[1] KATSANOS K, SABHARWAL T, ADAM A. Stenting of the upper gastrointestinal tract: current status. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2010;33(4):690-705.
[2] ZHU Y, YANG K, CHENG R, et al. The current status of biodegradable stent to treat benign luminal disease. Mater Today. 2017;20(9):516-529.
[3] SANCHEZ-REXACH E, MEAURIO E, SARASUA JR. Recent developments in drug eluting devices with tailored interfacial properties. Adv Colloid Interface Sci. 2017;249:181-191.
[4] YANG K, LING C, YUAN T, et al. Polymeric Biodegradable Stent Insertion in the Esophagus. Polymers (Basel). 2016;8(5):158.
[5] CHEN X, XIA Y, SHEN S, et al. Research on the Current Application Status of Magnesium Metal Stents in Human Luminal Cavities. J Funct Biomater. 2023;14(9):462.
[6] ABADI B, GOSHTASBI N, BOLOURIAN S, et al. Electrospun hybrid nanofibers: Fabrication, characterization, and biomedical applications. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022;10:986975.
[7] GUO SR, WANG ZM, ZHANG YQ, et al. In vivo evaluation of 5-fluorouracil-containing self-expandable nitinol stent in rabbits: Efficiency in long-term local drug delivery. J Pharm Sci. 2010;99(7):3009-3018.
[8] DAVIS PL 3RD, HARDISON S, SULLIVAN CA. Topical mithramycin-A modulates submucosal collagen deposition after esophageal burn injury in rats. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2011;145(3):435-441.
[9] JANG SI, KIM JH, KIM M, et al. Porcine feasibility and safety study of a new paclitaxel-eluting biliary stent with a Pluronic-containing membrane. Endoscopy. 2012;44(9):825-831.
[10] CHUNG MJ, KIM H, KIM KS, et al. Safety evaluation of self-expanding metallic biliary stents eluting gemcitabine in a porcine model. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2012;27(2):261-267.
[11] LEE JW, YANG SG, NA K. Gemcitabine-releasing polymeric films for covered self-expandable metallic stent in treatment of gastrointestinal cancer. Int J Pharm. 2012;427(2):276-283.
[12] ZHU YQ, CUI WG, CHENG YS, et al. Evaluation of biodegradable paclitaxel-eluting nanofibre-covered metal stents for the treatment of benign cardia stricture in an experimental model. Br J Surg. 2013;100(6):784-793.
[13] ZHU Y, HU C, LI B, et al. A highly flexible paclitaxel-loaded poly(ε-caprolactone) electrospun fibrous-membrane-covered stent for benign cardia stricture. Acta Biomater. 2013;9(9):8328-8336.
[14] SHI J, LV Y, YU L, et al. Interest of a new biodegradable stent coated with paclitaxel on anastomotic wound healing after biliary reconstruction. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2013;25(12):1415-1423.
[15] ZHU YQ, CUI WG, CHENG YS, et al. Biodegradable rapamycin-eluting nano-fiber membrane-covered metal stent placement to reduce fibroblast proliferation in experimental stricture in a canine model. Endoscopy. 2013; 45(6):458-468.
[16] KIM DH, JEONG YI, CHUNG CW, et al. Preclinical evaluation of sorafenib-eluting stent for suppression of human cholangiocarcinoma cells. Int J Nanomedicine. 2013;8:1697-711.
[17] 杨瑾,蔡秀军.紫杉醇生物可降解支架对猪损伤后胆管α平滑肌动蛋白及转化生长因子β1表达的影响[J].浙江医学,2014(5):394-397.
[18] CAI XB, ZHANG WX, WAN XJ, et al. The effect of a novel drug-eluting plastic stent on biliary stone dissolution in an ex vivo bile perfusion model. Gastrointest Endosc. 2014;79(1):156-162.
[19] WANG Y, CAI X, MEI J, et al. Colonic anastomosis with a doxycycline-coated stent: an experimental study in a porcine model. Dig Surg. 2014;31(2):87-94.
[20] WANG Z, LIU J, WU K, et al. Nitinol stents loaded with a high dose of antitumor 5-fluorouracil or paclitaxel: esophageal tissue responses in a porcine model. Gastrointest Endosc. 2015;82(1):153-160.e1.
[21] CAI XB, ZHANG WX, ZHANG RL, et al. Safety and efficacy of a novel plastic stent coated with stone-dissolving agents for the treatment of biliary stones in a porcine model. Endoscopy. 2015;47(5):457-461.
