[1] 李继恩,张静,付大清,等.老年膝关节骨性关节炎患者血清LncRNA BLACAT1和LncRNA-H19水平表达与病情严重程度的相关性研究[J].现代检验医学杂志,2024,39(4):34-39.
[2] 马永胜,刘洋,杨文铭,等.组织培养法保存新鲜同种异体骨软骨移植物的研究进展[J].实用骨科杂志,2024,30(3):199-204.
[3] 符轩齐,刘君,史雪峰,等.踝关节骨关节炎的阶梯化治疗[J].生物骨科材料与临床研究,2024,21(4):5-9.
[4] 范元赫,杨永菊,张宇,等.从“脾主肌肉”理论探讨肌少症和骨关节炎发病相关性研究进展[J].辽宁中医药大学学报,2024,26(8): 83-87.
[5] LIU L, ZHANG W, LIU T, et al. The physiological metabolite α-ketoglutarate ameliorates osteoarthritis by regulating mitophagy and oxidative stress. Redox Biol. 2023;62:102663.
[6] 刘梓冰,段建辉.健步虎潜丸联合海桐皮汤治疗早中期膝骨关节炎的疗效观察[J].云南中医中药杂志,2024,45(4):103-106.
[7] YAN YS, QU Z, YU DQ, et al. Sex Steroids and Osteoarthritis: A Mendelian Randomization Study. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021;12:683226.
[8] 綦惠,刘丹平,田大川,等.骨髓间充质干细胞源性外泌体对体外培养的软骨细胞增殖和迁移的调节作用[J].中国运动医学杂志,2019,38(1):40-45.
[9] QI H, SHEN E, SHU X, et al. ERK-estrogen receptor α signaling plays a role in the process of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes protecting against ovariectomy-induced bone loss. J Orthop Surg Res. 2023;18(1):250.
[10] HUANG B, SU Y, SHEN E, et al. Extracellular vesicles from GPNMB-modified bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells attenuate bone loss in an ovariectomized rat model. Life Sci. 2021;272:119208.
[11] QI H, LIU DP, XIAO DW, et al. Exosomes derived from mesenchymal stem cells inhibit mitochondrial dysfunction-induced apoptosis of chondrocytes via p38, ERK, and Akt pathways. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 2019;55(3):203-210.
[12] 张丽,王晨菲,陆春晖,等.达格列净联合水飞蓟宾治疗2型糖尿病合并非酒精性脂肪肝患者疗效分析[J].疑难病杂志,2024,23(3): 328-333.
[13] YAN S, DONG W, LI Z, et al. Metformin regulates chondrocyte senescence and proliferation through microRNA-34a/SIRT1 pathway in osteoarthritis. J Orthop Surg Res. 2023;18(1):198.
[14] MOHAMMED I, HOLLENBERG MD, DING H, et al. A Critical Review of the Evidence That Metformin Is a Putative Anti-Aging Drug That Enhances Healthspan and Extends Lifespan. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021;12:718942.
[15] QIU Y, JIANG X, LIU D, et al. The Hypoglycemic and Renal Protection Properties of Crocin via Oxidative Stress-Regulated NF-κB Signaling in db/db Mice. Front Pharmacol. 2020;11:541.
