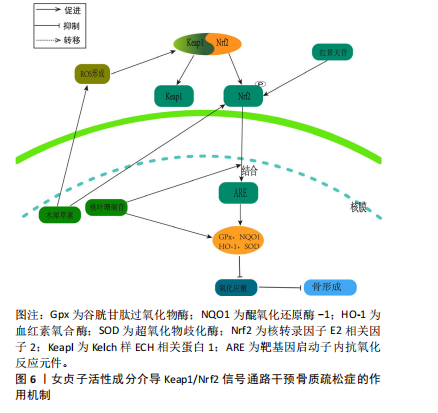
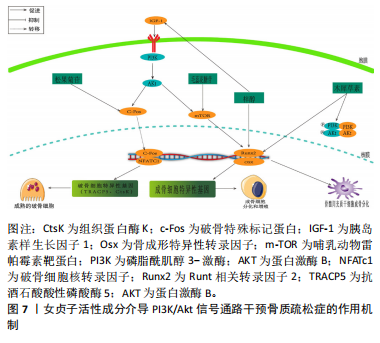
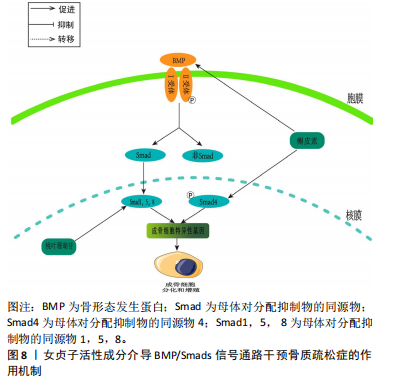
[1] García-Gómez MC, Vilahur G. Osteoporosis and vascular calcification: a shared scenario. Clin Investig Arterioscler. 2020;32(1):33-42.
[2] 中国骨质疏松症流行病学调查及“健康骨骼”专项行动结果发布[J].中华骨质疏松和骨矿盐疾病杂志,2019,12(4):317-318.
[3] 中华医学会骨质疏松和骨矿盐疾病分会,章振林.原发性骨质疏松症诊疗指南(2022)[J].中国全科医学,2023,26(14):1671-1691.
[4] QASEEM A, HICKS LA, ETXEANDIA-IKOBALTZETA I, et al. Pharmacologic treatment of primary osteoporosis or low bone mass to prevent fractures in adults: a living clinical guideline from the american college of physicians (version 1, update alert). Ann Intern Med. 2024;177(6): eL230113.
[5] GAO L, LI C, WANG Z, et al. Ligustri lucidi fructus as a traditional Chinese medicine: a review of its phytochemistry and pharmacology. Nat Prod Res. 2015;29(6):493-510.
[6] 黄婉,杨耀芳.女贞子及其有效成分的药理及临床研究进展[J].现代中西医结合杂志,2003,12(7):772-774.
[7] 姜斐.女贞子化学成分的提取分离鉴定及活性研究[D].南京:南京中医药大学,2010.
[8] 顾闻,刘特,陈久林,等.特女贞苷对血管内皮细胞氧化损伤的作用研究[J].中国中西医结合杂志,2018,38(9):1093-1098.
[9] XIA EQ, WANG BW, XU XR, et al. Microwave-assisted extraction of oleanolic acid and ursolic acid from Ligustrum lucidum Ait. Int J Mol Sci. 2011;12(8):5319-5329.
[10] QIN X, WEI Q, AN R, et al. Regulation of bone and fat balance by Fructus Ligustri Lucidi in ovariectomized mice. Pharm Biol. 2023;61(1):391-403.
[11] 王佳丽,单安山,刘天阳,等.女贞子CO2超临界萃取物对断奶仔猪小肠绒毛、盲肠菌群及血常规的影响[J].东北农业大学学报, 2013,44(12):10-15.
[12] 袁毅,沈丽新,潘燕.女贞子对2型糖尿病大鼠胰岛β细胞的作用及机制[J].中华中医药学刊,2019,37(1):206-208, 264.
[13] ZHANG Y, LIU L, GAO J, et al. New secoiridoids from the fruits of ligustrum lucidum ait with triglyceride accumulation inhibitory effects. Fitoterapia. 2013;91:107-112.
