORSKI E, SUNDEMO D, et al. Adolescents and female patients are at increased risk for contralateral anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction: a cohort study from the Swedish National Knee Ligament Register based on 17,682 patients. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2017;25(12):3938-3944.
[32] GREVENSTEIN D, OPPERMANN J, WINTER L, et al. First detection of primary cilia in injured human anterior cruciate ligament: A pilot study with pathophysiological reflections. Pathol Res Pract. 2022;237:154036.
[33] YANG JH, CHANG M, KWAK DS, et al. In vivo three-dimensional imaging analysis of femoral and tibial tunnel locations in single and double bundle anterior cruciate ligament reconstructions. Clin Orthop Surg. 2014;6(1):32-42.
[34] YAHIA LH, DROUIN G. Microscopical investigation of canine anterior cruciate ligament and patellar tendon: collagen fascicle morphology and architecture. J Orthop Res. 1989;7(2):243-251.
[35] KAKU N, SHIMADA T, TANAKA A, et al. Ultrastructure and three-dimensional architecture of the anterior cruciate ligament in the knee joints of young and old monkeys. Med Mol Morphol. 2020;53(1):7-14. |