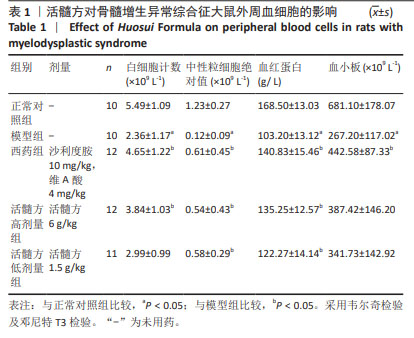
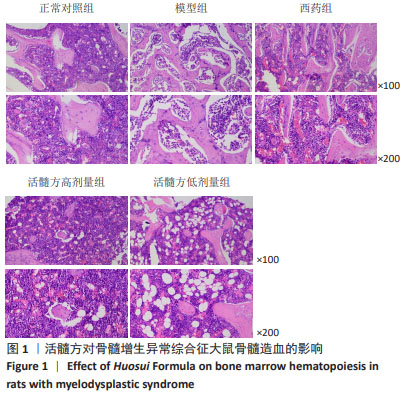
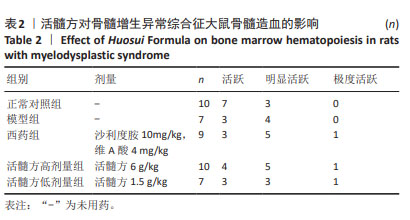
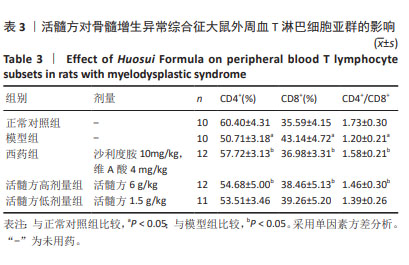
[1] GARCIA-MANERO G. Myelodysplastic syndromes: 2023 update on diagnosis, risk-stratification, and management. Am J Hematol. 2023; 98(8):1307-1325.
[2] FRUMM SM, SHIMONY S, STONE RM, et al. Why do we not have more drugs approved for MDS? A critical viewpoint on novel drug development in MDS. Blood Rev. 2023;60:101056.
[3] BODDU P, KANTARJIAN H, GARCIA-MANERO G, et al. The emerging role of immune checkpoint based approaches in AML and MDS. Leuk Lymphoma. 2018;59(4):790-802.
[4] 董萍萍,周永明.健脾补肾解毒方调节骨髓增生异常综合征T淋巴细胞亚群的疗效观察[J].四川中医,2021,39(2):59-62.
[5] 杨剑,孟咸中,朱红青,等.补肾解毒方联合阿扎胞苷治疗骨髓增生异常综合征疗效分析及对血常规指标的影响[J].临床和实验医学杂志,2023,22(11):1148-1152.
[6] 戴媺,于天启.补虚解毒法干预骨髓增生异常综合征的观察[J].广州医药,2013,44(6):14-17.
[7] 戴媺,陈志雄,于天启.十星丹联合西药治疗中低危骨髓增生异常综合征的临床观察[J].广州中医药大学学报,2013,30(5):633-636.
[8] 冯宝章,赵堂富,王素钦,等.骨髓增生异常综合征大鼠模型的建立及其鉴定[J].实验血液学杂志,1996(3):309-313.
[9] 陈信义,麻柔,李冬云.规范常见血液病中医病名建议[J].中国中西医结合杂志,2009,29(11):1040-1041.
[10] 丁皓,贾梦冉,张稚淳,等.陈信义教授“调平”思想论治MDS经验[J].现代中医临床,2020,27(1):63-65+70.
[11] 刘青果,张盛琪,高琰,等.基于“解毒化瘀、脾肾同治”理论辨治骨髓增生异常综合征经验[J].北京中医药,2022,41(12): 1417-1419.
[12] 汪凯,李昌桂,周永明.基于骨髓微环境从脾肾论治骨髓增生异常综合征[J].时珍国医国药,2023,34(11):2725-2728.
[13] 毛悦,靳楠,唐旭东.基于中医传承计算平台对中医药治疗骨髓增生异常综合征的用药规律研究[J].世界中西医结合杂志,2023, 18(6):1114-1118+1190.
[14] ZHANG H, SUN Y, FAN M, et al. Prevention effect of total ginsenosides and ginseng extract from Panax ginseng on cyclophosphamide-induced immunosuppression in mice. Phytother Res. 2023;37(8):3583-3601.
[15] YOU L, CHA S, KIM MY, et al. Ginsenosides are active ingredients in Panax ginseng with immunomodulatory properties from cellular to organismal levels. J Ginseng Res. 2022;46(6):711-721.
[16] XIAODAN S, YING C. Role of ginsenoside Rh2 in tumor therapy and tumor microenvironment immunomodulation. Biomed Pharmacother. 2022;156:113912.
[17] LI M, LI Q, DONG H, et al. Pilose antler polypeptides enhance chemotherapy effects in triple-negative breast cancer by activating the adaptive immune system. Int J Biol Macromol. 2022;222(Pt B): 2628-2638.
[18] 王清泉,宋景,王雨晴,等.鹿茸肽的提取纯化、药理作用、载体应用研究进展[J].中华中医药学刊,2024,42(5):137-146+286.