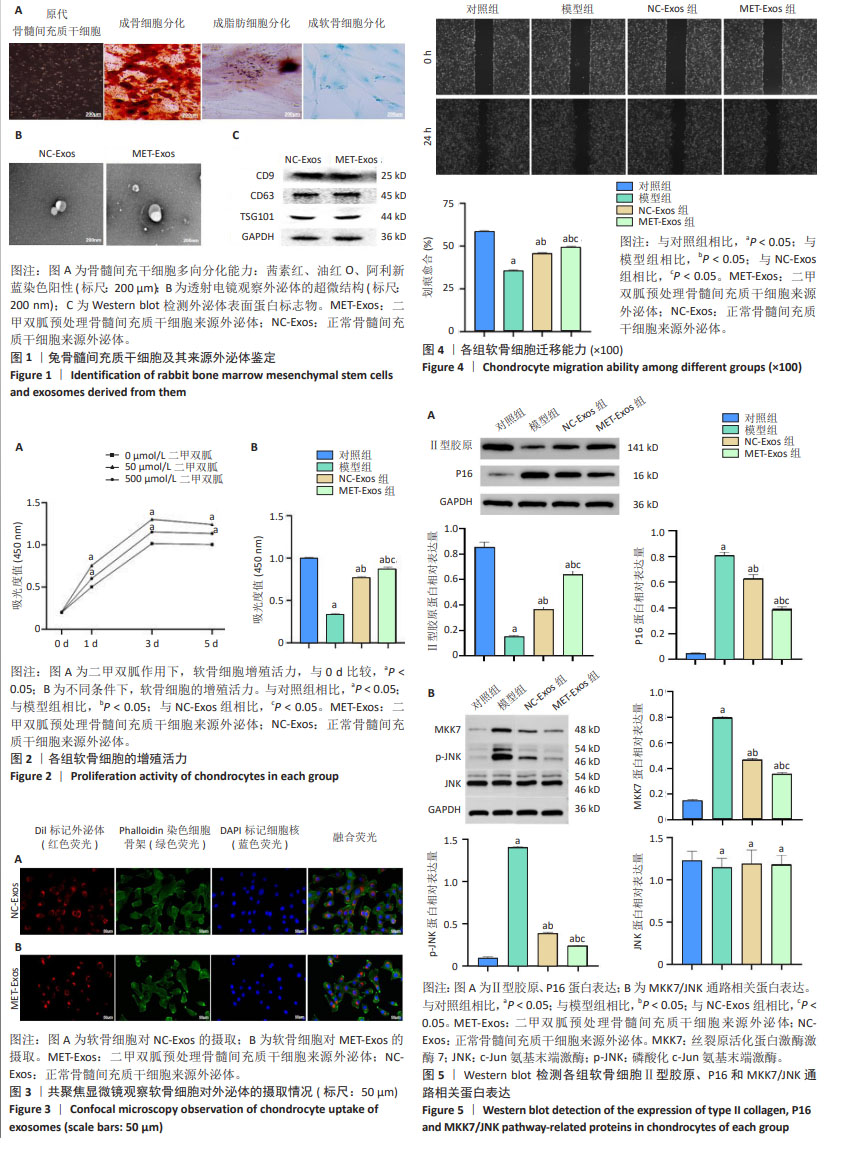
[16] 马民,吕志刚,杜以宽,等.BMSCs的分离培养、纯化与鉴定[J].中国老年学杂志,2009,29(24):3209-3213.
[17] 陶恩东,夏伟杰,王福林,等.骨髓间充质干细胞来源的外泌体通过PI3K/AKT信号通路逆转高糖诱导的骨髓间充质干细胞成骨功能障碍[J].温州医科大学学报,2024,54(8):641-649.
[18] 王小鑫,王丽丽,张益国,等.高效提取细胞培养上清外泌体方法的建立[J].中国生物制品学杂志,2024,37(8):975-982+988.
[19] CHEN D, XIA D, PAN Z, et al. Metformin protects against apoptosis and senescence in nucleus pulposus cells and ameliorates disc degeneration in vivo. Cell Death Dis. 2016;7(10):e2441.
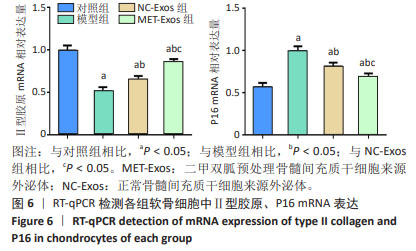
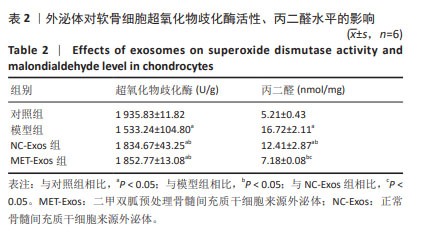
[20] 张梓宁,邓荣辉,余家阔.新型含Mn生物陶瓷粉体减轻软骨细胞的氧化应激损伤[J].中国组织工程研究,2025,29(16):3335-3342.