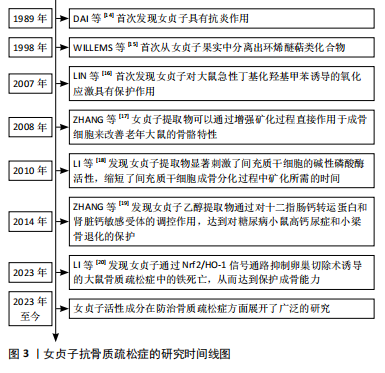
[14] DAI Y, HANG BQ, MONG QY, et al. Anti-inflammatory effect of fructus Ligustri Lucidi. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 1989;14(7):431-433,448.
[15] WILLEMS M. Quantitative determination of seco-iridoid glucosides from the fruits of ligustrum vulgare by HPLC. Planta Med. 1988;54(1):66-78.
[16] LIN HM, YEN FL, NG LT, et al. Protective effects of Ligustrum lucidum fruit extract on acute butylated hydroxytoluene-induced oxidative stress in rats. J Ethnopharmacol. 2007;111(1):129-136.
[17] ZHANG Y, LEUNG PC, CHE CT, et al. Improvement of bone properties and enhancement of mineralization by ethanol extract of Fructus Ligustri Lucidi. Br J Nutr. 2008;99(3):494-502.
[18] LI G, ZHANG XA, ZHANG JF, et al. Ethanol extract of Fructus Ligustri Lucidi promotes osteogenesis of mesenchymal stem cells. Phytother Res. 2010;24(4):571-576.
[19] ZHANG Y, DIAO TY, WANG L, et al. Protective effects of water fraction of Fructus Ligustri Lucidi extract against hypercalciuria and trabecular bone deterioration in experimentally type 1 diabetic mice. J Ethnopharmacol. 2014;158 Pt A:239-245.
[20] LI P, WANG Y, YAN Q, et al. Fructus Ligustri Lucidi inhibits ferroptosis in ovariectomy‑induced osteoporosis in rats via the Nrf2/HO‑1 signaling pathway. Biomed Rep. 2023;20(2):27.
[21] 刘美红,邹峥嵘.女贞子化学成分、药理作用及药动学研究进展[J].热带亚热带植物学报,2022,30(3):446-460.
[22] YU WX, POON CC, ZHOU LP, et al. Oleanolic acid exerts bone anabolic effects via activation of osteoblastic 25-hydroxyvitamin D 1-alpha hydroxylase. Biomed Pharmacother. 2024;173:116402.
[23] YANG Y, SHEN L, WANG P, et al. Anti-osteoporosis bioactivity evaluation in zebrafish model of raw and salt-processed Achyranthes bidentata followed by liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry analysis and correlation analysis. Biomed Chromatogr. 2023;37(12):e5742.
[24] XU Y, CHEN S, YU T, et al. High-throughput metabolomics investigates anti-osteoporosis activity of oleanolic acid via regulating metabolic networks using ultra-performance liquid chromatography coupled with mass spectrometry. Phytomedicine. 2018;51:68-76.
[25] CAO S, DONG XL, HO MX, et al. Oleanolic acid exerts osteoprotective effects and modulates vitamin d metabolism. Nutrients. 2018;10(2):247.
[26] ZHENG H, FENG H, ZHANG W, et al. Targeting autophagy by natural product Ursolic acid for prevention and treatment of osteoporosis. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2020;409:115271.
[27] CHENG M, LIANG XH, WANG QW, et al. Ursolic acid prevents retinoic acid-induced bone loss in rats. Chin J Integr Med. 2019;25(3):210-215.
[28] 杨然,陆远,郝昊,等.金银花环烯醚萜苷类化学成分和药理活性研究进展[J].中国中药杂志,2021,46(11):2746-2752.
[29] LAO A, CHEN Y, SUN Y, et al. Transcriptomic analysis provides a new insight: oleuropein reverses high glucose-induced osteogenic inhibition in bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells via Wnt10b activation. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022;10:990507.
