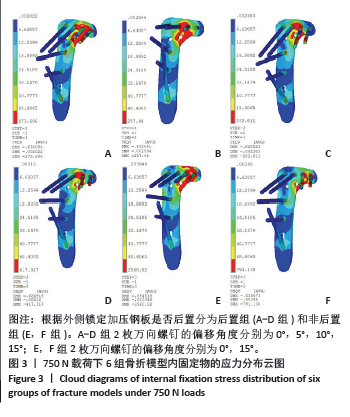
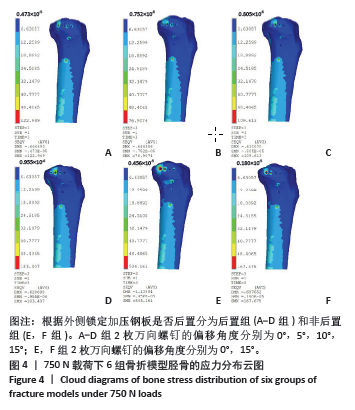
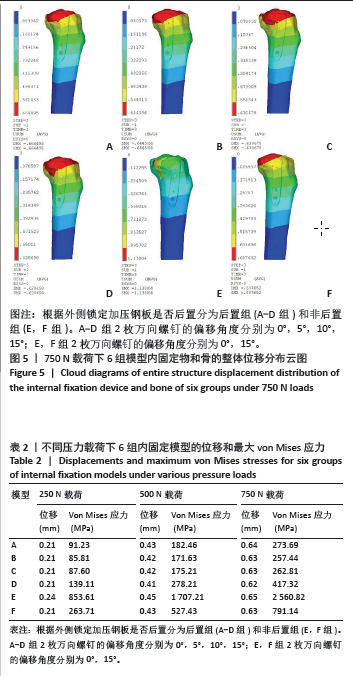
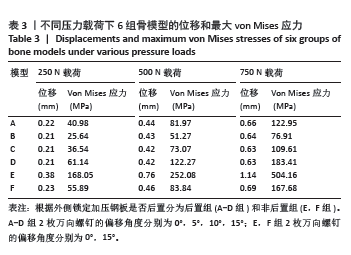
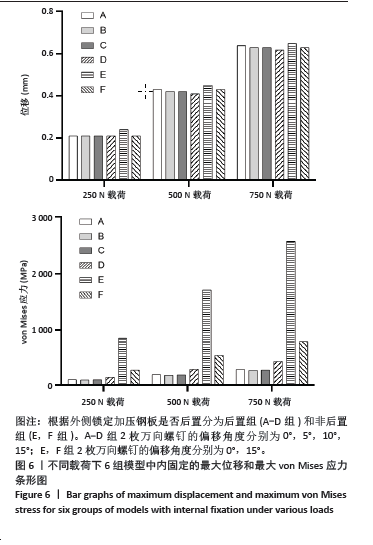
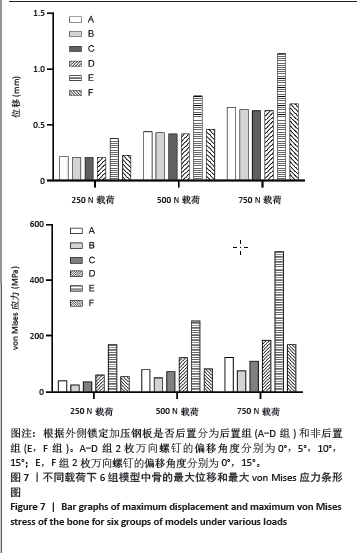
[1] ZHANG C, BAI H, MA T, et al. Biomechanics and finite element analysis of a novel plate designed for posterolateral tibial plateau fractures via the anterolateral approach. Sci Rep. 2023;13(1):20114.
[2] XIANG G, ZHI-JUN P, QIANG Z, et al. Morphological characteristics of posterolateral articular fragments in tibial plateau fractures. Orthopedics. 2013;36(10):e1256-e1261.
[3] ZHANG BB, WANG BH, MEI J, et al. Biomechanical study of a new rim plate fixation strategy for two kinds of posterolateral depression patterns of tibial plateau fractures: a finite element analysis. J Orthop Surg Res. 2023;18(1):840.
