中国组织工程研究 ›› 2025, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (26): 5695-5703.doi: 10.12307/2025.716
• 组织构建综述 tissue construction review • 上一篇 下一篇
细胞焦亡在运动系统疾病中的作用及相关分子机制
耿珑玉1,盛 黎1,白 硕2,高蓓瑶3,葛瑞东3,江 山3
- 1北京体育大学运动医学与康复学院,北京市 100091;2北京市朝阳区太阳宫社区卫生服务中心康复医学科,北京市 100028;3中日友好医院康复医学科,北京市 100029
-
收稿日期:2024-07-27接受日期:2024-09-26出版日期:2025-09-18发布日期:2025-02-28 -
通讯作者:葛瑞东,博士,副主任治疗师,中日友好医院康复医学科,北京市 100029 并列通讯作者:江山,主任医师,副教授,中日友好医院康复医学科,北京市 100029 -
作者简介:耿珑玉,女,2002年生,河北省廊坊市人,汉族,北京体育大学在读硕士,主要从事运动系统疾病的研究。 -
基金资助:中央高校基本科研业务费专项资金资助课题(校2020064),项目负责人:葛瑞东;中央高校基本科研业务费专项资金资助课题(2024043),项目负责人:盛黎
Role and molecular mechanism of pyroptosis in motor system diseases
Geng Longyu1, Sheng Li1, Bai Shuo2, Gao Beiyao3, Ge Ruidong3, Jiang Shan3
- 1School of Sports Medicine and Rehabilitation, Beijing Sport University, Beijing 100091, China; 2Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, Beijing Chaoyang District Taiyanggong Community Health Service Center, Beijing 100028, China; 3Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, China-Japan Friendship Hospital, Beijing 100029, China
-
Received:2024-07-27Accepted:2024-09-26Online:2025-09-18Published:2025-02-28 -
Contact:Ge Ruidong, PhD, Associate chief therapist, Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, China-Japan Friendship Hospital, Beijing 100029, China Co-corresponding author: Jiang Shan, Chief physician, Associate professor, Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, China-Japan Friendship Hospital, Beijing 100029, China -
About author:Geng Longyu, Master’s candidate, School of Sports Medicine and Rehabilitation, Beijing Sport University, Beijing 100091, China -
Supported by:the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities, Nos. 2020064 (to GRD) and 2024043 (to SL)
摘要:
文题释义:
细胞焦亡:是一种由Gasdermin家族蛋白介导的程序性细胞死亡,它由Caspase激活并伴随炎症反应,细胞焦亡可导致细胞膜孔隙形成和细胞裂解,并释放炎症因子。
运动系统疾病:包括肌肉、骨骼、肌腱、软骨等疾病,可分为急性和慢性,这些疾病可能导致运动系统的结构、功能异常。
背景:大量研究发现细胞焦亡与运动系统疾病的发生发展密切相关,但细胞焦亡在运动系统疾病中的研究综述较少。
目的:综述目前的临床与临床前研究,对细胞焦亡在运动系统疾病中的作用及相关分子机制进行总结,为未来靶向细胞焦亡治疗运动系统疾病提供参考。
方法:通过计算机检索PubMed数据库、中国知网的相关文献,检索时限为2000年1月至2024年1月。英文检索词为“pyroptosis,tendons,ligaments,cartilage,muscles,bones”;中文检索词为“焦亡,肌腱,韧带,软骨,骨骼肌,骨骼”。采用主题词和自由词结合的方式进行检索。初步检索422篇文献,其中英文文献334篇,中文文献88篇。排除重复文献、不相关文献后通过全篇阅读进一步排除不具有纳入价值的文献,最终纳入78篇文献进行综述。
结果与结论:①细胞焦亡的不同通路及后续引发的炎症反应能够影响运动系统疾病进展和损伤的修复进程;②过度的细胞焦亡不仅可以导致组织细胞的大量死亡,还可以通过细胞裂解后释放的炎症因子等物质加重组织炎症反应、降解细胞外基质,而损伤相关分子模式又可以作为上游信号进一步加重细胞焦亡;③目前针对细胞焦亡防治运动系统疾病的方法主要包括NOD样受体热蛋白结构域相关蛋白3抑制剂、中草药提取物、外泌体治疗、间充质干细胞治疗、运动疗法等;④综述表明,靶向干预细胞焦亡过程中的某些关键因子,或许可以作为一种治疗和预防运动系统疾病的新方向。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
中图分类号:
引用本文
耿珑玉, 盛 黎, 白 硕, 高蓓瑶, 葛瑞东, 江 山. 细胞焦亡在运动系统疾病中的作用及相关分子机制[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(26): 5695-5703.
Geng Longyu, Sheng Li, Bai Shuo, Gao Beiyao, Ge Ruidong, Jiang Shan . Role and molecular mechanism of pyroptosis in motor system diseases[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(26): 5695-5703.
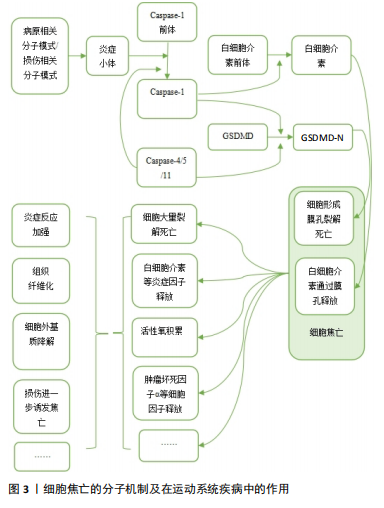
2.1.1 经典通路 细胞焦亡经典通路由Caspase-1介导,其过程涉及炎症小体激活、Caspase-1激活、Gasdermin-d (GSDMD)剪切以及细胞打孔后炎症因子的释放。炎症小体通常包含一个模式识别受体、一个衔接蛋白及Caspase-1前体。炎症小体中常见的模式识别受体包括NOD样受体家族、AIM2等,他们可以被各种损伤相关分子模式或病原相关分子模式激活。激活后的模式识别受体通过衔接蛋白与Caspase-1前体结合,Caspase-1前体自切产生活性形式的Caspase-1,Caspase-1直接将GSDMD裂解为