[30] SANTIAGO-MORA R, CASADO-DÍAZ A, DE CASTRO MD, et al. Oleuropein enhances osteoblastogenesis and inhibits adipogenesis: the effect on differentiation in stem cells derived from bone marrow. Osteoporos Int. 2011;22(2):675-684.
[31] CHEN L, ZHANG RY, XIE J, et al. STAT3 activation by catalpol promotes osteogenesis-angiogenesis coupling, thus accelerating osteoporotic bone repair. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021;12(1):108.
[32] CHENG J, XU HY, LIU MM, et al. Catalpol promotes the proliferation and differentiation of osteoblasts induced by high glucose by inhibiting KDM7A. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2020;13:705-712.
[33] LI Y, WANG MJ, LI S, et al. Effect of total glycosides from Eucommia ulmoides seed on bone microarchitecture in rats. Phytother Res. 2011; 25(12):1895-1907.
[34] MARTINIAKOVA M, BABIKOVA M, OMELKA R. Pharmacological agents and natural compounds: available treatments for osteoporosis. J Physiol Pharmacol. 2020. doi: 10.26402/jpp.2020.3.01.
[35] CHEN XF, LI XL, YANG M, et al. Osteoprotective effects of salidroside in ovariectomized mice and diabetic mice. Eur J Pharmacol. 2018; 819:281-288.
[36] XIE B, ZHOU H, LIU H, et al. Salidroside alleviates dexamethasone-induced inhibition of bone formation via transforming growth factor-beta/Smad2/3 signaling pathway. Phytother Res. 2023;37(5):1938-1950.
[37] LI F, YANG X, YANG Y, et al. Antiosteoporotic activity of echinacoside in ovariectomized rats. Phytomedicine. 2013;20(6):549-557.
[38] ALI D, OKLA M, ABUElREICH S, et al. Apigenin and Rutaecarpine reduce the burden of cellular senescence in bone marrow stromal stem cells. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024;15:1360054.
[39] CHOI EM. Apigenin increases osteoblastic differentiation and inhibits tumor necrosis factor-alpha-induced production of interleukin-6 and nitric oxide in osteoblastic MC3T3-E1 cells. Pharmazie. 2007;62(3):216-220.
[40] SUN J, PAN Y, LI X, et al. Quercetin attenuates osteoporosis in orchiectomy mice by regulating glucose and lipid metabolism via the GPRC6A/AMPK/mTOR signaling pathway. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022;13:849544.
[41] ZHENG L. Luteolin stimulates proliferation and inhibits late differentiation of primary rat calvarial osteoblast induced by high-dose dexamethasone via Sema3A /NRP1/Pleixin A1. Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2021;22(11):1538-1545.
[42] KIM TH, JUNG JW, HA BG, et al. The effects of luteolin on osteoclast differentiation, function in vitro and ovariectomy-induced bone loss. J Nutr Biochem. 2011;22(1):8-15.
[43] YAMAGUCHI M, LEVY RM. β-Caryophyllene promotes osteoblastic mineralization, and suppresses osteoclastogenesis and adipogenesis in mouse bone marrow cultures in vitro. Exp Ther Med. 2016;12(6):3602-3606.
[44] SHAN J, CHEN L, LU K. Protective effects of trans-caryophyllene on maintaining osteoblast function. IUBMB Life. 2017;69(1):22-29.
[45] PUJIA A, RUSSO C, MAUROTTI S, et al. Bergamot polyphenol fraction exerts effects on bone biology by activating ERK 1/2 and Wnt/β-catenin pathway and regulating bone biomarkers in bone cell cultures. Nutrients. 2018;10(9):1305.
[46] HONG G, HE X, SHEN Y, et al. Chrysosplenetin promotes osteoblastogenesis of bone marrow stromal cells via Wnt/β-catenin pathway and enhances osteogenesis in estrogen deficiency-induced bone loss. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019;10(1):277.
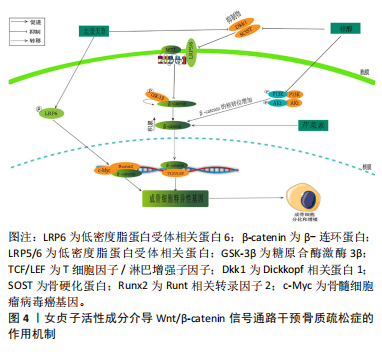
[47] LIU C, WANG L, ZHU R, et al. Rehmanniae Radix Preparata suppresses bone loss and increases bone strength through interfering with canonical Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway in OVX rats. Osteoporos Int. 2019;30(2):491-505.