[22] INDOLFI L, LIGORIO M, TING DT, et al. A tunable delivery platform to provide local chemotherapy for pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Biomaterials. 2016;93:71-82.
[23] ZHANG K, BAI Y, WANG X, et al. Surface modification of esophageal stent materials by a polyethylenimine layer aiming at anti-cancer function. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2017;28(8):125.
[24] KWAK TW, LEE HL, SONG YH, et al. Vorinostat-eluting poly(DL-lactide-co-glycolide) nanofiber-coated stent for inhibition of cholangiocarcinoma cells. Int J Nanomedicine. 2017;12:7669-7680.
[25] YUN D, KIM HO, SON HY, et al. Correction: Stent containing CD44-targeting polymeric prodrug nanoparticles that release paclitaxel and gemcitabine in a time interval-controlled manner for synergistic human biliary cancer therapy. J Mater Chem B. 2017;5(44): 8879-8879.
[26] JIN Z, WU K, HOU J, et al. A PTX/nitinol stent combination with temperature-responsive phase-change 1-hexadecanol for magnetocaloric drug delivery: Magnetocaloric drug release and esophagus tissue penetration. Biomaterials. 2018;153:49-58.
[27] HUANG C, CAI XB, GUO LL, et al. Drug-eluting fully covered self-expanding metal stent for dissolution of bile duct stones in vitro. World J Gastroenterol. 2019;25(26):3370-3379.
[28] WANG Z, ZHENG Q, GUAN S, et al. In vitro and in vivo assessment of the biocompatibility of an paclitaxel-eluting poly-l-lactide-coated Mg-Zn-Y-Nd alloy stent in the intestine. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2019;105: 110087.
[29] JANG SI, FANG S, BAEK YY, et al. Local Delivery of Gemcitabine Inhibits Pancreatic and Cholangiocarcinoma Tumor Growth by Promoting Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Degradation. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(5):1605.
[30] WANG Z, SUN Z, HAN B, et al. Biological behavior exploration of a paclitaxel-eluting poly-l-lactide-coated Mg-Zn-Y-Nd alloy intestinal stent in vivo. RSC Adv. 2020;10(26):15079-15090.
[31] 刘琳琳,秦娟,曾楚慧,等.聚乳酸/羟基乙酸可降解药物释放支架的探索[J].东南大学学报(医学版),2021,40(3):312-317.
[32] TIAN L, LU Z, LEI L, et al. Preparation, characterization and primary evaluation of trilayered biliary stent films for anti-cholangiocarcinoma and anti-biofilm formation. Int J Pharm. 2021;606:120869.
[33] ZENG CH, LIU LL, ZHU HD, et al. The Exploration of a Novel Biodegradable Drug-Eluting Biliary Stent: Preliminary Work. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2021;44(10):1633-1642.
[34] PARK JH, PARK J, PARK Y, et al. Acetazolamide-eluting biodegradable tubular stent prevents pancreaticojejunal anastomotic leakage. J Control Release. 2021;335:650-659.
[35] LIU LL, QIN J, ZENG CH, et al. Biodegradable PTX-PLGA-coated magnesium stent for benign esophageal stricture: An experimental study. Acta Biomater. 2022;146:495-505.
[36] SUN Z, WANG Z, GUAN S, et al. Degradation of Mg-Zn-Y-Nd alloy intestinal stent and its effect on the growth of intestinal endothelial tissue in rabbit model. J Magnes Alloy. 2022;10(8):2208-2219.
[37] LEE JR, YANG SW, KWON CI, et al. Anti-fibrotic and anti-stricture effects of biodegradable biliary stents braided with dexamethasone-impregnated sheath/core structured monofilaments. Acta Biomater. 2024;178:137-146.
[38] YANG Y, YANG Y, HOU Z, et al. Comprehensive review of materials, applications, and future innovations in biodegradable esophageal stents. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2023;11:1327517.
[39] 王敏,张银,范志宁.食管良性狭窄内镜下治疗的研究进展[J].中国微创外科杂志,2016,16(4):365-369.
[40] CHEN X, XIA Y, SHEN S, et al. Research on the Current Application Status of Magnesium Metal Stents in Human Luminal Cavities. J Funct Biomater. 2023;14(9):462.
[41] WANG L, HE J, YU J, et al. Review: Degradable Magnesium Corrosion Control for Implant Applications. Materials (Basel). 2022;15(18):6197.
