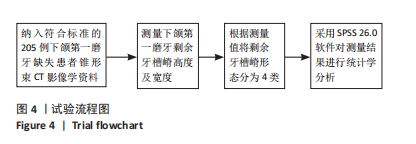
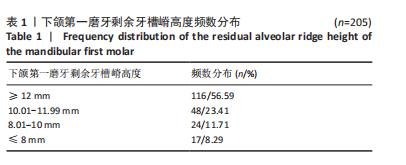
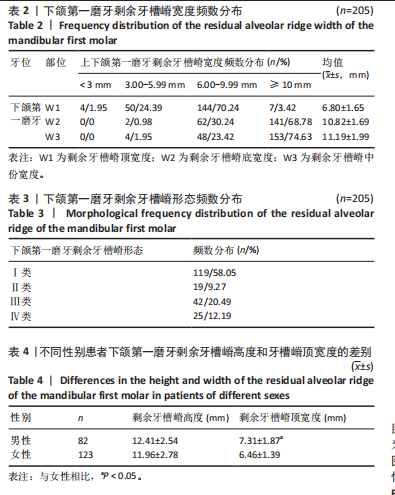
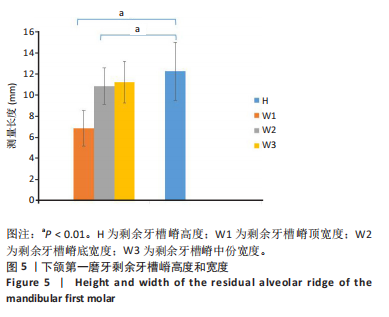
[1] BAIK UB, JUNG JY, JUNG HJ, et al. Alveolar bone changes after molar protraction in young adults with missing mandibular second premolars or first molars. Angle Orthod. 2022;92(1):64-72.
[2] ISMAIL A, AL YAFI F. The Role of Radiographic Imaging in the Diagnosis and Management of Periodontal and Peri-Implant Diseases. Dent Clin North Am. 2024;68(2):247-258.
[3] VALIZADEH S, BAHARESTANI M, AMID R, et al. Evaluation of Maxillary Alveolar Ridge Morphology and Residual Bone for Implant Placement by Cone Beam Computed Tomography (CBCT). J Long Term Eff Med Implants. 2022;32(2):61-71.
[4] 山道信之,系濑正通主编,张怡泓主译.上颌窦底提升术 依据锥形束牙科CT影像诊断的高成功率植牙手术[M].北京:人民军医出版社,2012.
[5] CORDARO L, TERHEYDEN H主编,宿玉成主译.口腔种植的牙槽嵴骨增量程序分阶段方案[M].沈阳:辽宁科学技术出版社,2016.
[6] NUNES LS, BORNSTEIN MM, SENDI P, et al. Anatomical characteristics and dimensions of edentulous sites in the posterior maxillae of patients referred for implant therapy. Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent. 2013; 33(3):337-345.
[7] ŞEKER BK, ORHAN K, ŞEKER E, et al. Cone Beam CT Evaluation of Maxillary Sinus Floor and Alveolar Crest Anatomy for the Safe Placement of Implants. Curr Med Imaging. 2020;16(7):913-920.
[8] ZHANG W, SKRYPCZAK A, WELTMAN R. Anterior maxilla alveolar ridge dimension and morphology measurement by cone beam computerized tomography (CBCT) for immediate implant treatment planning. BMC Oral Health. 2015;15:65.
[9] ALDAHLAWI S, NOURAH DM, AZAB RY, et al. Cone-Beam Computed Tomography (CBCT)-Based Assessment of the Alveolar Bone Anatomy of the Maxillary and Mandibular Molars: Implication for Immediate Implant Placement. Cureus. 2023;15(7):e41608.
[10] BENIC GI, HÄMMERLE CH. Horizontal bone augmentation by means of guided bone regeneration. Periodontol 2000. 2014;66(1):13-40.
[11] CUCCHI A, VIGNUDELLI E, NAPOLITANO A, et al. Evaluation of complication rates and vertical bone gain after guided bone regeneration with non-resorbable membranes versus titanium meshes and resorbable membranes. A randomized clinical trial. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res. 2017;19(5):821-832.
[12] ARNAL HM, ANGIONI CD, GAULTIER F, et al. Horizontal guided bone regeneration on knife-edge ridges: A retrospective case-control pilot study comparing two surgical techniques. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res. 2022;24(2):211-221.
[13] DUAN DH, WANG HL, XIAO WC, et al. Bone regeneration using titanium plate stabilization for the treatment of peri-implant bone defects: A retrospective radiologic pilot study. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res. 2022;24(6):792-800.
[14] MANTOVANI R, FERNANDES Y, MEZA-MAURICIO J, et al. Influence of Different Porosities of Titanium Meshes on Bone Neoformation: Pre-Clinical Animal Study with Microtomographic and Histomorphometric Evaluation. J Funct Biomater. 2023;14(10):485.
[15] SCHLEE M, WANG HL, STUMPF T, et al. Treatment of Periimplantitis with Electrolytic Cleaning versus Mechanical and Electrolytic Cleaning: 18-Month Results from a Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial. J Clin Med. 2021;10(16):3475.
[16] LOMBARDO G, MARINCOLA M, SIGNORIELLO A, et al. Single-Crown, Short and Ultra-Short Implants, in Association with Simultaneous Internal Sinus Lift in the Atrophic Posterior Maxilla: A Three-Year Retrospective Study. Materials (Basel). 2020;13(9):2208.