GSDMD-C和GSDMD-N,N端蛋白发生寡聚,随后在膜上形成分子孔道,直接破坏细胞膜,造成脂质体渗漏并使细胞膜裂解[4]。与此同时,活化的Caspase-1还可以对白细胞介素1β前体和白细胞介素18前体进行剪切,转化为其生物活性形式,随后通过GSDMD生成的膜孔释放到细胞外,增强机体的炎症反应[8]。
2.1.2 非经典通路 细胞焦亡的非经典通路由人体中的Caspase-4/5以及小鼠中的Caspase-11介导,脂多糖可以直接激活Caspase-4/5/11,使活化后的Caspase-4/5/11对GSDMD进行剪切,从而产生N端序列并形成膜孔,引起焦亡发生和炎症因子的释放。然而,Caspase-4/5/11不能直接参与炎症因子的激活,而是通过诱导Caspase-1的活化,对白细胞介素1β前体和白细胞介素18前体进行剪切,形成有活性的白细胞介素1β和白细胞介素18并释放到细胞外,进而引起机体的炎症反应[9]。
2.1.3 其他通路 除Caspase-1/4/5/11以外,Caspase家族的其他成员也可介导细胞焦亡。例如Gasdermin家族蛋白GSDME的N端和C端结构域之间包含一个经典的Caspase-3切割位点,可被Caspase-3切割活化进而诱发细胞焦亡[10]。在Caspase-8介导通路中,抑制转化生长因子β活化激酶1可激活Caspase-8,活化的Caspase-8可以裂解GSDMD,从而诱导细胞焦亡[11]。细胞毒性淋巴细胞中的颗粒酶Granzyme A能够水解GSDMB引发肿瘤细胞焦亡[12]。
2.2 细胞焦亡在运动系统疾病中的作用及分子机制
2.2.1 肌腱及韧带相关疾病与细胞焦亡 肌腱是一种主要由胶原蛋白(Ⅰ型胶原蛋白为主)和弹性蛋白组成的致密结缔组织,基本功能是将肌肉产生的力传递给骨骼,从而产生运动[13]。肌腱损伤是常见的运动系统疾病之一,急性超负荷、暴露于过度使用条件或内在组织变性等损伤机制,均可导致肌腱断裂或肌腱病的发生[14]。大量研究发现,细胞焦亡调节因子参与了肌腱病的发病机制,为治疗策略提供了新的见解。
THANKAM等[15]研究发现,损伤后的肩袖肌腱中NOD样受体热蛋白结构域相关蛋白3(NOD-like receptor thermal protein domain associated protein 3,NLRP3)、Caspase-1和白细胞介素1β等关键因子表达上调,并在愈合过程中逐渐下调。研究者在大量肩袖肌腱损伤患者的肩关节肌腱组织中发现了细胞内高迁移率族蛋白B1(high mobility group box 1 protein,HMGB1)的激活,HMGB1作为NLRP3炎症小体激活的上游信号可以促进焦亡的发生,进而加重肩袖肌腱的炎症反应。异位骨化相关研究表明,肌腱损伤后积累的衰老肌腱源性干细胞(tendon-derived stem cells,TDSCs)在异常的骨软骨愈合过程中起着重要作用。巨噬细胞焦亡可增强HMGB1的释放,该蛋白直接与肌腱源性干细胞中的Toll样受体9结合,诱导了肌腱源性干细胞衰老,从而促进了异位骨化形成[16]。创伤性脑损伤后,携带HMGB1的脑源性细胞外囊泡被损伤肌腱的成纤维细胞摄取,也可激活NLRP3炎症小体,从而加重成纤维细胞焦亡及钙化沉积,引起神经元性异位骨化。而NLRP3基因敲除小鼠体内焦亡的缓解可减轻软组织损伤后的衰老细胞负担和异位骨化的形成,进一步证实了NLRP3与异位骨化形成之间的联系[17]。
韧带是连接骨与骨之间的结缔组织,以保持关节的稳定性和支撑力。它由胶原纤维带组成,这些胶原纤维锚定在关节两端的骨骼上,被动地稳定关节,并在施加载荷时引导关节活动[18]。
盆底结缔组织由筋膜和韧带组成,细胞外基质是其主要成分,重复的机械刺激可导致细胞外基质降解,引起盆底支持组织损伤。研究发现,盆腔器官脱垂模型的盆底组织中NLRP3、Caspase-1等表达显著升高,提示焦亡与韧带损伤有关[19]。
综上,HMGB1作为损伤相关分子模式促进了NLRP3炎症小体的激活,进而诱导了肌腱细胞与巨噬细胞焦亡,加重肌腱损伤并促进异位骨化形成,此外,NLRP3介导的焦亡也存在于机械刺激导致的韧带损伤中。
2.2.2 软骨相关疾病与细胞焦亡 软骨存在于滑膜关节、脊柱、肋骨、外耳、鼻、气道以及儿童和青少年的生长板中。人体软骨主要有3种类型:透明软骨、纤维软骨和弹性软骨[20]。目前研究较多的焦亡参与的软骨相关疾病包括骨关节炎、椎间盘退行性变等。
骨关节炎是世界上最常见的关节慢性退行性疾病,该病几乎可累及人体的所有关节,常见症状包括关节疼痛和关节功能紊乱。骨关节炎与一系列病理过程有关,如滑膜纤维化、细胞外基质破坏、慢性炎症和血管生成[21]。软骨细胞发生焦亡后,可释放基质金属蛋白酶、分解素、血小板反应蛋白解整合素金属肽酶、白细胞介素1β、白细胞介素18和肿瘤坏死因子α[22],其中基质金属蛋白酶1/3/13和血小板反应蛋白解整合素金属肽酶4/5已被证明是软骨细胞外基质成分降解的主要因素[23-24]。滑膜纤维化是骨关节炎的另一种基本病理改变,其发病机制是炎症和氧化应激结合。研究发现,缺氧诱导因子1α可通过促进成纤维细胞焦亡加重膝骨关节炎大鼠滑膜纤维化,这种作用可被GSDMD或缺氧诱导因子1α siRNA消除,提示成纤维细胞的焦亡参与了骨关节炎的病理过程[25]。肥胖也是骨关节炎发生、进展的重要危险因素之一。氧化低密度脂蛋白和胆固醇等因子可激活NLRP3炎症小体。VANDANMAGSAR等[26]发现,肥胖诱导的脂肪沉积对炎症小体有激活作用,从而促进细胞焦亡,引发炎症反应。此外,肥胖患者血液中脂多糖水平也会升高,脂多糖激活Caspase-4/5/11,通过非典型炎症小体途径启动焦亡,导致炎症性软骨细胞死亡和软骨丢失增加[27]。微晶体被认为是能够激活炎症小体的主要损伤相关分子模式,骨关节炎患者的关节滑液和组织中通常会存在碱性磷酸钙和二水焦磷酸钙晶体[28],其中碱性磷酸钙可以促进巨噬细胞和单核细胞通过激活NLRP3炎性小体诱导焦亡发生,产生白细胞介素1β,进而诱导软骨退行性变,加重骨关节炎的病理过程[29]。
椎间盘位于椎体之间,是连接相邻椎体的纤维软骨组织,由软骨终板、纤维环和髓核组成,椎间盘的重要成分是胶原纤维、弹性蛋白纤维和聚集聚糖[30]。腰痛是运动系统的一种常见症状,椎间盘退行性变被广泛认为是腰痛的主要原因之一[31]。多项研究表明,退行性椎间盘中炎症小体相关蛋白NLRP3及其下游分子Caspase-1和白细胞介素1β的表达均有上调,并且其表达随椎间盘退变程度而上升,提示焦亡可能在椎间盘退变的病理过程中发挥作用。
软骨终板变性和撕裂作为椎间盘退行性变的起始因子之一,通过破坏椎间盘的营养供应参与或加速椎间盘退行性变,椎间盘退行性变患者的软骨终板中NLRP3、Caspase-1、白细胞介素1β表达量均随撕脱的进展而升高,表明焦亡参与了椎间盘退行性变患者软骨终板的变性过程,导致腰痛的进展[32]。LE MAITRE等[33]研究发现,在椎间盘退行性变患者的纤维环组织软骨样细胞中白细胞介素1β阳性细胞比例尤为突出,并且随着退行性变的严重程度而增加其表达程度,这些白细胞介素1β阳性细胞可能是由椎间盘内的异常焦亡介导产生的,而大量白细胞介素1β的释放也可以作为上游信号加重焦亡发生。LU等[34]通过人髓核标本检测发现,Toll样受体9、核因子κB和NLRP3炎症小体的表达水平与椎间盘退行性变程度相关,进一步研究发现,氧化应激可损伤髓核细胞的线粒体导致线粒体通透性转换孔打开,使线粒体DNA释放到细胞质中,作为损伤相关分子模式的一部分,线粒体DNA可被Toll样受体9识别,并触发核因子κB和NLRP3炎症小体的表达,诱导髓核细胞焦亡和炎症反应,加剧椎间盘退行性变发生。此外,线粒体自噬也参与了髓核细胞焦亡的过程,通过改善白细胞介素1β诱导的线粒体功能障碍和活性氧积累,可以促进线粒体自噬抑制NLRP3炎性小体的激活[35]。A20作为髓核细胞中的一种抗炎分子,通过促进线粒体自噬和稳定线粒体动力学来减轻髓核细胞的焦亡和凋亡[36]。高胆固醇血症可能是椎间盘退行性变的潜在危险因素,与标准饮食相比,高胆固醇饮食大鼠表现出腰椎间盘退行性特征,且这种特性可通过降胆固醇药物阿托伐他汀来消除。在外源性胆固醇处理的大鼠髓核细胞中,胆固醇可通过激活内质网应激,从而诱导髓核细胞焦亡和细胞外基质降解[37]。
