中国组织工程研究 ›› 2025, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (14): 2969-2978.doi: 10.12307/2025.612
• 组织构建实验造模 experimental modeling in tissue construction • 上一篇 下一篇
苦参总黄酮改善非酒精性脂肪肝的作用机制及斑马鱼实验验证
古玉凤1,邓丙英1,李倪仁1,曾译萱1,鲁思凡1,朱 晨2,陈 磊3,刘 怡1,4,5
- 1南方医科大学中医药学院,广东省广州市 510510;2广州中医药大学第二附属医院药学部,广东省广州市 510120;3广东药科大学中药学院,广东省广州市 510006;4广东省中药制剂重点实验室,广东省广州市 510515;5广东省中西医结合防治情志病基础研究卓越中心,广东省广州市 510515
Mechanisms of total flavonoids from Sophora flavescens for the treatment of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and experimental validation in zebrafish
Gu Yufeng1, Deng Bingying1, Li Niren1, Zeng Yixuan1, Lu Sifan1, Zhu Chen2, Chen Lei3, Liu Yi1, 4, 5
- 1School of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Southern Medical University, Guangzhou 510510, Guangdong Province, China; 2Department of Pharmacy, The Second Affiliated Hospital of Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510120, Guangdong Province, China; 3School of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Guangdong Pharmaceutical University, Guangzhou 510006, Guangdong Province, China; 4Guangdong Provincial Key Laboratory of