[19] HOU Z, FANG G. Research Progress of Anti-tumor Effects of Curcuma zedoaria and its Active Ingredients Through Immune Regulation Mechanism. J Clin Nurs Res. 2021;5(4):1-7.
[20] 华天琦,刘宇灵,林龙飞,等.莪术油化学成分、抗肿瘤作用及制剂研究进展[J].中国药房,2024,35(11):1396-1402.
[21] 高凤洋,张大方,李超英.中药青黛炮制及药理作用的研究进展[J].长春中医药大学学报,2020,36(1):180-183+188.
[22] 黄玉静,熊德上,徐酉华,等.益髓理血饮减少二甲基苯蒽诱导的骨髓增生异常综合征大鼠骨髓细胞凋亡[J].中南大学学报(医学版),2017,42(1):26-34.
[23] 黄玉静,熊德上,徐酉华,等.益髓理血饮对二甲基苯蒽诱导骨髓增生异常综合征模型大鼠骨髓病态造血的影响及机制[J].中药材, 2016,39(3):619-624.
[24] 王志晓,马骏,赵文秀,等.回生胶囊对二甲基苯蒽诱导的骨髓增生异常综合征模型大鼠的影响[J].中兽医医药杂志,2019,38(3): 30-34.
[25] 贾新颜,陈晨,唐剑飞,等.三子补血汤对骨髓增生异常综合征患者Treg及Th17细胞水平的影响[J].中国当代医药,2023,30(31): 41-45.
[26] 王文儒,丁宇斌,唐旭东.青黄散为主复方治疗骨髓增生异常综合征综述[J].中华中医药杂志,2023,38(6):2757-2761.
[27] 范腾.复方青黄散调控HIF1A/GATA信号通路改善骨髓增生异常综合征红系造血[D].北京:中国中医科学院,2020.
[28] RODRIGUEZ-SEVILLA JJ, COLLA S. T-cell dysfunctions in myelodysplastic syndromes. Blood. 2024;143(14):1329-1343.
[29] 欧阳,吴俣.骨髓增生异常综合征免疫异常机制的研究新进展[J].国际输血及血液学杂志,2021,44(1):22-28.
[30] ZHANG X, YANG X, MA L, et al. Immune dysregulation and potential targeted therapy in myelodysplastic syndrome. Ther Adv Hematol. 2023;14:20406207231183330.
[31] SEIDEL JA, OTSUKA A, KABASHIMA K. Anti-PD-1 and Anti-CTLA-4 Therapies in Cancer: Mechanisms of Action, Efficacy, and Limitations. Front Oncol. 2018;8:86.
[32] AREF S, EL AGDAR M, EL SEBAIE A, et al. Prognostic Value of CD200 Expression and Soluble CTLA-4 Concentrations in Intermediate and High-Risk Myelodysplastic Syndrome Patients. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2020;21(8):2225-2230.
[33] TCVETKOV NY, MOROZOVA E, EPIFANOVSKAYA OS, et al. Profile of Checkpoint Molecules Expression on Bone Marrow Cell Populations in Patients with High-Risk Myelodysplastic Syndrome. Blood. 2020;136: 43-44.
[34] 姜怡,蔡雨晴,刘苓霜.sCTLA-4与恶性肿瘤关系的研究进展[J].实用肿瘤杂志,2019,34(1):94-98.
[35] CHIEN KS, KIM K, NOGUERAS-GONZALEZ GM, et al. Phase II study of azacitidine with pembrolizumab in patients with intermediate-1 or higher-risk myelodysplastic syndrome. Br J Haematol. 2021;195(3): 378-387.
[36] RAVANDI F, ASSI R, DAVER N, et al. Idarubicin, cytarabine, and nivolumab in patients with newly diagnosed acute myeloid leukaemia or high-risk myelodysplastic syndrome: a single-arm, phase 2 study. Lancet Haematol. 2019;6(9):e480-e488.
[37] YANG X, MA L, ZHANG X, et al. Targeting PD-1/PD-L1 pathway in myelodysplastic syndromes and acute myeloid leukemia. Exp Hematol Oncol. 2022;11(1):11.
[38] ZEIDAN AM, BOSS I, BEACH CL, et al. A randomized phase 2 trial of azacitidine with or without durvalumab as first-line therapy for older patients with AML. Blood Adv. 2022;6(7):2219-2229.
[39] HONG M, XIE Y, ZHAO J, et al. PD-1 Inhibitors Can be the First-Line Therapy for Myelodysplastic Syndrome (MDS) --Study on the Bone Marrow Immune Microenvironment of MDS By Multispectral Imaging of Multiplex Immunofluorescence. Blood 2022;140 (Supplement 1): 12303-12304.
[40] COATS T, SMITH A, MOURIKIS TP, et al. Mass Cytometry Reveals PD1 Upregulation Is an Early Step in MDS Disease Progression. Blood. 2016; 128:4296-4296.
[41] 张志鹏,陈子琦,田建辉.中医药减毒增效作用在免疫检查点治疗中的应用进展[J].中国临床药理学与治疗学,2024,29(3):339-347.
[42] 房莹,常春康.骨髓增生异常综合征小鼠移植模型研究进展[J].中华血液学杂志,2020,41(4):344-347. |