[48] ZHU Y, WANG Y, JIA Y, et al. Catalpol promotes the osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells via the Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019;10(1):37.
[49] LIU H, GUO Y, ZHU R, et al. Fructus Ligustri Lucidi preserves bone quality through induction of canonical Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway in ovariectomized rats. Phytother Res. 2021;35(1):424-441.
[50] PAN FF, SHAO J, SHI CJ, et al. Apigenin promotes osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells and accelerates bone fracture healing via activating Wnt/β-catenin signaling. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2021;320(4):E760-E771.
[51] ONO T, HAYASHI M, SASAKI F, et al. RANKL biology: bone metabolism, the immune system, and beyond. Inflamm Regen. 2020;40:2.
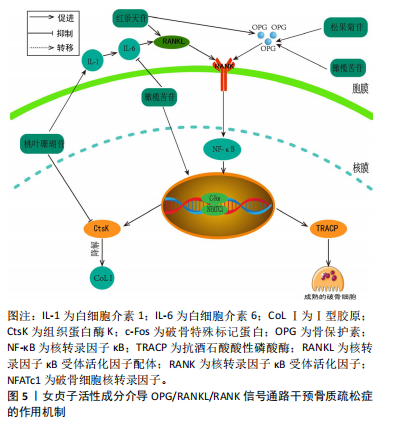
[52] LIU FL, CHEN CL, LEE CC, et al. The simultaneous inhibitory effect of niclosamide on RANKL-induced osteoclast formation and osteoblast differentiation. Int J Med Sci. 2017;14(9):840-852.
[53] KANG JY, KANG N, YANG YM, et al. The role of Ca2+-NFATc1 signaling and its modulation on osteoclastogenesis. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(10):3646.
[54] PARK B, SONG HS, KWON JE, et al. Effects of Salvia miltiorrhiza extract with supplemental liquefied calcium on osteoporosis in calcium-deficient ovariectomized mice. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2017; 17(1):545.
[55] ZHENG H, QI S, CHEN C. Salidroside improves bone histomorphology and prevents bone loss in ovariectomized diabetic rats by upregulating the OPG/RANKL ratio. Molecules. 2018;23(9):2398.
[56] LI F, YANG Y, ZHU P, et al. Echinacoside promotes bone regeneration by increasing OPG/RANKL ratio in MC3T3-E1 cells. Fitoterapia. 2012; 83(8):1443-1450.
[57] LIU H, ZHAO A, HUANG Y, et al. Efficacy and mechanisms of oleuropein in postmenopausal osteoporosis. Comput Math Methods Med. 2022; 2022:9767113.
[58] ZHANG Y, LIU X, LI Y, et al. Aucubin slows the development of osteoporosis by inhibiting osteoclast differentiation via the nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2-mediated antioxidation pathway. Pharm Biol. 2021;59(1):1556-1565.
[59] BELLEZZA I, GIAMBANCO I, MINELLI A, et al. Nrf2-Keap1 signaling in oxidative and reductive stress. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res. 2018;1865(5):721-733.
[60] TONELLI C, CHIO IIC, TUVESON DA. Transcriptional regulation by Nrf2. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2018;29(17):1727-1745.
[61] ZHANG Z, QU J, ZHENG C, et al. Nrf2 antioxidant pathway suppresses Numb-mediated epithelial-mesenchymal transition during pulmonary fibrosis. Cell Death Dis. 2018;9(2):83.
[62] RYTER SW. Heme oxgenase-1, a cardinal modulator of regulated cell death and inflammation. Cells. 2021;10(3):515.
[63] PUENTES-PARDO JD, MORENO-SANTUAN S, CARAZO Á, et al. Heme oxygenase-1 in gastrointestinal tract health and disease. Antioxidants (Basel). 2020;9(12):1214.