[4] LU Y, XU Y, REN C, et al. A feasibility study of robot-assisted percutaneous reduction and fixation technique for treating posterolateral depression tibial plateau fractures. Sci Rep. 2023; 13(1):22026.
[5] HU Z, REN W, PENG J, et al. Biomechanics and finite element analysis comparing posterior T-plates with LCP for fixation of posterolateral tibial plate fractures. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2023;11:1286993.
[6] LI J, ALI KA, XIA C, et al. Anterolateral approach for posterolateral tibial plateau fractures. Acta Orthop Belg. 2023;89(2):354-361.
[7] HU S, CHEN S, CHANG S, et al. Treatment of Isolated Posterolateral Tibial Plateau Fracture with a Horizontal Belt Plate through the Anterolateral Supra-Fibular-Head Approach. Biomed Res Int. 2020; 2020:4186712.
[8] MAO W, CHEN G, ZHU Y, et al. Treatment of tibial plateau fractures involving the posterolateral column using the extended anterolateral approach. Medicine (Baltimore). 2021;100(38):e27316.
[9] LU Y, BAI H, WANG Q, et al. The study of biomechanics and finite element analysis on a novel plate for tibial plateau fractures via anterolateral supra-fibular-head approach. Sci Rep. 2023;13(1):13516.
[10] HU Z, REN W, ZHANG W, et al. Potential problem and solution of lateral plate postposition for the posterolateral tibial plateau fracture. J Orthop Surg Res. 2023;18(1):984.
[11] LIU ZD, LI XF, QIAN L, et al. Lever reduction using polyaxial screw and rod fixation system for the treatment of degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis with spinal stenosis: technique and clinical outcome. J Orthop Surg Res. 2015;10:29.
[12] HUANG L, XIONG C, GUO Z, et al. Comparison of monoplanar and polyaxial screw fixation systems in percutaneous intermediate fixation for thoracolumbar fractures. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2022;23(1):172.
[13] ELERIAN S, SINGH T, N AJ, et al. Early Results of a Variable-Angle Volar Locking Plate for Distal Radius Fractures: A Bi-centre Study. Cureus. 2021;13(9):e18321.
[14] VLČEK M, PECH J, MUSIL V, et al. [Conservative and Surgical Treatment for Distal Ulna Fractures Associated with Distal Radius Fractures]. Acta Chir Orthop Traumatol Cech. 2015;82(6):412-417.
[15] 程晓东, 魏小飞, 俞宇,等.经皮相邻椎体单平面螺钉联合伤椎万向螺钉内固定治疗胸腰椎骨折的疗效观察[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2023,38(1):53-55.
[16] 朱梁豫, 李兴华, 王爱国.闭口万向螺钉骶髂固定系统联合脊柱内固定系统治疗不稳定型骶骨骨折[J].颈腰痛杂志,2020,41(3): 345-347.
[17] NOURBAKHSH A, HIRSCHFELD AG, DHULIPALA S, et al. Biomechanical Comparison of Fixed- versus Variable-Angle Locking Screws for Distal Humerus Comminuted Fractures. Clin Orthop Surg. 2019;11(3): 302-308.
[18] 卢永辉, 董伟强, 白波.老年人多节段腰椎管狭窄症应用椎弓根钉系统治疗的特点[J].中国老年学杂志,2004,24(9):824-825.
[19] HAMANDI F, SIMON G, LAUGHLIN R, et al. Biomechanical Behavior of a Variable Angle Locked Tibiotalocalcaneal Construct. Bioengineering (Basel). 2020;7(1):27.
[20] KACZMAREK J, BARTKOWIAK T, PACZOS P, et al. What Is the Cost of Off-Axis Insertion of Locking Screws? A Biomechanical Comparison of a 3.5 mm Fixed-Angle and 3.5 mm Variable-Angle Stainless Steel Locking Plate Systems. Vet Comp Orthop Traumatol. 2022;35(5):339-346.
[21] TIDWELL JE, ROUSH EP, ONDECK CL, et al. The biomechanical cost of variable angle locking screws. Injury. 2016;47(8):1624-1630.
[22] SUN H, HE QF, ZHANG BB, et al. A biomechanical evaluation of different fixation strategies for posterolateral fragments in tibial plateau fractures and introduction of the ‘magic screw’. Knee. 2018;25(3): 417-426.
