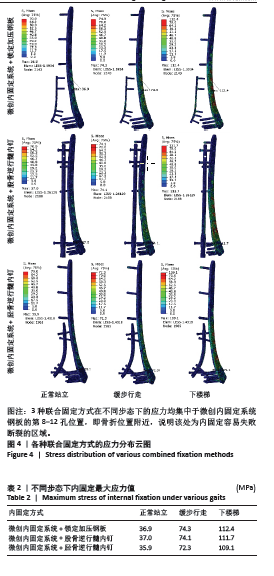
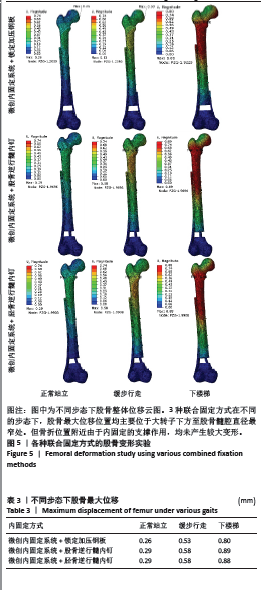
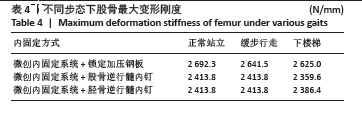
[1] ELSOE R, CECCOTTI AA, LARSEN P. Population-based epidemiology and incidence of distal femur fractures. Int Orthop. 2018;42(1):191-196.
[2] SINGH R, AMBADE R, LANDGE S, et al. Comprehensive Review on Distal Femur Fractures: From Epidemiology to Treatment Strategies. Cureus. 2024;16(4):e57937.
[3] HAKE ME, DAVIS ME, PERDUE AM, et al. Modern Implant Options for the Treatment of Distal Femur Fractures. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2019; 27(19):e867-e875.
[4] NESTER M, BORRELLI J JR. Distal femur fractures management and evolution in the last century. Int Orthop. 2023;47(8):2125-2135.
[5] RINEHART D, YOUNGMAN T, AHN J, et al. Review of patient-reported outcomes in periprosthetic distal femur fractures after total knee arthroplasty: a plate or intramedullary nail? Arthroplasty. 2021; 3(1):24.
[6] TAMPERE T, OLLIVIER M, JACQUET C, et al. Knee arthroplasty for acute fractures around the knee. EFORT Open Rev. 2020;5(10):713-723.
[7] TAHAMI M, VAZIRI AS, TAHMASEBI MN, et al. Practical approach to the native distal femur fractures in the elderly: A rapid review over the recent trends. Injury. 2022;53(7):2389-2394.
[8] WILSON JL, SQUIRES M, MCHUGH M, et al. The geriatric distal femur fracture: nail, plate or both? Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2023;33(5): 1485-1493.
[9] ABDELMONEM AH, SABER AY, EI SAGHEIR M, et al. Evaluation of the Results of Minimally Invasive Plate Osteosynthesis Using a Locking Plate in the Treatment of Distal Femur Fractures. Cureus. 2022;14(3):e23617.
[10] GURUNG R, TERRILL A, WHITE G, et al. Severity of Complications after Locking Plate Osteosynthesis in Distal Femur Fractures. J Clin Med. 2024;13(5):1492.
[11] PFEUFER D, ZELLER A, MEHAFFEY S, et al. Weight-bearing restrictions reduce postoperative mobility in elderly hip fracture patients. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2019;139(9):1253-1259.
[12] SAIN A, SHARMA V, FAROOQUE K, et al. Dual Plating of the Distal Femur: Indications and Surgical Techniques. Cureus. 2019;11(12): e6483.
[13] 孟亚强, 岳晓东. 单一切口双钢板治疗股骨远端粉碎性骨折的疗效[J]. 临床骨科杂志,2024,27(1):97-101.
[14] 曹浙标, 季烈峰, 任伟峰. 外侧微创内固定系统联合内侧重建钢板内固定治疗股骨远端骨折的疗效观察[J]. 中国骨与关节损伤杂志, 2022,37(8):838-840.
[15] KONTAKIS MG, GIANNOUDIS PV. Nail plate combination in fractures of the distal femur in the elderly: A new paradigm for optimum fixation and early mobilization? Injury. 2023;54(2):288-291.
[16] PASSIAS BJ, EMMER TC, SULLIVAN BD, et al. Treatment of Distal Femur Fractures with a Combined Nail-Plate Construct: Techniques and Outcomes. J Long Term Eff Med Implants. 2021;31(3):15-26.
[17] UPADHYAY P, SYED F, RAMOUTRA DN, et al. The missing piece of the trauma armoury-medial femoral condyle plate. Injury. 2022;53(3): 1237-1240.