[64] VIJAYAN V, WAGENER FADTG, IMMENSCHUH S. The macrophage heme-heme oxygenase-1 system and its role in inflammation. Biochem Pharmacol. 2018;153:159-167.
[65] WANG YF, CHANG YY, ZHANG XM, et al. Salidroside protects against osteoporosis in ovariectomized rats by inhibiting oxidative stress and promoting osteogenesis via Nrf2 activation. Phytomedicine. 2022;99:154020.
[66] WANG K, ZHOU C, LI L, et al. Aucubin promotes bone-fracture healing via the dual effects of anti-oxidative damage and enhancing osteoblastogenesis of hBM-MSCs. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2022;13(1):424.
[67] SUH KS, CHON S, CHOI EM. Luteolin alleviates methylglyoxal-induced cytotoxicity in osteoblastic MC3T3-E1 cells. Cytotechnology. 2016;68(6):2539-2552.
[68] MCGONNELL IM, GRIGORIADIS AE, LAM EW, et al. A specific role for phosphoinositide 3-kinase and AKT in osteoblasts? Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2012;3:88.
[69] YEON JT, KIM KJ, SON YJ, et al. Idelalisib inhibits osteoclast differentiation and pre-osteoclast migration by blocking the PI3Kδ-Akt-c-Fos/NFATc1 signaling cascade. Arch Pharm Res. 2019;42(8):712-721.
[70] HAN SY, KIM YK. Berberine suppresses RANKL-induced osteoclast differentiation by inhibiting c-Fos and NFATc1 expression. Am J Chin Med. 2019;47(2):439-455.
[71] BAKKER AD, GAKES T, HOGERVORST JM, et al. Mechanical stimulation and IGF-1 enhance mRNA translation rate in osteoblasts via activation of the AKT-mTOR pathway. J Cell Physiol. 2016;231(6):1283-1290.
[72] JIANG T, GU H, WEI J. Echinacoside inhibits osteoclast function by down-regulating PI3K/AKT/c-fos to alleviate osteolysis caused by periprosthetic joint infection. Front Pharmacol. 2022;13:930053.
[73] LI S, CUI Y, LI M, et al. Acteoside derived from cistanche improves glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis by activating PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway. J Invest Surg. 2023;36(1):2154578.
[74] GONG W, ZHANG N, CHENG G, et al. Rehmannia glutinosa libosch extracts prevent bone loss and architectural deterioration and enhance osteoblastic bone formation by regulating the IGF-1/PI3K/mTOR pathway in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(16):3964.
[75] LIANG G, ZHAO J, DOU Y, et al. Mechanism and experimental verification of luteolin for the treatment of osteoporosis based on network pharmacology. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022;13:866641.
[76] YU D, HUANG C, JIANG C, et al. Features of a simvastatin-loaded multi-layered co-electrospun barrier membrane for guided bone regeneration. Exp Ther Med. 2021;22(1):713.
[77] Muñoz J, Akhavan NS, Mulliins AP, et al. Macrophage polarization and osteoporosis: a review. Nutrients. 2020;12(10):2999.
[78] WANG Z, BAO HW, XU YJ. Cnidium lactone prevents bone loss in an ovariectomized rat model through the estrogen-α/BMP-2/Smad signaling pathway. J Gene Med. 2020;22(8):e3198.
[79] LI Y, HU W, HAN G, et al. Involvement of bone morphogenetic protein-related pathways in the effect of aucubin on the promotion of osteoblast differentiation in MG63 cells. Chem Biol Interact. 2018; 283:51-58.
[80] LI Y, ZHANG Y, ZHANG X, et al. Aucubin exerts anti-osteoporotic effects by promoting osteoblast differentiation. Aging (Albany NY). 2020;12(3):2226-2245.
[81] 郑红,唐薇,角建林,等.槲皮素通过促进成骨分化治疗去势骨质疏松症大鼠的分子机制[J].中药药理与临床,2017,33(5):16-20.
[82] MA Z, TANG X, CHEN Y, et al. Epimedii folium and ligustri lucidi fructus promote osteoblastogenesis and inhibit osteoclastogenesis against osteoporosis via acting on osteoblast-osteoclast communication. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2023;2023:7212642.
|