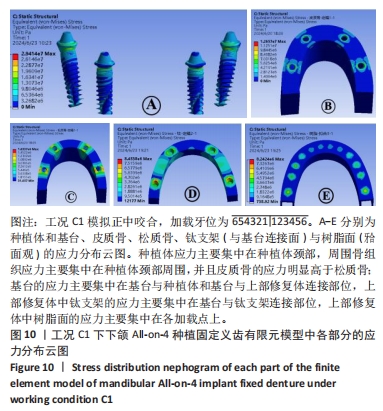
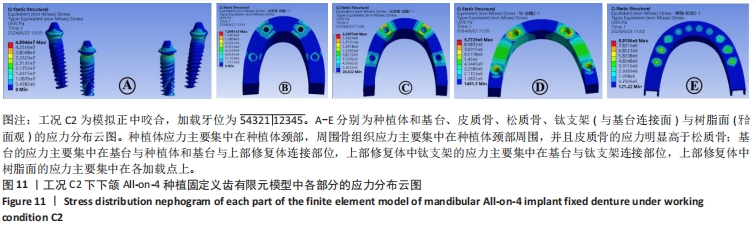
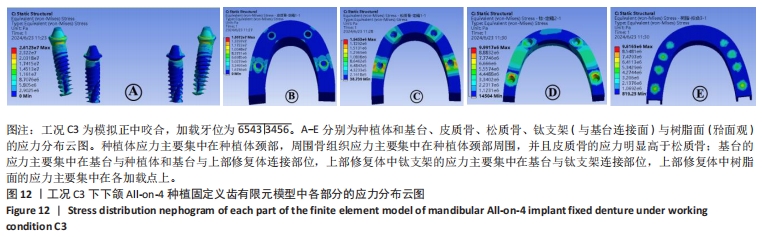
[1] OH SH, KIM Y, PARK JY, et al. Comparison of fixed implant-supported prostheses, removable implant supported prostheses, and complete dentures: patient satisfaction and oral health-related quality of life. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2016;27(2):e31-e37.
[2] YAO CJ, CAO C, BORNSTEIN MM, et al. Patient-reported outcome measures
of edentulous patients restored with implant-supported removable and fixed prostheses: A systematic review. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2018;29 Suppl 16:241-254.
[3] REISSMANN DR, DARD M, LAMPRECHT R, et al. Oral health-related quality of life in subjects with implant-supported prostheses: A systematic review. J Dent. 2017;65:22-40.
[4] ELSYAD MA, ELGAMAL M, MOHAMMED ASKAR O, et al. Patient satisfaction and oral health-related quality of life (OHRQoL) of conventional denture, fixed prosthesis and milled bar overdenture for All-on-4 implant rehabilitation. A crossover study. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2019;30(11):1107-1117.
[5] MALÓ P, RANGERT B, NOBRE M. “All-on-Four” immediate-function concept with Branemark System implants for completely edentulous mandibles: a retrospective clinical study. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res. 2003;5 Suppl 1:2-9.
[6] CHAN MH, NUDELL YA. All-on-4 Concept Update. Dent Clin North Am. 2021;65(1):211-227.
[7] GRANDI T, SIGNORINI L. Rehabilitation of the completely edentulous mandible by all-on-four treatment concept: a retrospective cohort study with up to 10 years follow-up. Medicina (Kaunas). 2021;58(1):10.
[8] 陆婧,李英,孟茂花,等.三维有限元方法分析“All-on-4”技术的生物力学特征[J].中国组织工程研究,2024,28(22):3591-3596.
[9] 张海萍,许天民,林久祥.β函数拟合正常(牙合)牙弓形态的研究[J].口腔正畸学,2005,12(1):19-23.
[10] TAKAHASHI T, SHIMAMURA I, SAKURAI K.Influence of number and inclination angle of implants on stress distribution in mandibular cortical bone with All-on-4 Concept. J Prosthodont Res. 2010;54(4): 179-184.
[11] 王璨,顾卫平,蒋煜彬,等.不同种植设计对下颌无牙颌应力影响的有限元分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2022,26(4):573-578.
[12] HAROUN F, OZAN O. Evaluation of Stresses on Implant, Bone, and Restorative Materials Caused by Different Opposing Arch Materials in Hybrid Prosthetic Restorations Using the All-on-4 Technique. Materials (Basel). 2021;14(15):4308.
[13] 王煜婷,张少锋,董岩,等.All-on-4种植体参数对周围骨应力影响的三维有限元分析[J].实用口腔医学杂志,2014,30(2):193-197.
[14] 温颖,郑东翔,张振庭,等.全口无牙颌应用种植固定修复后的咬合力分布研究[J].北京口腔医学,2008,16(6):325-328.
[15] 王琰玲,殷新民.不同侧方(牙合)型者尖对尖颌位时相对(牙合)力的比较研究[J].口腔医学,2009,29(9):476-478.