[42] SHEN X, ZHANG H, LI X, et al. A hydrophobic layer prepared by cyclic grafting of polydimethylsiloxane on magnesium: improved corrosion resistance and biocompatibility. Regen Biomater. 2022;9:rbac068.
[43] ZHAO Y, TIAN C, WU K, et al. Vancomycin-Loaded Polycaprolactone Electrospinning Nanofibers Modulate the Airway Interfaces to Restrain Tracheal Stenosis. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2021;9:760395.
[44] LI Z, JIAO D, ZHANG W, et al. Antibacterial and antihyperplasia polylactic acid/silver nanoparticles nanofiber membrane-coated airway stent for tracheal stenosis. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2021;206:111949.
[45] LEE CH, LIN YH, CHANG SH, et al. Local sustained delivery of acetylsalicylic acid via hybrid stent with biodegradable nanofibers reduces adhesion of blood cells and promotes reendothelialization of the denuded artery. Int J Nanomedicine. 2014;9:311-326.
[46] 杨凯,朱悦琦,程英升.食管良性狭窄药物镁合金可降解支架研究现状及展望[J].介入放射学杂志,2015(5):452-456.
[47] ISHIHARA R. Endoscopic Stenting for Malignant Dysphagia in Patients with Esophageal Cancer. Curr Oncol. 2023;30(7):5984-5994.
[48] LEI L, LIU X, GUO S, et al. 5-Fluorouracil-loaded multilayered films for drug controlled releasing stent application: Drug release, microstructure, and ex vivo permeation behaviors. J Control Release. 2010;146(1):45-53.
[49] LU F, LEI L, SHEN YY, et al. Effects of amphiphilic PCL-PEG-PCL copolymer addition on 5-fluorouracil release from biodegradable PCL films for stent application. Int J Pharm. 2011;419(1-2):77-84.
[50] JACKSON CE, JOHNSON LSJ, WILLIAMS DA, et al. A viewpoint on material and design considerations for oesophageal stents with extended lifetime. J Mater Sci. 2022;57:1-24.
[51] BLERO D, HUBERTY V, DEVIÈRE J. Novel biliary self-expanding metal stents: indications and applications. Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2015;9(3): 359-367.
[52] WU T, YANG Y, SU H, et al. Recent developments in antibacterial or antibiofilm compound coating for biliary stents. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2022;219:112837.
[53] SONG G, ZHAO HQ, LIU Q, et al. A review on biodegradable biliary stents: materials and future trends. Bioact Mater. 2022;17:488-495.
[54] ASGE TECHNOLOGY COMMITTEE; TOKAR JL, BANERJEE S, et al. Drug-eluting/biodegradable stents. Gastrointest Endosc. 2011;74(5):954-958.
[55] CHUN HJ, KIM ES, HYUN JJ, et al. Gastrointestinal and biliary stents. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2010;25(2):234-243.
[56] HWANG F, BUKUR M. Contemporary management of common bile duct stone: What you need to know. J Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2023;95(6): 832-838.
[57] WHELESS M, AGARWAL R, GOFF L, et al. Current Standards, Multidisciplinary Approaches, and Future Directions in the Management of Extrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma. Curr Treat Options Oncol. 2024; 25(1):127-160.
[58] XIA M, QIN W, HU B. Endobiliary radiofrequency ablation for unresectable malignant biliary strictures: Survival benefit perspective. Dig Endosc. 2023; 35(5):584-591.
[59] FERREIRA-SILVA J, MEDAS R, GIROTRA M, et al. Futuristic Developments and Applications in Endoluminal Stenting. Gastroenterol Res Pract. 2022; 2022:6774925.
[60] KOCHAR R, SHAH N. Enteral stents: from esophagus to colon. Gastrointest Endosc. 2013;78(6):913-918.
[61] PANIAGUA GARCÍA-SEÑORÁNS M, SÁNCHEZ SANTOS R, CANO VALDERRAMA Ó, et al. Stent as bridge to surgery decreases postoperative complications without worsening oncological outcomes: retrospective unicentric cohort study and stent placement protocol. Surg Endosc. 2023; 37(8):6298-6307.
[62] 王培.聚己内酯类生物高分子支架在组织工程领域的应用[J].中国组织工程研究,2021,25(34):5506-5510.
[63] 杨顺,赵明月,涂希玲,等.脱细胞基质复合支架在组织再生中的应用[J].中国组织工程研究,2023,27(30):4856-4861.