[17] MALCHIODI L, CARICASULO R, CUCCHI A, et al. Evaluation of Ultrashort and Longer Implants with Microrough Surfaces: Results of a 24- to 36-Month Prospective Study. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2017;32(1):171-179.
[18] SRINIVASAN M, VAZQUEZ L, RIEDER P, et al. Efficacy and predictability of short dental implants (<8 mm): a critical appraisal of the recent literature. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2012;27(6):1429-1437.
[19] DEPORTER D.短种植体与超短种植体[M].沈阳:辽宁科学技术出版社,2021.
[20] RAVIDÀ A, WANG IC, BAROOTCHI S, et al. Meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials comparing clinical and patient-reported outcomes between extra-short (≤6 mm) and longer (≥10 mm) implants. J Clin Periodontol. 2019;46(1):118-142.
[21] XU X, HU B, XU Y, et al. Short versus standard implants for single-crown restorations in the posterior region: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J Prosthet Dent. 2020;124(5):530-538.
[22] 满毅,杨幕童.种植机器人、动态导航及全程导板在口腔种植领域的临床应用进展[J].中国口腔种植学杂志,2023,28(3):146-151.
[23] MARQUES-GUASCH J, RODRIGUEZ-BAUZÁ R, SATORRES-NIETO M, et al. Accuracy of dynamic implant navigation surgery performed by a novice operator. Int J Comput Dent. 2022;25(4):377-385.
[24] MA F, SUN F, WEI T, et al. Comparison of the accuracy of two different dynamic navigation system registration methods for dental implant placement: A retrospective study. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res. 2022; 24(3):352-360.
[25] 赵金荣,苏天月,刘鹏慧,等.动态导航系统与静态导板系统在口腔种植手术中精确性的模型对比研究[J].实用口腔医学杂志, 2023,39(5):630-635.
[26] FENG Y, YAO Y, YANG X. Effect of a dynamic navigation device on the accuracy of implant placement in the completely edentulous mandible: An in vitro study. J Prosthet Dent. 2023;130(5):731-737.
[27] 贾沙沙,王晓静.自主式口腔种植机器人手术系统与数字化静态导板的牙种植精确度对比:一项回顾性临床研究[C]//中华口腔医学会口腔种植专业委员会第14次全国口腔种植学术会议论文集.上海:2023.
[28] TAO B, FENG Y, FAN X, et al. The accuracy of a novel image-guided hybrid robotic system for dental implant placement: An in vitro study. Int J Med Robot. 2023;19(1):e2452.
[29] BOLDING SL, REEBYE UN. Accuracy of haptic robotic guidance of dental implant surgery for completely edentulous arches. J Prosthet Dent. 2022;128(4):639-647.
[30] TAO B, FENG Y, FAN X, et al. Accuracy of dental implant surgery using dynamic navigation and robotic systems: An in vitro study. J Dent. 2022; 123:104170.
[31] MORASCHINI V, LOURO RS, SON A, et al. Long-term survival and success rate of dental implants placed in reconstructed areas with extraoral autogenous bone grafts: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res. 2024. doi: 10.1111/cid.13319. Epub ahead of print.
[32] AL HAYDAR B, KANG P, MOMEN-HERAVI F. Efficacy of Horizontal Alveolar Ridge Expansion Through the Alveolar Ridge Split Procedure: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2023;38(6):1083-1096.
[33] PARTHIBAN PS, LAKSHMI RV, MAHENDRA J, et al. A contemporary approach for treatment planning of horizontally resorbed alveolar ridge: Ridge split technique with simultaneous implant placement using platelet rich fibrin membrane application in mandibular anterior region. Indian J Dent Res. 2017;28(1):109-113.
[34] WAECHTER J, LEITE FR, NASCIMENTO GG, et al. The split crest technique and dental implants: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2017;46(1):116-128.
[35] DE SOUZA CSV, DE SÁ BCM, GOULART D, et al. Split Crest Technique with Immediate Implant to Treat Horizontal Defects of the Alveolar Ridge: Analysis of Increased Thickness and Implant Survival. J Maxillofac Oral Surg. 2020;19(4):498-505.
[36] ANITUA E, BEGOÑA L, ORIVE G. Clinical evaluation of split-crest technique with ultrasonic bone surgery for narrow ridge expansion: status of soft and hard tissues and implant success. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res. 2013;15(2):176-187.
[37] LIN Y, LI G, XU T, et al. The efficacy of alveolar ridge split on implants: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Oral Health. 2023;23(1):894.
[38] SAKKAS A, WILDE F, HEUFELDER M, et al. Autogenous bone grafts in oral implantology-is it still a “gold standard”? A consecutive review of 279 patients with 456 clinical procedures. Int J Implant Dent. 2017;3(1):23.
[39] GALINDO-MORENO P, ABRIL-GARCÍA D, CARRILLO-GALVEZ AB, et al. Maxillary sinus floor augmentation comparing bovine versus porcine bone xenografts mixed with autogenous bone graft. A split-mouth randomized controlled trial. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2022;33(5):524-536.
[40] DRAENERT FG, HUETZEN D, NEFF A, et al. Vertical bone augmentation procedures: basics and techniques in dental implantology. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2014;102(5):1605-1613.
[41] KHAOHOEN A, POWCHAROEN W, SORNSUWAN T, et al. Accuracy of implant placement with computer-aided static, dynamic, and robot-assisted surgery: a systematic review and meta-analysis of clinical trials. BMC Oral Health. 2024;24(1):359. |