综上,细胞焦亡广泛存在于骨关节炎的一系列病理过程中,软骨细胞和成纤维细胞的焦亡在加重自身损伤的同时还可诱导细胞外基质降解和滑膜纤维化,肥胖和微晶体沉积作为骨关节炎的高危因素也可通过激活细胞焦亡,加重软骨退行性变。多项研究在椎间盘退行性变的发生过程中发现了NLRP3介导的焦亡,氧化应激、线粒体自噬、内质网应激均可以作为激活NLRP3的上游条件加重椎间盘退行性变。
2.2.3 骨骼肌相关疾病与细胞焦亡 骨骼肌是人体主要的蛋白质储存库,对运动和能量代谢至关重要,多种生理和病理状况都可影响骨骼肌的结构和形态。近期研究发现细胞焦亡及其后续的炎症反应在骨骼肌疾病中发挥重要作用。
肌肉萎缩是骨骼肌蛋白质合成和降解失衡的结果,分为原发性肌肉萎缩和继发性肌肉萎缩[38]。杜氏肌营养不良症是一种原发性肌肉萎缩,研究发现杜氏肌营养不良症模型小鼠中NLRP3等焦亡相关分子mRNA水平显著升高[39]。创伤导致的神经损伤可引起继发性肌肉萎缩,在敲除NLRP3基因的动物肌肉组织中,失神经诱导的肌肉萎缩标志物MuRF1和Atrogin-1表达受到抑制,显著改善了肌肉萎缩[40]。此外,一些药物的不良反应也可导致肌肉萎缩,在地塞米松诱导的C2C12肌管萎缩中,焦亡相关分子NLRP3、Caspase-1和GSDMD的mRNA表达被激活,并且通过沉默GSDMD,可缓解地塞米松诱导的Atrogin-1和MuRF1表达增加[41]。Smyd1是一种组蛋白甲基转移酶,对肌肉发育至关重要,香烟烟雾暴露通过抑制Smyd1表达,引发P2RX7诱导的肌管C2C12细胞焦亡,导致C2C12细胞分化异常和肌管形成受损,造成成年动物的肌肉萎缩[42]。胚胎期香烟烟雾暴露也可上调P2RX7诱导的细胞焦亡,诱导先天性畸形足肌肉表型[43]。除病理性因素之外,衰老也可引起骨骼肌容量下降。老年骨骼肌减少症小鼠模型表现为炎症状态,肿瘤坏死因子α水平升高,肿瘤坏死因子α过表达可激活C2C12肌管中的Caspase-8和Caspase-3来诱导GSDME介导的焦亡,降低骨骼肌的质量与力量[44]。
特发性炎症性肌病是一组异质性自身免疫性疾病,患者通常具有肌无力、肌耐力低下等症状,分为皮肌炎、多发性肌炎、包涵体肌炎、无肌病性皮肌炎等亚型。细胞焦亡的多种通路在特发性炎症性肌病的病理过程中发挥作用。研究发现,丙酮酸激酶同工酶M2(pyruvate kinase M2,PKM2)和NLRP3炎症小体在皮肌炎/多发性肌炎的肌纤维中表达上调并呈正相关,并且在皮肌炎和多发性肌炎患者的肌肉组织中发现了多个与糖酵解相关的过程被异常调节,研究者认为皮肌炎/多发性肌炎中PKM2依赖的糖酵解通过激活NLRP3炎症小体促进骨骼肌细胞焦亡[45]。皮肌炎肌肉标本中线粒体凋亡通路相关分子以及GSDME的表达均升高,其中Caspase-3可切割GSDME,将线粒体凋亡转化为焦亡,从而导致束周萎缩[46]。有研究使用小鼠实验性免疫性肌炎模型模拟人类肌炎,证实了Caspase-4/5/11介导的非典型性焦亡途径也参与了特发性炎症性肌病的发病机制[47]。
综上,在多种原发性和继发性肌肉萎缩的研究中,均发现了NLRP3介导的C2C12细胞焦亡,且在胚胎与成体动物模型中,这些C2C12细胞焦亡都可造成不同程度的肌肉萎缩。在特发性炎症性肌病的研究中,GSDMD介导的经典与非经典焦亡与GSDME介导的焦亡均发生了上调。
2.2.4 骨相关疾病与细胞焦亡 骨的稳定性由破骨细胞介导的骨吸收和成骨细胞介导的骨形成精确控制,当平衡被打破时,骨组织的微结构会出现异常。骨质疏松症是一种常见的全身性骨骼疾病,分为原发性和继发性两大类,患者骨小梁体积减少,骨脆性增强,骨折风险增加。
骨髓间充质干细胞具有分化为成骨细胞的潜能,在骨形成过程中发挥着至关重要的作用。RUAN等[48]在骨质疏松症患者骨组织标本中发现了焦亡的异常激活和成骨能力的受损,而抑制Caspase-1介导的焦亡可促进骨髓间充质干细胞的体外成骨分化。PAN等[49]研究显示,过表达长链非编码RNA SNHG1可明显促进HMGB1及GSDMD-N的表达,通过激活焦亡来抑制骨髓间充质干细胞的成骨分化。泛素特异性蛋白酶1(ubiquitin specific protease 1,USP1)通过抑制核因子κB-NLRP3介导的焦亡,对小鼠胚胎成骨细胞前体细胞MC3T3-E1起到保护作用,泛素连接酶(TNF receptor associated factor 6,TRAF6)被公认为是抑制破骨细胞功能的治疗靶点,USP1似乎可以通过抑制TRAF6泛素化来调控核因子κB信号通路,提示USP1在改善骨质疏松症中的潜力[50]。绝经后骨质疏松症是一类常见的继发性骨质疏松,雌激素缺乏被认为是骨质疏松症进展的关键诱因。在去卵巢的骨质疏松症小鼠模型中,研究者发现了炎症反应的增强和成骨活性的抑制,体外研究显示,小鼠成骨细胞中细胞焦亡和炎症反应标志物显著增加,成骨分化标志物明显减少,而NLRP3基因敲除可抑制这种细胞焦亡并促进成骨分化,改善去卵巢诱导的骨小梁数量减少[51]。在糖尿病骨质疏松的相关研究中,Behera等[52]发现糖尿病小鼠体内的焦亡反应减少了骨髓间充质干细胞中成骨标志物RUNX2和骨钙素的表达,且通过副神经依赖作用激活破骨细胞的生成。研究发现,老年性骨质疏松症患者中,PKM2显著过表达,通过NLRP3/Caspase-1/GSDMD信号通路介导骨髓间充质干细胞焦亡,从而抑制成骨,研究者通过动物实验证实,使用PKM2抑制剂可有效阻断与衰老相关的骨髓间充质干细胞中NLRP3激活和焦亡,并减少老年性骨质疏松症小鼠的骨丢失[53]。
综上,在骨质疏松的发生、发展进程中,细胞焦亡及后续炎症反应可通过抑制成骨细胞分化、增加成骨细胞死亡或促进破骨细胞功能等途径参与骨质疏松的病理过程。
细胞焦亡的分子机制及在运动系统疾病中的作用见图3。
2.3 靶向细胞焦亡治疗运动系统疾病
2.3.1 肌腱及韧带相关疾病 二硫仑被确定为GSDMD介导的焦亡和炎症细胞因子释放的有效抑制剂,以GSDMD为靶点,可减弱巨噬细胞焦亡、白细胞介素1β和HMGB1的释放[54]。研究表明,肌腱损伤小鼠经二硫仑处理后裂解的GSDMD得到有效抑制,促进了肌腱纤维重塑,这些发现揭示了GSDMD介导的巨噬细胞焦亡可能参与了肌腱损伤中纤维生成重塑的过程[55]。PE?IN-FRANCH等[56]使用3 mA经皮电刺激作用于跟腱损伤小鼠,发现电流引起少量NLRP3炎症小体激活,可诱导焦亡发生并释放白细胞介素1β,从而启动局部炎症反应,适当的炎症反应通过增加Ⅰ型胶原,改善胶原纤维排列来促进肌腱再生,而此过程几乎不会引起炎症小体介导的焦亡。在肌腱重塑过程中,中等的应力负荷有利于肌腱愈合,而超载对肌腱有害,可产生分解代谢反应[57]。循环拉伸通过促进过氧化
氢(H2O2)诱导的NLRP3炎症小体的激活来加速肌腱细胞中白细胞介素1β的成熟。此外,循环拉伸可通过破坏丝状肌动蛋白来增强NLRP3炎症小体的激活,进一步激活NLRP3/白细胞介素1β通路发挥促炎作用,从而触发甚至加剧局部炎症反应,最终导致肌腱损伤修复不良[58]。