[64] 李芹,孙扬永,吴昊,等.茶多酚处理脱细胞牛心包组织支架作为人工食管修补材料的可行性[J].中国组织工程研究,2023,27(12):1832-1836. |
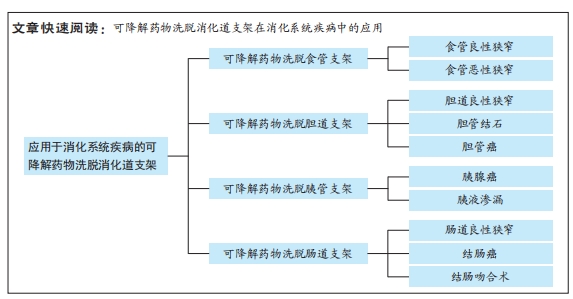




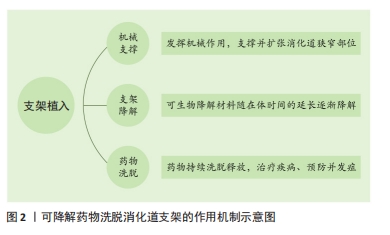
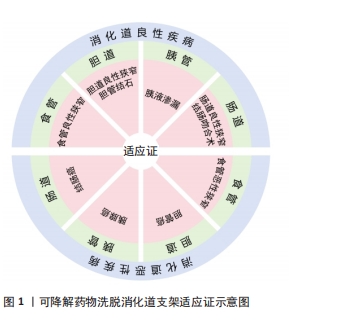 可降解药物洗脱支架以生物可降解材料为主体,搭载抗炎、抗增殖或其他功能性药物,兼具生物可降解材料和药物洗脱支架的优点。支架植入后降解为无毒、无害的化合物,并且随人体代谢排出体外,同时搭载的药物洗脱释放,在支架植入治疗部位缓释所需药物,达到抗炎、抗增生、降低狭窄复发率等目的。可降解药物洗脱消化道支架的作用机制如图2所示。理想的可降解药物洗脱消化道支架应具备[2-4]:良好的机械性能与径向支撑力;可完全生物降解,无需移除,降解产物无毒副作用,可被人体自然代谢吸收;良好的顺应性与组织相容性;优越的载药释药能力;可追踪性。
可降解药物洗脱支架以生物可降解材料为主体,搭载抗炎、抗增殖或其他功能性药物,兼具生物可降解材料和药物洗脱支架的优点。支架植入后降解为无毒、无害的化合物,并且随人体代谢排出体外,同时搭载的药物洗脱释放,在支架植入治疗部位缓释所需药物,达到抗炎、抗增生、降低狭窄复发率等目的。可降解药物洗脱消化道支架的作用机制如图2所示。理想的可降解药物洗脱消化道支架应具备[2-4]:良好的机械性能与径向支撑力;可完全生物降解,无需移除,降解产物无毒副作用,可被人体自然代谢吸收;良好的顺应性与组织相容性;优越的载药释药能力;可追踪性。
 目前常用的可生物降解消化道支架材料主要为聚合物类和金属类。可降解聚合物包含聚乳酸、聚L-乳酸、右旋聚乳酸、聚乙醇酸、聚乳酸-羟基乙酸和聚己内酯等,可降解金属主要为镁基合金等。镁基合金具有良好的机械性能、生物降解性和生物相容性,被广泛应用于心血管及消化系统领域,例如制备胆道支架等[5]。纳米纤维是直径小于1 000 nm的超微细纤维,主要通过拉伸法、微相分离、静电纺丝等技术制备。近年来,静电纺丝技术逐渐成为纳米纤维常用的制备手段,由其制备的电纺纳米纤维在支架制备和药物输送方面具有独特优势,是制备可降解药物洗脱消化道支架的理想材料[6]。
目前常用的可生物降解消化道支架材料主要为聚合物类和金属类。可降解聚合物包含聚乳酸、聚L-乳酸、右旋聚乳酸、聚乙醇酸、聚乳酸-羟基乙酸和聚己内酯等,可降解金属主要为镁基合金等。镁基合金具有良好的机械性能、生物降解性和生物相容性,被广泛应用于心血管及消化系统领域,例如制备胆道支架等[5]。纳米纤维是直径小于1 000 nm的超微细纤维,主要通过拉伸法、微相分离、静电纺丝等技术制备。近年来,静电纺丝技术逐渐成为纳米纤维常用的制备手段,由其制备的电纺纳米纤维在支架制备和药物输送方面具有独特优势,是制备可降解药物洗脱消化道支架的理想材料[6]。