[21] LIU RF, HU L, WU JN, et al. Changes in tumor suppressors and inflammatory responses during hydrogen peroxide-induced senescence in rat fibroblasts. Free Radic Res. 2022;56(1):77-89.
[22] ASADA S, FUKUDA K, NISHISAKA F, et al. Hydrogen peroxide induces apoptosis of chondrocytes; involvement of calcium ion and extracellular signal-regulated protein kinase. Inflamm Res. 2001;50(1):19-23.
[23] GÜLDEN M, JESS A, KAMMANN J, et al. Cytotoxic potency of H2O2 in cell cultures: impact of cell concentration and exposure time. Free Radic Biol Med. 2010;49(8):1298-1305.
[24] JANG S, LEE K, JU JH. Recent Updates of Diagnosis, Pathophysiology, and Treatment on Osteoarthritis of the Knee. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(5): 2619.
[25] ZHOU J, HUANG J, LI Z, et al. Identification of aging-related biomarkers and immune infiltration characteristics in osteoarthritis based on bioinformatics analysis and machine learning. Front Immunol. 2023;14:1168780.
[26] NEDUNCHEZHIYAN U, VARUGHESE I, SUN AR, et al. Obesity, Inflammation, and Immune System in Osteoarthritis. Front Immunol. 2022;13:907750.
[27] SARSENOVA M, ISSABEKOVA A, ABISHEVA S, et al. Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Based Therapy for Rheumatoid Arthritis. Int J Mol Sci. 2021; 22(21):11592.
[28] 易林,向文远,张文豪,等.补肾痹通方联合骨髓间充质干细胞对损伤软骨细胞的保护机制及SOX9、MMP-13表达的影响[J].陕西中医,2024,45(6): 728-732+739.
[29] ZHANG L, JIAO G, REN S, et al. Exosomes from bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells enhance fracture healing through the promotion of osteogenesis and angiogenesis in a rat model of nonunion. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2020;11(1):38.
[30] ZHANG J, RONG Y, LUO C, et al. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes prevent osteoarthritis by regulating synovial macrophage polarization. Aging (Albany NY). 2020;12(24):25138-25152.
[31] YU H, HUANG Y, YANG L. Research progress in the use of mesenchymal stem cells and their derived exosomes in the treatment of osteoarthritis. Ageing Res Rev. 2022;80:101684.
[32] JIN Y, XU M, ZHU H, et al. Therapeutic effects of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosomes on osteoarthritis. J Cell Mol Med. 2021;25(19):9281-9294.
[33] ZHANG S, TEO KYW, CHUAH SJ, et al. MSC exosomes alleviate temporomandibular joint osteoarthritis by attenuating inflammation and restoring matrix homeostasis. Biomaterials. 2019;200:35-47.
[34] KIM YG, CHOI J, KIM K. Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes for Effective Cartilage Tissue Repair and Treatment of Osteoarthritis. Biotechnol J. 2020; 15(12):e2000082.
[35] XU X, LIANG Y, LI X, et al. Exosome-mediated delivery of kartogenin for chondrogenesis of synovial fluid-derived mesenchymal stem cells and cartilage regeneration. Biomaterials. 2021;269:120539.
[36] 安香霖,鲁金月,董辉,等.中药多糖调控肿瘤微环境的研究进展[J].现代药物与临床,2022,37(9):2142-2147.
[37] 唐骜,舒晴,贾绍辉,等.脂肪间充质干细胞外泌体改善骨质疏松症的研究进展[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2023,29(5):707-712.
[38] 田艺苑,邓智中,张安瑞,等.川芎嗪在中枢神经损伤中的作用及机制研究进展[J].延安大学学报(医学科学版),2023,21(1):79-84.
[39] 侯德淼,唐梓晋,李卓,等.外泌体在老年骨科疾病中治疗应用的研究进展[J].中国老年学杂志,2024,44(5):1267-1273.