WU等[19]通过体内和体外实验发现,脂肪间充质干细胞可通过降低盆底组织中活性氧的积累,阻断NLRP3/Caspase-1信号通路抑制焦亡,同时还可增加治疗部位抗氧化剂相关蛋白的表达,减少炎症因子的产生。此外,脂肪间充质干细胞还可在体内和体外诱导巨噬细胞由M1向M2极化,从而抑制炎症因子的释放和细胞焦亡,恢复细胞外基质的代谢平衡,促进盆底组织的修复。
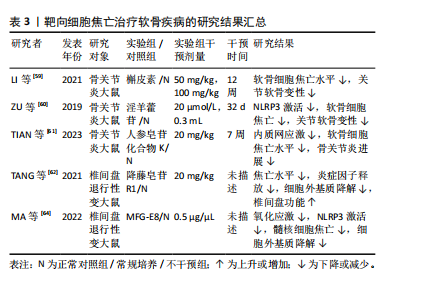
综上,通过靶向抑制GSDMD或避免肌腱损伤后的剧烈拉伸来减少NLRP3的过度激活可能是预防炎症加重的有效方法。此外,活性氧作为NLRP3的上游激活信号之一,也可能成为通过减轻焦亡修复韧带损伤的靶点。关于靶向细胞焦亡治疗肌腱及韧带疾病的相关研究结果见表2。
2.3.2 软骨相关疾病 近年来研究发现,中药提取物在骨关节炎的治疗中疗效显著。体外实验发现,槲皮素可通过抑制NLRP3信号通路缓解白细胞介素1β诱导的软骨细胞损伤[59]。在动物模型中,淫羊藿苷通过抑制NLRP3信号介导的Caspase-1通路减少焦亡来减轻骨关节炎中的软骨细胞损伤[60]。人参皂苷化合物K通过抑制软骨细胞内质网应激介导的NLRP3激活和焦亡来改善骨关节炎[61]。
降藤皂苷R1广泛应用于椎间盘退行性变的治疗,研究表明,降藤皂苷R1显著抑制大鼠椎间盘退行性变模型中NLRP3、GSDMD、Caspase-1、白细胞介素1β和肿瘤坏死因子α诱导的细胞外基质降解,表明降藤皂苷R1可能通过抑制核因子κB/NLRP3通路来保护椎间盘退行性变[62]。研究表明,氧化应激失衡条件下,髓核中TXNIP显著上调[63]。在人和大鼠髓核组织以及H2O2处理的髓核细胞中乳脂球表皮生长因子8 (milk fat globule EGF factor 8,MFG-E8)的表达均有所降低,而外源性补充MFG-E8可通过Nrf2/TXNIP/ NLRP3轴挽救H2O2诱导的氧化应激、线粒体功能障碍和NLRP3炎性小体的激活,并保护髓核细胞免受焦亡和细胞外基质降解[64]。
综上所述,靶向NLRP3炎症小体可作为治疗骨关节炎的有效途径,通过调控核因子κB、氧化应激、线粒体自噬等上游信号来抑制NLRP3的激活,可以作为治疗椎间盘退行性变的潜在方法。关于靶向细胞焦亡治疗软骨疾病的相关研究结果见表3。
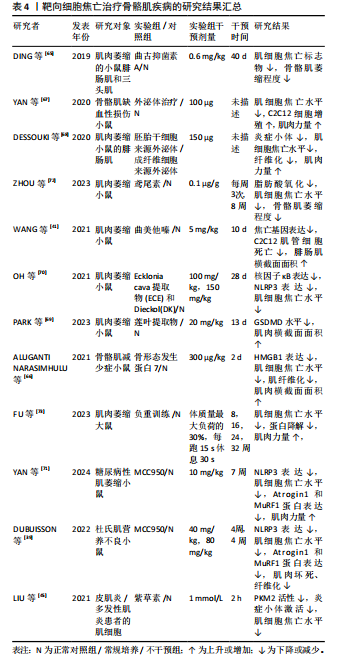
2.3.3 骨骼肌相关疾病 抑制细胞焦亡的上游通路可以作为一种可行的方法,在继发性肌肉萎缩的治疗中,曲古抑菌素A可通过抑制HDAC1/2,抑制细胞焦亡上调,改善肌肉萎缩和组织形态学改变[65]。在地塞米松诱导的肌肉萎缩中,曲美他嗪通过激活PI3K/AKT通路,可缓解地塞米松诱导的焦亡相关基因上调及C2C12肌管萎缩[41]。骨形态发生蛋白7可靶向HMGB1及其下游焦亡通路,显著提升糖尿病小鼠肌肉质量与体质量的比值及肌细胞面积,并减少糖尿病诱导的肌纤维化[66]。外泌体治疗的相关研究发现,环状RNA circHIPK3参与了焦亡调控,脐带间充质干细胞来源外泌体可通过释放circHIPK3,刺激C2C12细胞增殖,抑制骨骼肌细胞焦亡,从而促进骨骼肌缺血性损伤的修复[67]。胚胎干细胞来源外泌体可抑制阿霉素给药后NLRP3炎症小体的形成,从而减轻药物诱导的肌肉细胞毒性,改善肌肉组织萎缩和纤维化[68]。此外,研究发现中草药提取物也可抑制骨骼肌细胞焦亡,莲叶乙醇提取物能够通过抑制GSDMD介导的焦亡减轻地塞米松注射引起的肌肉质量和功能下降[69]。紫草素作为PKM2抑制剂,可通过抑制NLRP3炎症小体的激活来防止肌细胞焦亡,可能具有作为特发性炎症性肌病治疗方法的潜力[45]。直接抑制NLRP3炎症小体也可以用于治疗焦亡参与的骨骼肌相关疾病,Ecklonia cava提取物(ECE)和Dieckol(DK)可通过调节NLRP3炎症小体和焦亡来减轻地塞米松诱导的肌肉萎缩[70]。MCC950是一种特异性NLRP3抑制剂,通过抑制NLRP3介导的焦亡改善糖尿病患者的肌肉稳态和肌肉功能,联合有氧运动能够降低Atrogin1和MuRF1蛋白表达水平,更有效的增加肌肉力量和运动性能[71]。此外,MCC950可通过此途径减轻杜氏肌营养不良表型[39]。鸢尾素通过抑制脂肪酸氧化和骨骼肌细胞焦亡来改善慢性肾病患者肌肉萎缩[72]。负重运动训练可抑制大鼠肌肉中的蛋白降解及焦亡关键蛋白表达,从而减轻与年龄相关的肌肉萎缩[73]。
综上,干细胞来源外泌体在治疗肌萎缩方面具有很大潜力,也有大量研究发现使用靶向抑制剂或中药提取物抑制NLRP3或GSDMD激活可有效减轻肌肉萎缩。运动疗法也可减轻骨骼肌细胞焦亡,这可能与运动诱导产生的鸢尾素作用有关。关于靶向细胞焦亡治疗骨骼肌疾病的相关研究结果见表4。
2.3.4 骨相关疾病 TAO等[74]通过体内实验发现,尿石素A可通过浓度依赖性的方式抑制核因子κB配体的受体激活物触发的焦亡,从而抑制破骨细胞生成,有效减少卵巢切除引起的全身骨量减少。运动疗法作为糖尿病常见的疗法之一,对于糖尿病继发的骨质疏松也起到一定作用,有研究者使用为期8周每周5次的跑步运动干预糖尿病小鼠,发现由运动诱导产生的鸢尾素可通过减轻炎症小体相关的细胞焦亡信号来减轻糖尿病小鼠的骨丢失[52]。知母/黄柏草本提取物可通过降低NLRP3、Asc、Caspase-1、GSDMD和白细胞介素1β的表达,从而减轻糖尿病大鼠椎体中成骨细胞焦亡,改善糖尿病大鼠椎体骨质疏松的进展[75]。晚期糖基化终末产物与糖尿病引起的骨质疏松密切相关,有研究使用最常见的晚期糖基化终末产物类型羧甲基赖氨酸进行细胞和动物实验,发现在羧甲基赖氨酸处理的骨髓间充质干细胞中LncRNA ORLNC1表达增加,过表达ORLNC1能够通过上调NLRP3相关蛋白的表达促进
骨髓间充质干细胞的焦亡,提示LncRNA在治疗糖尿病骨质疏松中的潜在可能[76]。此外,CHEN等[77]研究发现,外源性过表达神经肽Y能够加重去卵巢大鼠的结肠炎症,使肠屏障完整性受损,血清脂多糖升高,从而激活成骨细胞焦亡,进一步减少骨形成,而Y1受体拮抗剂(Y1Ra)给药后大鼠骨小梁的微结构得到改善,骨丢失受到抑制,证实了神经肽Y介导的脑-肠-骨轴的存在,这可能是治疗绝经后骨质疏松的一个新靶点。
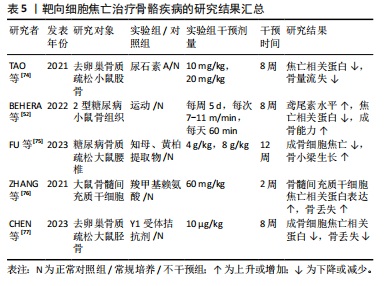
综上所述,使用运动疗法或中药提取物抑制炎症小体激活,或通过针对焦亡上游通路核因子κB等间接抑制焦亡,可能是治疗骨质疏松的可行方向。关于靶向细胞焦亡治疗骨骼疾病的相关研究结果见表5。
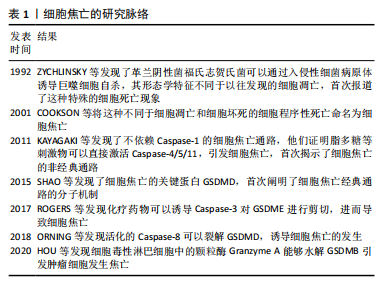