[18] ROLLOCK NC, GADINSKY NE, KLINGER CE, et al. The effects of dual plating on the vascularity of the distal femur. Bone Joint J. 2020; 102-B(4):530-538
[19] PENG B, WAN T, TAN W, et al. Novel Retrograde Tibial Intramedullary Nailing for Distal Tibial Fractures. Front Surg. 2022;9:899483.
[20] 熊远飞, 刘晖, 许遵营, 等. 胫骨逆行髓内钉在高危人群胫骨远端关节外骨折中的应用研究[J]. 骨科,2024,15(1):71-75.
[21] GREENFIELD J, APPELMANN P, WUNDERLICH F, et al. Retrograde tibial nailing of far distal tibia fractures: a biomechanical evaluation of double- versus triple-distal interlocking. Eur J Trauma Emerg Surg. 2022;48(5):3693-3700.
[22] WRIGHT DJ, DESANTO DJ, MCGARRY MH, et al. Supplemental Fixation of Supracondylar Distal Femur Fractures: A Biomechanical Comparison of Dual-Plate and Plate-Nail Constructs. J Orthop Trauma. 2020;34(8):434-440.
[23] 汪金平, 杨天府, 钟凤林,等. 股骨生物力学特性的有限元分析[J]. 中华创伤骨科杂志,2005,7(10):931-934.
[24] 陈柄泽. 不同骨折复位质量下垂直型股骨颈骨折四种不同内固定方式治疗的有限元分析[D].广州: 南方医科大学,2022.
[25] WOLFRAM U, SCHWIEDRZIK J. Post-yield and failure properties of cortical bone. Bonekey Rep. 2016;5:829.
[26] 李瑞扬,罗从风. 双钢板内固定治疗股骨远端骨折研究进展[J].国际骨科学杂志,2021,42(6):329-332.
[27] ESPEY R, STEVENSON L, TUCKER A. Combined nail-plate constructs in the management of osteoporotic native distal femoral fractures: a systematic review of the available evidence. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2023;33(8):3215-3223.
[28] STOFFEL K, SOMMER C, LEE M, et al. Double fixation for complex distal femoral fractures. EFORT Open Rev. 2022;7(4):274-286.
[29] LIPORACE FA, ANEJA A, CARROLL EA, et al. Maintaining the Neutral Axis in the Treatment of Distal Femur Fractures Via Dual Plate or Nail Plate Combination Technique: When and How? J Orthop Trauma. 2021;35(Suppl 5):S38-S40.
[30] CHEN MJ, GOODNOUGH LH, SALAZAR BP, et al. Impact on periosteal vasculature after dual plating of the distal femur: a cadaveric study. OTA Int. 2021;4(2):e131.
[31] SHI BY, BRODKE DJ, O’HARA N, et al. Nail Plate Combination Fixation Versus Lateral Locked Plating for Distal Femur Fractures: A Multicenter Experience. J Orthop Trauma. 2023;37(11):562-567.
[32] 谢威,黄子阳,黄泽茂,等. 微创内固定系统与逆行髓内钉内固定治疗股骨远端骨折的Meta分析[J]. 中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2022, 37(4):355-358.
[33] QUINZI DA, CHILDS S, LIPOF JS, et al. The Treatment of Periprosthetic Distal Femoral Fractures After Total Knee Replacement: A Critical Analysis Review. JBJS Rev. 2020;8(9):e2000003.
[34] 徐志,仲鹤鹤,向浩,等. 股骨干骨折3种不同固定方式的有限元分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2022,26(33):5271-5277.
[35] 史方石,袁维. 有限元法在骨科器械和植入物中的应用综述[J].科学技术与工程,2023,23(30):12775-12785.
[36] 胡浩,陆骅.有限元分析在股骨远端骨折内固定中的应用研究进展[J].实用临床医药杂志,2023,27(6):145-148.
[37] 陈丁,于娇娜,于洋,等. 有限元分析3种内固定方式治疗伴有内侧骨缺损的C3型股骨远端骨折[J]. 中南大学学报(医学版),2023, 48(11):1711-1720.
[38] 卢俊浩,时宁文,柏茂盛,等. 三种不同内固定方案治疗股骨远端粉碎性骨折疗效及安全性的研究[J]. 创伤外科杂志,2022,24(10): 770-776.
[39] YU X, GUO Y, KANG Q, et al. Effects and mechanisms of mechanical stress on secondary fracture healing. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2013;18(4):1344-1348.
[40] 蔡成阔,石博文,计国旗,等. 环形外固定架对长骨斜形骨折断端固定效果的生物力学研究[J]. 中华骨科杂志,2021,41(22): 1640-1646. |