[40] 郭天赐,刘爱峰,陈继鑫,等.间充质干细胞源性外泌体对骨性关节炎治疗机制的研究进展[J].组织工程与重建外科,2021,17(3): 262-265.
[41] 王颖,郝楠,谢戬芳.褪黑素在骨关节炎中作用机制的研究进展[J].安徽医学,2024,45(6):794-797.
[42] 吴志文,申恩谱,李贝贝,等.高表达软骨调素1骨髓间充质干细胞来源外泌体促进骨关节炎软骨细胞的增殖[J].中国组织工程研究,2023,27(33):5277-5282.
[43] 申恩谱,黄霸,刘丹平,等.褪黑素预处理的骨髓间充质干细胞外泌体促进骨髓间充质干细胞成骨[J].中国组织工程研究,2022,26(30):4800-4805.
[44] 孔令俊,李想,邓叶龙,等.二甲双胍调控成骨细胞相关信号通路作用机制研究进展[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2024,30(8):1244-1248.
[45] LI J, ZHANG B, LIU WX, et al. Metformin limits osteoarthritis development and progression through activation of AMPK signalling. Ann Rheum Dis. 2020;79(5):635-645.
[46] 刘敏,白爽,杨倩,等.臭氧水关节腔注射通过调节炎症和氧化应激促进大鼠膝关节软骨损伤后修复[J].中国中医骨伤科杂志, 2024,32(4):13-17+23.
[47] JIANG Y, LI T, YANG J, et al. Sustained intra-articular reactive oxygen species scavenging and alleviation of osteoarthritis by biocompatible amino-modified tantalum nanoparticles. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2023;11:1118850.
[48] 徐东,于振和,杨玉景,等.膝骨性关节炎氧化应激水平介导玻璃酸钠疗效的临床研究[J].吉林医学,2024,45(5):1062-1064.
[49] HE R, WEI Y, PENG Z, et al. α-Ketoglutarate alleviates osteoarthritis by inhibiting ferroptosis via the ETV4/SLC7A11/GPX4 signaling pathway. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2024;29(1):88.
[50] GUO Z, LIN J, SUN K, et al. Deferoxamine Alleviates Osteoarthritis by Inhibiting Chondrocyte Ferroptosis and Activating the Nrf2 Pathway. Front Pharmacol. 2022;13:791376.
[51] 姚翠翠,王璐,刘镇亚,等.针刺调控MAPK信号通路治疗急性胰腺炎作用机制研究进展[J].中国中医急症,2023,32(12):2253-2256.
[52] 丁洪波,季晓珍,许永安.间充质干细胞及其外泌体在治疗ALI/ARDS中的机制研究进展[J].中国急救医学,2024,44(6):548-553.
[53] 齐伟,刘建军,王凯,等.当归活性成分治疗骨关节炎的药理学机制研究进展[J].中国医院药学杂志,2024,44(14):1708-1714.
[54] 钟绵森,唐福波,张迪,等.基于MAPK信号通路探讨针灸治疗膝骨关节炎作用机制的研究进展[J].广西医学,2023,45(21):2643-2646.
[55] YU J, LI X, CAO J, et al. Components of the JNK-MAPK pathway play distinct roles in hepatocellular carcinoma. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2023;149(19):17495-17509.
[56] CALIZ AD, VERTII A, FISCH V, et al. Mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 7 in inflammatory, cancer, and neurological diseases. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022;10:979673.
[57] LUO J, PENG S, BAI W, et al. Matrilin-2 prevents the TNFα-induced apoptosis of WB-F344 cells via suppressing JNK pathway. Biotechnol Appl Biochem. 2019; 66(3):309-315.
[58] LEE N, HEO YJ, CHOI SE, et al. Anti-inflammatory Effects of Empagliflozin and Gemigliptin on LPS-Stimulated Macrophage via the IKK/NF-κB, MKK7/JNK, and JAK2/STAT1 Signalling Pathways. J Immunol Res. 2021; 2021:9944880.