| [1] BRIGGS AM, CROSS MJ, HOY DG, et al. Musculoskeletal Health Conditions Represent a Global Threat to Healthy Aging: A Report for the 2015 World Health Organization World Report on Ageing and Health. Gerontologist. 2016;56 Suppl 2:S243-S255. [2] BRIGGS AM, WOOLF AD, DREINHÖFER K, et al. Reducing the global burden of musculoskeletal conditions. Bull World Health Organ. 2018;96(5):366-368. [3] 吴惠一,袁琴,张洋,等.1990-2019年我国肌肉骨骼疾病负担分析.中华疾病控制杂志,2023,27(6):655-661. [4] SHI J, GAO W, SHAO F. Pyroptosis: Gasdermin-Mediated Programmed Necrotic Cell Death. Trends Biochem Sci. 2017;42(4):245-254. [5] RAO Z, ZHU Y, YANG P, et al. Pyroptosis in inflammatory diseases and cancer. Theranostics. 2022;12(9):4310-4329. [6] ZYCHLINSKY A, PREVOST MC, SANSONETTI PJ. Shigella flexneri induces apoptosis in infected macrophages. Nature. 1992;358(6382):167-169. [7] COOKSON BT, BRENNAN MA. Pro-inflammatory programmed cell death. Trends Microbiol. 2001;9(3):113-114. [8] SHI J, ZHAO Y, WANG K, et al. Cleavage of GSDMD by inflammatory caspases determines pyroptotic cell death. Nature. 2015;526(7575):660-665. [9] SHI J, ZHAO Y, WANG Y, et al. Inflammatory caspases are innate immune receptors for intracellular LPS. Nature. 2014;514(7521):187-192. [10] ROGERS C, FERNANDES-ALNEMRI T, MAYES L, et al. Cleavage of DFNA5 by caspase-3 during apoptosis mediates progression to secondary necrotic/pyroptotic cell death. Nat Commun. 2017;8:14128. [11] ORNING P, WENG D, STARHEIM K, et al. Pathogen blockade of TAK1 triggers caspase-8-dependent cleavage of gasdermin D and cell death. Science. 2018; 362(6418):1064-1069. [12] HOU J, ZHAO R, XIA W, et al. PD-L1-mediated gasdermin C expression switches apoptosis to pyroptosis in cancer cells and facilitates tumour necrosis. Nat Cell Biol. 2020;22(10):1264-1275. [13] KANNUS P. Structure of the tendon connective tissue. Scand J Med Sci Sports. 2000;10(6):312-320. [14] THOMOPOULOS S, PARKS WC, RIFKIN DB, et al. Mechanisms of tendon injury and repair. J Orthop Res. 2015;33(6):832-839. [15] THANKAM FG, ROESCH ZK, DILISIO MF, et al. Association of Inflammatory Responses and ECM Disorganization with HMGB1 Upregulation and NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation in the Injured Rotator Cuff Tendon. Sci Rep. 2018; 8(1):8918. [16] LI J, WANG X, YAO Z, et al. NLRP3-Dependent Crosstalk between Pyroptotic Macrophage and Senescent Cell Orchestrates Trauma-Induced Heterotopic Ossification During Aberrant Wound Healing. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2023;10(19): e2207383. [17] LU W, YAN J, WANG C, et al. Interorgan communication in neurogenic heterotopic ossification: the role of brain-derived extracellular vesicles. Bone Res. 2024; 12(1):11. [18] LIM WL, LIAU LL, NG MH, et al. Current Progress in Tendon and Ligament Tissue Engineering. Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2019;16(6):549-571. [19] WU X, ZHANG F, MAO X, et al. The mechanism of adipose mesenchymal stem cells to stabilize the immune microenvironment of pelvic floor injury by regulating pyroptosis and promoting tissue repair. Mater Today Bio. 2023;24:100910. [20] KRISHNAN Y, GRODZINSKY AJ. Cartilage diseases. Matrix Biol. 2018;71-72:51-69. [21] HAWKER GA. Osteoarthritis is a serious disease. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2019;37 Suppl 120(5):3-6. [22] HE Z, NIE P, LU J, et al. Less mechanical loading attenuates osteoarthritis by reducing cartilage degeneration, subchondral bone remodelling, secondary inflammation, and activation of NLRP3 inflammasome. Bone Joint Res. 2020; 9(10):731-741. [23] WANG M, SAMPSON ER, JIN H, et al. MMP13 is a critical target gene during the progression of osteoarthritis. Arthritis Res Ther. 2013;15(1):R5.
