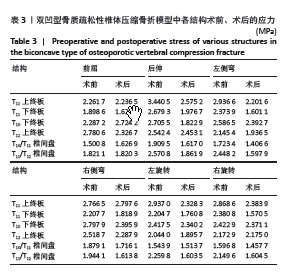
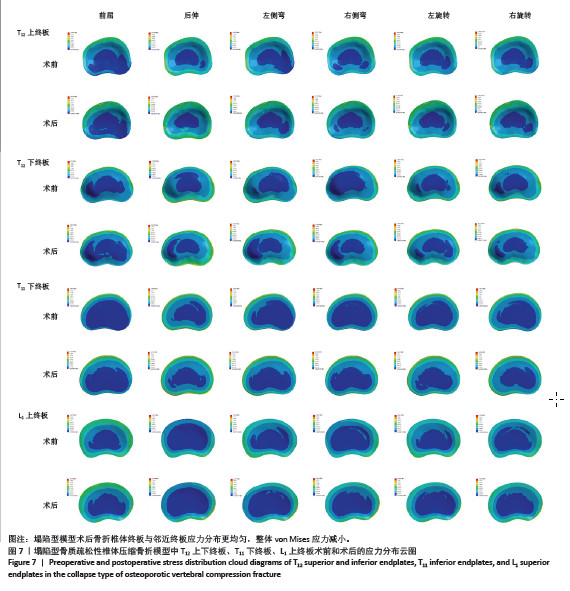
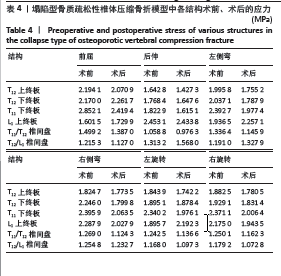
[1] 中华医学会骨质疏松和骨矿盐疾病分会,章振林.原发性骨质疏松症诊疗指南(2022)[J].中国全科医学,2023,26(14):1671-1691.
[2] WANG F, SUN R, ZHANG SD, et al. Comparison of thoracolumbar versus non-thoracolumbar osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures in risk factors, vertebral compression degree and pre-hospital back pain. J Orthop Surg Res. 2023;18(1):643.
[3] KAWANISHI M, TANAKA H, ITO Y, et al. Treatment for Osteoporotic Vertebral Fracture - A Short Review of Orthosis and Percutaneous Vertebroplasty and Balloon Kyphoplasty. Neurospine. 2023;20(4):1124-1131.
[4] 任亚楠.椎体强化术治疗骨质疏松椎体压缩性骨折的生物力学分析[D].天津:天津理工大学,2023.
[5] CAZZATO RL, BELLONE T, SCARDAPANE M, 等.椎体强化术可降低骨质疏松性椎体压缩骨折病人的12个月死亡率和发病率[J].国际医学放射学杂志,2022,45(1):117.
[6] ZHU D, HU JN, WANG L, et al. A Modified Unilateral Extrapedicular Approach Applied to Percutaneous Kyphoplasty to Treat Lumbar Osteoporotic Vertebral Compression Fracture: A Retrospective Analysis. Pain Physician. 2023;26(3):E191-E201.
[7] 顾晨希,虞宵,黄安全,等.单侧椎体后外上方入路与双侧椎弓根入路行椎体成型术治疗骨质疏松性椎体压缩骨折的生物力学对比研究[J].生物骨科材料与临床研究,2022,19(5):16-20+26.
[8] 杨春雷,王岩群,王卫国,等.研究单侧与双侧经皮椎体后凸成形术治疗老年骨质疏松性胸腰椎压缩性骨折的效果[J].中国现代药物应用,2024,18(4):30-33.
[9] 柴大起,马成才.单侧与双侧椎弓根穿刺经皮椎体后凸成形术治疗老年骨质疏松性椎体压缩骨折的疗效比较[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2022,37(7):708-711.
[10] 张立创,杨雯,丁广江,等. 个体化单侧椎弓根外入路与双侧椎弓根入路椎体成形后骨水泥的弥散效果 [J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025,29(4):800-808.
[11] 包志强,陈国强,陈贤艺,等.骨质疏松性胸腰椎压缩骨折经皮椎体成形术后非手术椎体继发骨折的危险因素分析[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2024,39(1):73-76.
[12] WANG JN, XIE W, SONG DW, et al. Recurrence of Local Kyphosis After Percutaneous Kyphoplasty: The Neglected Injury of the Disc-Endplate Complex. Clin Interv Aging. 2023;18:827-834.
[13] MELTON LJ, LANE AW, COOPER C, et al. Prevalence and incidence of vertebral deformities. Osteoporos Int. 1993;3(3):113-119.