[59] LIN Z, MIAO J, ZHANG T, et al. JUNB-FBXO21-ERK axis promotes cartilage degeneration in osteoarthritis by inhibiting autophagy. Aging Cell. 2021;20(2):e13306.
[60] YAN J, FENG G, YANG Y, et al. Nintedanib ameliorates osteoarthritis in mice by inhibiting synovial inflammation and fibrosis caused by M1 polarization of synovial macrophages via the MAPK/PI3K-AKT pathway. FASEB J. 2023;37(10):e23177.
[61] YAN J, NI B, SHENG G, et al. Rhoifolin Ameliorates Osteoarthritis via Regulating Autophagy. Front Pharmacol. 2021;12:661072.
[62] HUA X, XIANG D, GUO M, et al. Induction of RAC1 protein translation and MKK7/JNK-dependent autophagy through dicer/miR-145/SOX2/miR-365a axis contributes to isorhapontigenin (ISO) inhibition of human bladder cancer invasion. Cell Death Dis. 2022;13(8):753.
[63] LI S, LI J, ZHAO Z, et al. Delavatine A Attenuates OGD/R-Caused PC12 Cell Injury and Apoptosis through Suppressing the MKK7/JNK Signaling Pathway. Biol Pharm Bull. 2022;45(12):1743-1753.
[64] GE HX, ZOU FM, LI Y, et al. JNK pathway in osteoarthritis: pathological and therapeutic aspects. J Recept Signal Transduct Res. 2017;37(5):431-436.
[65] LI Z, MENG D, LI G, et al. Celecoxib Combined with Diacerein Effectively Alleviates Osteoarthritis in Rats via Regulating JNK and p38MAPK Signaling Pathways. Inflammation. 2015;38(4):1563-1572.
[66] CUI X, QIAN DW, JIANG S, et al. Scutellariae Radix and Coptidis Rhizoma Improve Glucose and Lipid Metabolism in T2DM Rats via Regulation of the Metabolic Profiling and MAPK/PI3K/Akt Signaling Pathway. Int J Mol Sci. 2018;19(11):3634.
[67] HE X, GAO F, HOU J, et al. Metformin inhibits MAPK signaling and rescues pancreatic aquaporin 7 expression to induce insulin secretion in type 2 diabetes mellitus. J Biol Chem. 2021;297(2):101002.
[68] COLOMBO M, RAPOSO G, THÉRY C. Biogenesis, secretion, and intercellular interactions of exosomes and other extracellular vesicles. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2014;30:255-289.
[69] HAEUSGEN W, HERDEGEN T, WAETZIG V. The bottleneck of JNK signaling: molecular and functional characteristics of MKK4 and MKK7. Eur J Cell Biol. 2011;90(6-7):536-544.
[70] CALIZ AD, YOO HJ, VERTII A, et al. Mitogen Kinase Kinase (MKK7) Controls Cytokine Production In Vitro and In Vivo in Mice. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(17):9364.
[71] ZHANG Z, LI M, MA X, et al. GADD45β-I attenuates oxidative stress and apoptosis via Sirt3-mediated inhibition of ER stress in osteoarthritis chondrocytes. Chem Biol Interact. 2018;296:76-82.
[72] YOON HJ, CHO SY, KIM HG, et al. Protective Effects of Changbudodam-tang on Cell Death Signals on the Bone Marrow-Derived Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells via Regulation of MKK7/JNK/c-Jun Signaling Pathway. J Pharmacopuncture. 2024;27(2):131-141.
[73] 夏帅.基于P38/JNK MAPK信号通路探讨针刀疗法抗KOA兔软骨细胞凋亡的作用机制[D].合肥:安徽中医药大学,2023.
[74] ZHANG H, SHAO Y, YAO Z, et al. Mechanical overloading promotes chondrocyte senescence and osteoarthritis development through downregulating FBXW7. Ann Rheum Dis. 2022;81(5):676-686.
[75] 曾麒,宋世雷,陈跃平.DUSP1/MAPK信号通路影响巨噬细胞极化促进骨愈合的研究进展[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2024,39(7):721-724. |