[24] FOSANG AJ, BEIER F. Emerging Frontiers in cartilage and chondrocyte biology. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol. 2011;25(6):751-766. [25] ZHANG L, ZHANG L, HUANG Z, et al. Increased HIF-1α in Knee Osteoarthritis Aggravate Synovial Fibrosis via Fibroblast-Like Synoviocyte Pyroptosis. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2019;2019:6326517. [26] VANDANMAGSAR B, YOUM YH, RAVUSSIN A, et al. The NLRP3 inflammasome instigates obesity-induced inflammation and insulin resistance. Nat Med. 2011; 17(2):179-188. [27] CORR EM, CUNNINGHAM CC, HELBERT L, et al. Osteoarthritis-associated basic calcium phosphate crystals activate membrane proximal kinases in human innate immune cells. Arthritis Res Ther. 2017;19(1):23. [28] DERFUS BA, KURIAN JB, BUTLER JJ, et al. The high prevalence of pathologic calcium crystals in pre-operative knees. J Rheumatol. 2002;29(3):570-574. [29] PAZÁR B, EA HK, NARAYAN S, et al. Basic calcium phosphate crystals induce monocyte/macrophage IL-1β secretion through the NLRP3 inflammasome in vitro. J Immunol. 2011;186(4):2495-2502. [30] RAJ PP. Intervertebral disc: anatomy-physiology-pathophysiology-treatment. Pain Pract. 2008;8(1):18-44. [31] KIRNAZ S, CAPADONA C, WONG T, et al. Fundamentals of Intervertebral Disc Degeneration. World Neurosurg. 2022;157:264-273. [32] TANG P, ZHU R, JI WP, et al. The NLRP3/Caspase-1/Interleukin-1β Axis Is Active in Human Lumbar Cartilaginous Endplate Degeneration. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2016;474(8):1818-1826. [33] LE MAITRE CL, FREEMONT AJ, HOYLAND JA. The role of interleukin-1 in the pathogenesis of human intervertebral disc degeneration. Arthritis Res Ther. 2005;7(4):R732-R745. [34] LU P, ZHENG H, MENG H, et al. Mitochondrial DNA induces nucleus pulposus cell pyroptosis via the TLR9-NF-κB-NLRP3 axis. J Transl Med. 2023;21(1):389. [35] MA Z, TANG P, DONG W, et al. SIRT1 alleviates IL-1β induced nucleus pulposus cells pyroptosis via mitophagy in intervertebral disc degeneration. Int Immunopharmacol. 2022;107:108671. [36] PENG X, ZHANG C, ZHOU ZM, et al. A20 attenuates pyroptosis and apoptosis in nucleus pulposus cells via promoting mitophagy and stabilizing mitochondrial dynamics. Inflamm Res. 2022;71(5-6):695-710. [37] YAN J, LI S, ZHANG Y, et al. Cholesterol Induces Pyroptosis and Matrix Degradation via mSREBP1-Driven Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress in Intervertebral Disc Degeneration. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022;9:803132. [38] YIN L, LI N, JIA W, et al. Skeletal muscle atrophy: From mechanisms to treatments. Pharmacol Res. 2021;172:105807. [39] DUBUISSON N, DAVIS-LÓPEZ DE CARRIZOSA MA, VERSELE R, et al. Inhibiting the inflammasome with MCC950 counteracts muscle pyroptosis and improves Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Front Immunol. 2022;13:1049076. [40] YOU Z, HUANG X, XIANG Y, et al. Ablation of NLRP3 inflammasome attenuates muscle atrophy via inhibiting pyroptosis, proteolysis and apoptosis following denervation. Theranostics. 2023;13(1):374-390. [41] WANG L, JIAO XF, WU C, et al. Trimetazidine attenuates dexamethasone-induced muscle atrophy via inhibiting NLRP3/GSDMD pathway-mediated pyroptosis. Cell Death Discov. 2021;7(1):251. [42] LI F, XU M, MIAO J, et al. Down-regulated Smyd1 participated in the inhibition of myoblast differentiation induced by cigarette smoke extract. Toxicol Lett. 2023;383:98-111. [43] LOU Y, MIAO J, LI F, et al. Maternal smoking during pregnancy aggravated muscle phenotype in FHL1-/y offspring mice similar to congenital clubfoot through P2RX7-mediated pyroptosis. Toxicol Lett. 2021;345:54-60. [44] WU J, LIN S, CHEN W, et al. TNF-α contributes to sarcopenia through caspase-8/caspase-3/GSDME-mediated pyroptosis. Cell Death Discov. 2023;9(1):76. [45] LIU D, XIAO Y, ZHOU B, et al. PKM2-dependent glycolysis promotes skeletal muscle cell pyroptosis by activating the NLRP3 inflammasome in dermatomyositis/polymyositis. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2021;60(5):2177-2189. [46] LIU M, LI L, DAI T, et al. Gasdermine E-Dependent Mitochondrial Pyroptotic Pathway in Dermatomyositis: A Possible Mechanism of Perifascicular Atrophy. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 2020;79(5):551-561. [47] MA M, CHAI K, DENG R. Study of the correlation between the noncanonical pathway of pyroptosis and idiopathic inflammatory myopathy. Int Immunopharmacol. 2021;98:107810. [48] RUAN H, ZHANG H, FENG J, et al. Inhibition of Caspase-1-mediated pyroptosis promotes osteogenic differentiation, offering a therapeutic target for osteoporosis. Int Immunopharmacol. 2023;124(Pt B):110901. [49] PAN K, LU Y, CAO D, et al. Long Non-coding RNA SNHG1 Suppresses the Osteogenic Differentiation of Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells by Binding with HMGB1. Biochem Genet. 2024;62(4):2869-2883. [50] SUN D, PENG Y, GE S, et al. USP1 Inhibits NF-κB/NLRP3 Induced Pyroptosis through TRAF6 in Osteoblastic MC3T3-E1 Cells. J Musculoskelet Neuronal Interact. 