[23] KUMAR VK, PRASAD K, SANSGIRI T, et al. Self-Drilling Versus Self-Tapping Screws: A 3D Finite Element Analysis. Craniomaxillofac Trauma Reconstr. 2021;14(1):4-10.
[24] REN W, ZHANG W, JIANG S, et al. The Study of Biomechanics and Clinical Anatomy on a Novel Plate Designed for Posterolateral Tibial Plateau Fractures via Anterolateral Approach. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022;10:818610.
[25] ZHAO K, SHAN C, LUXIMON Y. Contributions of individual muscle forces to hip, knee, and ankle contact forces during the stance phase of running: a model-based study. Health Inf Sci Syst. 2022; 10(1):11.
[26] ZHANG BB, HU H, ZHAN S, et al. Biomechanical analysis of “Barrel hoop plate” technique for the posterolateral fragments of tibial plateau fractures with different displacement tendency. Injury. 2020; 51(11):2465-2473.
[27] 林旺,王盈盈,郭卫中,等.胫骨平台后外侧柱骨折扩大外侧入路内固定增强力学稳定性及膝关节功能[J].中国组织工程研究,2021,25(24):3826-3831.
[28] CARRERA I, GELBER PE, CHARY G, et al. Fixation of a split fracture of the lateral tibial plateau with a locking screw plate instead of cannulated screws would allow early weight bearing: a computational exploration. Int Orthop. 2016;40(10):2163-2169.
[29] LOBENHOFFER P, GERICH T, BERTRAM T, et al. [Particular posteromedial and posterolateral approaches for the treatment of tibial head fractures]. Unfallchirurg. 1997;100(12):957-967.
[30] FROSCH KH, BALCAREK P, WALDE T, et al. A new posterolateral approach without fibula osteotomy for the treatment of tibial plateau fractures. J Orthop Trauma. 2010;24(8):515-520.
[31] SOLOMON LB, STEVENSON AW, BAIRD RP, et al. Posterolateral transfibular approach to tibial plateau fractures: technique, results, and rationale. J Orthop Trauma. 2010;24(8):505-514.
[32] YOON YC, SIM JA, KIM DH, et al. Combined lateral femoral epicondylar osteotomy and a submeniscal approach for the treatment of a tibial plateau fracture involving the posterolateral quadrant. Injury. 2015;46(2):422-426.
[33] CARLSON DA. Posterior bicondylar tibial plateau fractures. J Orthop Trauma. 2005;19(2):73-78.
[34] CHANG SM, ZHENG HP, LI HF, et al. Treatment of isolated posterior coronal fracture of the lateral tibial plateau through posterolateral approach for direct exposure and buttress plate fixation. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2009;129(7):955-962.
[35] 程邦君,毛冯缘,黄燕峰,等.胫骨外侧锁定接骨板联合前侧拉力螺钉或后外侧支撑接骨板治疗Schatzker Ⅱ型胫骨平台骨折合并后外侧骨折的临床研究[J].中华骨与关节外科杂志,2023,16(11): 1021-1027.
[36] 蒋靓君,郑强,冯刚,等.扩展前外侧入路治疗伴后外侧骨块的胫骨平台骨折[J].中华骨科杂志,2018,38(19):1161-1169.
[37] HOEKSTRA H, VANHEES J, VAN DEN BERG J, et al. Extended lateral column tibial plateau fractures. How do we do it? Injury. 2018;49(10): 1878-1885.
[38] 郭亮,徐广,夏欣,等.腓骨头上入路锁定加压钢板治疗胫骨平台后外侧髁骨折[J].临床骨科杂志,2023,26(3):425-428.
[39] YAN Z, ZOU C, KENMEGNE GR, et al. Newly designed plate for the treatment of posterolateral tibial plateau fractures: a finite element analysis. J Orthop Surg Res. 2024;19(1):201.
[40] ANDONOV Y. Lateral tibial plateau fractures with posterior comminution. Can a rim plate offer sufficient support? Acta Orthop Belg. 2023;89(2):275-279.
[41] KÄÄB MJ, FRENK A, SCHMELING A, et al. Locked internal fixator: sensitivity of screw/plate stability to the correct insertion angle of the screw. J Orthop Trauma. 2004;18(8):483-487. |