[16] 王惠芸.我国人牙的测量和统计[J].中华口腔科杂志,1959,7(3): 149-155.
[17] 皮昕.口腔解剖生理学[M].6版.北京:人民卫生出版社,2007: 288-289.
[18] DO TA, LE HS, SHEN YW, et al. Risk factors related to late failure of dental implant-a systematic review of recent studies. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020;17(11):3931.
[19] SZABÓ ÁL, NAGY ÁL, LÁSZLÓFY C, et al. Distally tilted implants according to the all-on-four® treatment concept for the rehabilitation of complete edentulism: a 3.5-year retrospective radiographic study of clinical outcomes and marginal bone level changes. Dent J (Basel). 2022;10(5):82.
[20] BOZYEL D, TAŞAR FARUK S. Biomechanical behavior of All-on-4 and M-4 configurations in an atrophic maxilla: a 3D finite element method. Med Sci Monit. 2021;27:e929908.
[21] PANDEY C, ROKAYA D, BHATTARAI BP. Contemporary Concepts in Osseointegration of Dental Implants: A Review. Biomed Res Int. 2022; 2022:6170452.
[22] TURKER N, BUYUKKAPLAN US, SADOWSKY SJ, et al. Finite element stress analysis of applied forces to implants and supporting tissues using the “All-on-Four” concept with different occlusal schemes. J Prosthodont. 2019;28(2):185-194.
[23] KIM Y, OH TJ, MISCH CE, et al. Occlusal considerations in implant therapy:clinical guidelines with biomechanical rationale. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2005;16(1):26-35.
[24] ABDUO J, TENNANT M. Impact of lateral occlusion schemes:a systematic review. J Prosthet Dent. 2015;114(2):193-204.
[25] MIRALLES R. Canine-guide occlusion and group function occlusion are equally acceptable when restoring the dentition. J Evid Based Dent Pract. 2016;16(1):41-43.
[26] TURKER N, ALKIS HT, SADOWSKY SJ, et al. Effects of occlusal scheme on all-on-four abutments, screws, and prostheses: a three-dimensional finite element study. J Oral Implantol. 2021;47(1):18-24.
[27] 王佐林,范震.无牙颌种植修复设计[J].口腔颌面外科杂志,2013, 23(1):1-7.
[28] 李晓茜,马晓妮,徐欣.无牙颌种植固定修复的咬合分析[J].华西口腔医学杂志,2018,36(6):628-63229
[29] 马斐斐,林野,邸萍,等.T-Scan Ⅲ咬合分析系统测量无牙颌All-on-4种植修复后力分布初探[J].中华口腔医学杂志,2016,51(9): 517-520.
[30] 庞丽娇,杨海萍,胡婷姿,等.All-on-4种植固定修复的咬合设计[J].口腔医学,2021,41(8):765-768.
[31] 木志翔,刘婷,陈陶,等.两种上颌无牙颌种植固定修复方案的有限元分析[J].口腔医学研究,2019,35(10):931-935.
[32] STOICHKOV B, KIROV D. Analysis of the causes of dental implant fracture: a retrospective clinical study. Quintessence Int. 2018;49(4): 279-286.
[33] SHETTY R, SINGH I, SUMAYLI HA, et al. Effect of prosthetic framework material, can lever length and opposing arch on peri-implant strain in an all-on-four implant prostheses. Niger J Clin Pract. 2021;24(6):866-873.
[34] GREENSTEIN G, CAVALLARO J JR. Cantilevers extending from unilateral implant-supported fixed prostheses: a review of the literature and presentation of practical guidelines. J Am Dent Assoc. 2010;141(10):1221-1230.
[35] DRAGO C. Ratios of cantilever lengths and anterior-posterior spreads of definitive hybrid full-arch, screw-retained prostheses: results of a clinical study. J Prosthodont. 2018;27(5):402-408.
[36] GOMES LCL, PIERRE FZ, TRIBST JPM, et al. Occlusal scheme effect on the biomechanical response of full-arch dental prosthesis supported by titanium implants: A systematic review. Metals. 2021;11:1574.
[37] BOZYEL D, TAAR FARUK S. Biomechanical behavior of All-on-4 and M-4 configurations in an Atrophic Maxilla: A 3D Finite Element Method. Med Sci Monit. 2021;27:e929908.
[38] MOHAMED AMA, ASKAR MG, El HOMOSSANY MEB. Stresses induced by one piece and two piece dental implants in All-on-4® implant supported prosthesis under simulated lateral occlusal loading: non linear finite element analysis study. BMC Oral Health. 2022;22(1):196.
[39] WANG Q, ZHANG ZZ, BAI SZ, et al. Biomechanical analysis of stress around the tilted implants with different cantilever lengths in all-on-4 concept. BMC Oral Health. 2022;22(1):469.
[40] SEZER T, KILIC K, ESIM E. Effect of implant diameter and bruxism on biomechanical performance in maxillary All-on-4 treatment: A 3D finite element analysis. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2022;37(4):709-721.
|