2022;22(4):536-545. [51] YANG C, SONG B, HAN L, et al. Study on the mechanism of NLRP3 effect on the skeleton of de-ovalized mice. Biochem Biophys Rep. 2023;35:101496. [52] BEHERA J, ISON J, VOOR MJ, et al. Exercise-Linked Skeletal Irisin Ameliorates Diabetes-Associated Osteoporosis by Inhibiting the Oxidative Damage-Dependent miR-150-FNDC5/Pyroptosis Axis. Diabetes. 2022;71(12):2777-2792. [53] LI Z, WANG B, WANG R, et al. Identification of PKM2 as a pyroptosis-related key gene aggravates senile osteoporosis via the NLRP3/Caspase-1/GSDMD signaling pathway. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2024;169:106537. [54] HU JJ, LIU X, XIA S, et al. FDA-approved disulfiram inhibits pyroptosis by blocking gasdermin D pore formation. Nat Immunol. 2020;21(7):736-745. [55] ZHOU Q, WANG W, YANG F, et al. Disulfiram Suppressed Peritendinous Fibrosis Through Inhibiting Macrophage Accumulation and Its Pro-inflammatory Properties in Tendon Bone Healing. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022;10:823933. [56] PEÑIN-FRANCH A, GARCÍA-VIDAL JA, MARTÍNEZ CM, et al. Galvanic current activates the NLRP3 inflammasome to promote Type I collagen production in tendon. Elife. 2022;11:e73675. [57] CILLI F, KHAN M, FU F, et al. Prostaglandin E2 affects proliferation and collagen synthesis by human patellar tendon fibroblasts. Clin J Sport Med. 2004;14(4): 232-236. [58] CHEN Q, ZHOU J, ZHANG B, et al. Cyclic Stretching Exacerbates Tendinitis by Enhancing NLRP3 Inflammasome Activity via F-Actin Depolymerization. Inflammation. 2018;41(5):1731-1743. [59] LI W, WANG Y, TANG Y, et al. Quercetin Alleviates Osteoarthritis Progression in Rats by Suppressing Inflammation and Apoptosis via Inhibition of IRAK1/NLRP3 Signaling. J Inflamm Res. 2021;14:3393-3403. [60] ZU Y, MU Y, LI Q, et al. Icariin alleviates osteoarthritis by inhibiting NLRP3-mediated pyroptosis. J Orthop Surg Res. 2019;14(1):307. [61] TIAN Y, FENG X, ZHOU Z, et al. Ginsenoside Compound K Ameliorates Osteoarthritis by Inhibiting the Chondrocyte Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress-Mediated IRE1α-TXNIP-NLRP3 Axis and Pyroptosis. J Agric Food Chem. 2023; 71(3):1499-1509. [62] TANG K, SU W, HUANG C, et al. Notoginsenoside R1 suppresses inflammatory response and the pyroptosis of nucleus pulposus cells via inactivating NF-κB/NLRP3 pathways. Int Immunopharmacol. 2021;101(Pt B):107866. [63] CHEN Y, CAO X, PAN B, et al. Verapamil attenuates intervertebral disc degeneration by suppressing ROS overproduction and pyroptosis via targeting the Nrf2/TXNIP/NLRP3 axis in four-week puncture-induced rat models both in vivo and in vitro. Int Immunopharmacol. 2023;123:110789. [64] MA H, XIE C, CHEN Z, et al. MFG-E8 alleviates intervertebral disc degeneration by suppressing pyroptosis and extracellular matrix degradation in nucleus pulposus cells via Nrf2/TXNIP/NLRP3 axis. Cell Death Discov. 2022;8(1):209. [65] DING J, LI F, CONG Y, et al. Trichostatin A inhibits skeletal muscle atrophy induced by cigarette smoke exposure in mice. Life Sci. 2019;235:116800. [66] ALUGANTI NARASIMHULU C, SINGLA DK. Amelioration of diabetes-induced inflammation mediated pyroptosis, sarcopenia, and adverse muscle remodelling by bone morphogenetic protein-7. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 2021;12(2): 403-420. [67] YAN B, ZHANG Y, LIANG C, et al. Stem cell-derived exosomes prevent pyroptosis and repair ischemic muscle injury through a novel exosome/circHIPK3/FOXO3a pathway. Theranostics. 2020;10(15):6728-6742. [68] DESSOUKI FBA, KUKREJA RC, SINGLA DK. Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes Ameliorate Doxorubicin-Induced Muscle Toxicity through Counteracting Pyroptosis. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2020;13(12):450. [69] PARK E, CHOI H, TRUONG CS, et al. The Inhibition of Autophagy and Pyroptosis by an Ethanol Extract of Nelumbo nucifera Leaf Contributes to the Amelioration of Dexamethasone-Induced Muscle Atrophy. Nutrients. 2023;15(4):804. [70] OH S, YANG J, PARK C, et al. Dieckol Attenuated Glucocorticoid-Induced Muscle Atrophy by Decreasing NLRP3 Inflammasome and Pyroptosis. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(15):8057. [71] YAN X, FU P, ZHANG Y, et al. MCC950 Ameliorates Diabetic Muscle Atrophy in Mice by Inhibition of Pyroptosis and Its Synergistic Effect with Aerobic Exercise. Molecules. 2024;29(3):712. [72] ZHOU T, WANG S, PAN Y, et al. Irisin Ameliorated Skeletal Muscle Atrophy by Inhibiting Fatty Acid Oxidation and Pyroptosis Induced by Palmitic Acid in Chronic Kidney Disease. Kidney Blood Press Res. 2023;48(1):628-641. [73] FU P, GONG L, YANG L, et al. Weight bearing training alleviates muscle atrophy and pyroptosis of middle-aged rats. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023;14: 1202686. [74] TAO H, LI W, ZHANG W, et al. Urolithin A suppresses RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis and postmenopausal osteoporosis by, suppresses inflammation and downstream NF-κB activated pyroptosis pathways. Pharmacol Res. 2021;174:105967. [75] FU F, LUO H, DU Y, et al. AR/PCC herb pair inhibits osteoblast pyroptosis to alleviate diabetes-related osteoporosis by activating Nrf2/Keap1 pathway. J Cell Mol Med. 2023;27(22):3601-3613. [76] ZHANG L, LI S, LI J, et al. LncRNA ORLNC1 Promotes Bone Marrow Mesenchyml Stem Cell Pyroptosis Induced by Advanced Glycation End Production by Targeting miR-200b-3p/Foxo3 Pathway. Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2021;17(6):2262-2275. [77] CHEN Z, LV M, LIANG J, et al. Neuropeptide Y-Mediated Gut Microbiota Alterations Aggravate Postmenopausal Osteoporosis. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2023;10(33):e2303015. [78] WANG S, WANG H, FENG C, et al. The regulatory role and therapeutic application of pyroptosis in musculoskeletal diseases. Cell Death Discov. 2022;8(1):492. |
| [1] | 赖鹏宇, 梁 冉, 沈 山. 组织工程技术修复颞下颌关节:问题与挑战[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(在线): 1-9. |
| [2] | 张艺博, 卢健棋, 毛美玲, 庞 延, 董 礼, 杨尚冰, 肖 湘. 类风湿关节炎与冠状动脉粥样硬化的因果关系:GWAS数据库血清代谢物和炎症因子数据[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(在线): 1-9. |
| [3] | 余 帅, 刘家伟, 朱 彬, 潘 檀, 李兴龙, 孙广峰, 于海洋, 丁 亚, 王宏亮. 小分子药物治疗骨关节炎的热点问题及应用前景[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(9): 1913-1922. |
| [4] | 赵济宇, 王少伟. 叉头框转录因子O1信号通路与骨代谢[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(9): 1923-1930. |
| [5] | 李开颖, 魏晓歌, 宋 斐, 杨 楠, 赵振宁, 王 燕, 穆 静, 马惠昇. 理筋手法调控兔骨骼肌损伤修复中瘢痕形成的作用机制[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(8): 1600-1608. |
| [6] | 李花园, 李 春, 刘君伟, 王 亭, 李 龙, 武永利. 温针灸干预慢性疲劳综合征大鼠骨骼肌PINK1/Parkin通路的变化[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(8): 1618-1625. |
| [7] | 王选强, 张文洋, 李 阳, 孔维签, 李 伟, 王 乐, 厉中山, 白 石. 低频脉冲磁场慢性暴露对健康成年股四头肌收缩力及形态的影响[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(8): 1634-1642. |
| [8] | 于经邦, 吴亚云. 非编码RNA在肺纤维化过程中的调控作用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(8): 1659-1666. |
| [9] | 王秋月, 靳 攀, 蒲 锐. 运动干预与细胞焦亡在骨关节炎中的作用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(8): 1667-1675. |
| [10] | 袁维勃, 刘 婵, 余丽梅. 肝脏类器官在肝脏疾病模型与移植治疗中的应用潜力[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(8): 1684-1692. |
| [11] | 尹 路, 蒋川锋, 陈俊杰, 易 明, 王子赫, 石厚银, 汪国友, 沈骅睿. 沙苑子苷A对关节软骨细胞凋亡的影响[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(8): 1541-1547. |
| [12] | 李帝均, 酒精卫, 刘海峰, 闫 磊, 李松岩, 王 斌. 明胶三维微球装载人脐带间充质干细胞修复慢性肌腱病[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(7): 1356-1362. |
| [13] | 刘 琪, 李林臻, 李玉生, 焦泓焯, 杨 程, 张君涛. 淫羊藿苷含药血清促进3种细胞共培养体系中软骨细胞增殖和干细胞成软骨分化[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(7): 1371-1379. |
| [14] | 彭洪成, 彭国璇, 雷安毅, 林 圆, 孙 红, 宁 旭, 尚显文, 邓 进, 黄明智. 血小板衍生生长因子BB参与生长板损伤修复的作用与机制[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(7): 1497-1503. |
| [15] | 喻 婷, 吕冬梅, 邓 浩, 孙 涛, 程 钎. 淫羊藿苷预处理增强人牙周膜干细胞对M1型巨噬细胞的影响[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(7): 1328-1335. |
细胞焦亡是一种程序性细胞死亡,它由Gasdermin家族蛋白介导并伴随炎症反应,根据半胱天冬酶(Caspase)的亚型可以分为Caspase-1依赖的经典途径、Caspase-4/5/11依赖的非经典途径和其他途径,细胞焦亡可导致细胞膜孔隙形成和细胞裂解,并释放炎症因子激活炎症反应[4]。正常情况下,适度焦亡有利于维持细胞内稳态,增强免疫功能,帮助宿主抵御病原体感染,但过度焦亡会导致大量细胞死亡和严重的炎症反应,从而造成组织损伤[5]。细胞裂解死亡和炎症反应广泛发生于肌腱病、骨质疏松症、骨关节炎、椎间盘退变、肌萎缩症等多种运动系统疾病中,因此,近年来国内外学者开始从细胞焦亡入手探究其对运动系统疾病的影响及作用机制,并发掘潜在的临床治疗价值。
通过梳理近25年来有关运动系统疾病中细胞焦亡的作用及机制研究,回顾细胞焦亡对运动系统疾病的作用,并总结归纳细胞焦亡影响运动系统疾病的分子机制。文章重点关注了肌腱与韧带、软骨、骨、骨骼肌4种组织的常见疾病,旨在依据实验数据结果,探究细胞焦亡在其中的作用及机制,并对未来靶向细胞焦亡治疗和预防运动系统疾病打下基础。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
1.1 资料来源
1.1.1 检索人及检索时间 第一作者于2023年12月进行检索。
1.1.2 检索文献时限 2000年1月至2024年1月。
1.1.3 检索数据库 PubMed数据库、中国知网。
1.1.4 检索词 英文检索词为“pyroptosis,tendons,ligaments,cartilage,muscles,bones”;中文检索词为“焦亡,肌腱,韧带,软骨,骨骼肌,骨骼”。
1.1.5 检索策略 采用主题词和自由词结合的方式进行检索,以 PubMed和中国知网为例,具体检索策略见图1。
1.1.6 手工检索情况 无。
1.1.7 检索文献量 PubMed数据库检索得到文献334篇,中国知网检索得到文献88篇。
1.2 入组标准
1.2.1 纳入标准 ①文献研究类型为具有完整实验步骤的、与主题词相关的临床试验或临床前实验;②实验对象为人体或动物体分离出的正常肌肉骨骼组织,或通过人工干预制造的运动系统疾病病理模型;③实验研究结果为组织层面或分子信号转导机制方面发生的变化。
1.2.2 排除标准 ①综述、会议类文献;②与主题相关性不高的文献;③实验对象、干预措施以及结果等不符合纳入标准的研究;④风湿免疫病相关的文献。
1.3 文献质量评估及数据提取 通过数据库检索共获取文献422篇,去除重复文献49篇,阅读题目、摘要后去除与文章无关的文献185篇,阅读全文后进一步排除110篇文献,最终纳入文献78篇。具体文献筛选流程见图2。
3.1 既往他人在该领域研究的贡献 大量研究证实了细胞焦亡及其后续的炎症反应在多种运动系统疾病的发生、发展过程中发挥了作用,靶向细胞焦亡及其上游相关通路可作为有效治疗运动系统疾病的途径之一。
3.2 作者综述区别于他人他篇的特点 目前关注细胞焦亡在运动系统疾病中的影响及治疗策略相关的综述较少,仅有1篇。WANG等[78]探讨了细胞焦亡在骨关节炎、类风湿性关节炎、骨质疏松症、痛风性关节炎、强直性脊柱炎等常见的运动系统疾病中的作用,并按治疗方式总结了靶向细胞焦亡治疗运动系统疾病的可行策略。
此综述以近25年的相关文献作为参考,从细胞焦亡的分子机制、细胞焦亡在运动系统疾病中的作用以及治疗策略3个方面进行总结,侧重于细胞焦亡在运动系统不同组织中的分子机制及治疗方法,更为全面地纳入了肌腱与韧带相关的研究,在治疗方法的总结上涵盖了药物治疗以外的治疗策略,包括运动疗法、物理疗法等。
3.3 综述的局限性 文中部分参考文献的时间跨度较大,动物模型不统一,且实验主要集中在动物实验或细胞实验,有关细胞焦亡对运动系统疾病影响的临床研究较少。
3.4 综述的重要意义 文章归纳总结了细胞焦亡在运动系统疾病中的研究进展,为治疗和预防运动系统疾病提供了临床思路,并对未来相关领域的研究方向进行了展望。通过分析近25年细胞焦亡对运动系统疾病影响的相关研究,总结了焦亡的典型、非典型和其他通路,讨论了焦亡在几种运动系统疾病中的作用机制及相关治疗策略,包括肌腱及韧带、软骨、骨骼肌、骨的常见疾病。此外,多项研究发现核因子κB通路、氧化应激、线粒体自噬等也可介导细胞焦亡引起损伤。目前针对焦亡治疗运动系统疾病的策略主要包括直接抑制焦亡相关分子、外泌体治疗、间充质干细胞治疗、中药提取物间接抑制焦亡、运动疗法等。然而,目前多数靶向细胞焦亡治疗运动系统疾病的研究大都基于体外或动物模型实验,而临床试验较少,由于啮齿动物和人类之间焦亡的途径存在差异,相关研究仍具有局限性。因此,为了未来更好地开发运动系统疾病的治疗方法,需要研究者进行更多临床研究,为治疗和预防运动系统疾病提供更高效的方法。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||