[14] ISMAIL AA, COOPER C, FELSENBERG D, et al. Number and type of vertebral deformities: epidemiological characteristics and relation to back pain and height loss. European Vertebral Osteoporosis Study Group. Osteoporos Int. 1999;9(3):206-213.
[15] 权祯,秦大平,张晓刚,等.骨质疏松性椎体压缩骨折强化术后骨组织-骨水泥界面生物力学应力再平衡机制的有限元研究[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2023,33(12):1107-1118.
[16] 吴智华,李任,潘慧玲,等.骨水泥弥散类型对强化椎体生物力学特性影响的有限元分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2023,27(30):4763-4768.
[17] 程明,彭诗语,江娇,等.不同治疗方法对骨质疏松性胸腰椎压缩骨折椎体力学稳定性影响的有限元分析[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2022,36(12):1519-1523.
[18] BOGER A, HEINI P, WINDOLF M, et al. Adjacent vertebral failure after vertebroplasty: a biomechanical study of low-modulus PMMA cement. Eur Spine J. 2007;16(12):2118-2125.
[19] PENG Y, DU X, HUANG L, et al. Optimizing bone cement stiffness for vertebroplasty through biomechanical effects analysis based on patient-specific three-dimensional finite element modeling. Med Biol Eng Comput. 2018;56(11):2137-2150.
[20] 赵文韬,秦大平,张晓刚,等.骨质疏松性椎体压缩骨折椎体强化术后不同椎体高度对相邻椎体应力影响的有限元分析[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2018,24(9):1141-1147.
[21] LIANG D, YE LQ, JIANG XB, et al. Biomechanical effects of cement distribution in the fractured area on osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures: a three-dimensional finite element analysis. J Surg Res. 2015; 195(1):246-256.
[22] ZUO XH, CHEN YB, XIE P, et al. Finite element analysis of wedge and biconcave deformity in four different height restoration after augmentation of osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures. J Orthop Surg Res. 2021;16(1):138.
[23] YANG H, LIU H, WANG S, et al. Review of Percutaneous Kyphoplasty in China. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2016;41 Suppl 19:B52-B58.
[24] ZINDRICK MR, WILTSE LL, DOORNIK A, et al. Analysis of the morphometric characteristics of the thoracic and lumbar pedicles. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1987;12(2):160-166.
[25] 蒲俊刚,范伟力,赵建华,等.单侧个体化经椎弓根旁入路穿刺椎体成形术在中段胸椎骨质疏松性椎体压缩骨折中的应用[J].创伤外科杂志,2019,21(8):574-578.
[26] 熊小明,宋偲茂,万趸,等.CT影像数据指导单侧入路经皮椎体后凸成形术治疗椎体压缩性骨折[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2012,20(22): 2035-2038.
[27] 刘祥飞,何金国,蒋钰钢,等.单侧与双侧入路椎体成形术治疗老年骨质疏松性椎体压缩骨折的有限元分析及临床应用[J].医用生物力学,2018,33(3):218-223.
[28] XIONG XM, SUN YL, SONG SM, et al. Efficacy of unilateral transverse process-pedicle and bilateral puncture techniques in percutaneous kyphoplasty for Kummell disease. Exp Ther Med. 2019;18(5):3615-3621.
[29] 郭营,李宝田,李骁腾,等.改良单侧经皮椎体后凸成形术结合对侧经皮椎体成形术治疗骨质疏松性椎体压缩性骨折的效果[J].临床医学工程,2024,31(4):459-460.
[30] 张志伟,李利,黄兹谕,等.单、双侧椎弓根入路及单侧椎弓根外入路椎体成形治疗胸腰段椎体压缩性骨折:骨水泥灌注量与渗漏率[J].中国组织工程研究,2020,24(9):1353-1358.
[31] 高旭,邢文华.有限元分析法在脊柱外科领域的应用[J].中国组织工程研究,2023,27(18):2921-2927.
[32] 贺凯,邢文华,李峰,等.有限元法在脊柱胸腰段骨折生物力学分析中的应用及发展方向[J].中国组织工程研究,2025,29(15): 3244-3252.
[33] 陈荣彬,李勇,白杰,等.三种骨水泥弥散类型对胸腰段椎体强化术后术椎应力影响的三维有限元分析[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2020, 30(7):628-637.
[34] 李安明,史国号,王国柱,等.椎体成形术对相邻椎体生物力学影响的有限元分析[J].重庆医学,2021,50(2):215-219.
[35] 李家琼,王冬梅,孙璟川,等.骨水泥对椎体成形术治疗胸腰椎骨质疏松压缩性骨折的生物力学影响[J].医用生物力学,2018,33(1): 6-12.
[36] Zuo XH, Chen YB, Xie P, et al. Finite element analysis of wedge and biconcave deformity in four different height restoration after augmentation of osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures. J Orthop Surg Res. 2021;16(1):138.
|