Chinese Medicine Pharmaceutics, Guangzhou 510515, Guangdong Province, China; 5Guangdong Basic Research Center of Excellence for Integrated Traditional and Western Medicine for Qingzhi Diseases, Guangzhou 510515, Guangdong Province, China
摘要:
文题释义:
网络药理学:是基于系统生物学的原理阐释疾病发展的过程,研究药物、疾病和靶点之间的协同关系,预测疾病治疗作用靶点和信号通路。
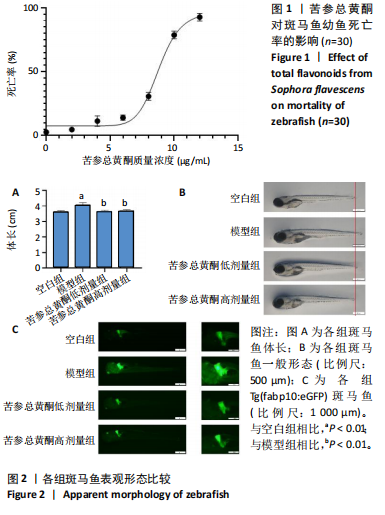
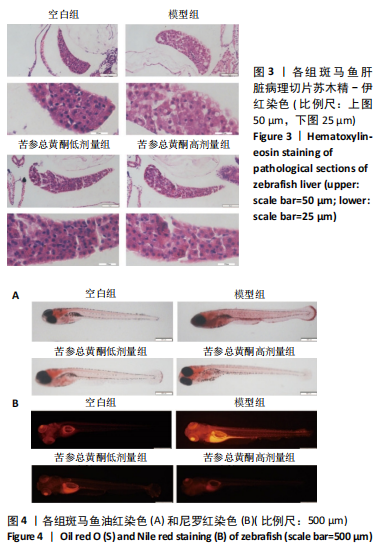
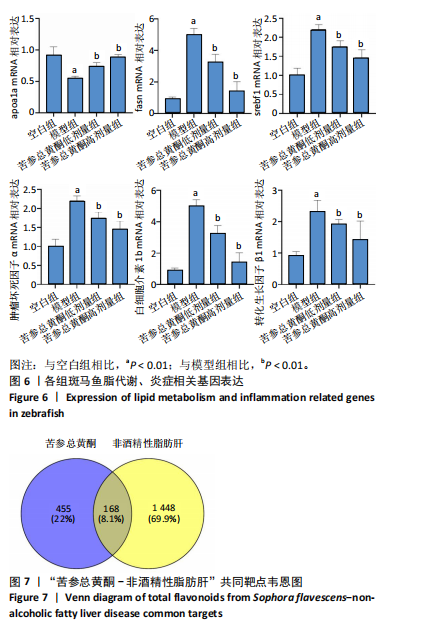
斑马鱼非酒精性脂肪肝模型:斑马鱼具有体型小、养殖成本低、发育迅速、产卵量大、基因组与人类同源性高等特点,受精后5 d斑马鱼的消化系统发育成熟,且幼鱼胚胎透明,可直接观察内脏,可以克服哺乳动物耗时长、用药量大、实验强度大以及细胞模型条件要求严苛、作用环节单一等缺陷。应用蛋黄粉溶液浸泡诱导非酒精性脂肪肝斑马鱼模型,能使幼鱼肝脏出现明显病理损伤。
背景:苦参总黄酮具有抗炎、调节免疫、抗氧化、抗肝损伤等多种药理作用,其对非酒精性脂肪肝的治疗效果和作用机制尚不明确。
目的:利用生物信息学、网络药理学方法及斑马鱼实验验证苦参总黄酮治疗非酒精性脂肪肝的作用机制。
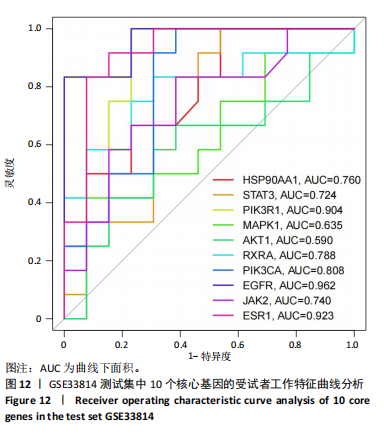
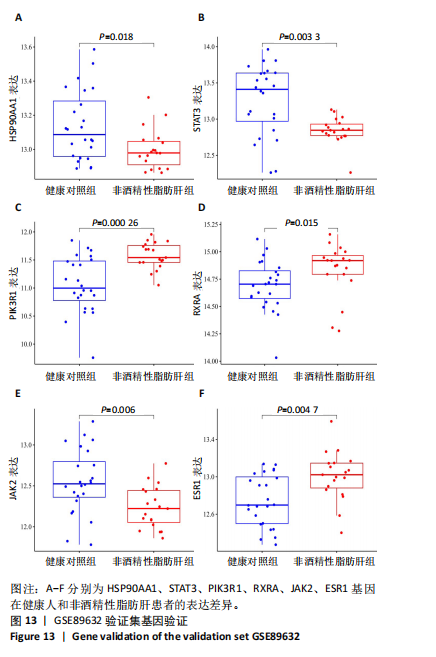
方法:构建非酒精性脂肪肝斑马鱼模型,观察苦参总黄酮治疗后斑马鱼肝脏脂质累积情况、病理形态改变,以及脂质累积、炎症基因的表达变化。通过TCMSP、Swiss Target Prediction、Bat-man数据库获取苦参总黄酮活性成分与非酒精性脂肪肝相关靶点;利用STRING数据库进行蛋白互作网络分析,GO功能富集和KEGG通路富集分析。基于GSE33814数据集,筛选出“苦参总黄酮-非酒精性脂肪肝”交集靶点的差异表达基因并运用R4.3.2软件进行相关性分析、受试者操作特征曲线分析,通过验证集GSE89632验证核心基因;RT-qPCR和Western blot实验验证核心通路相关基因和蛋白表达。
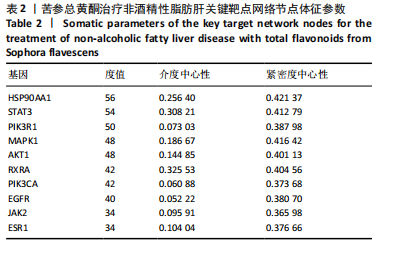
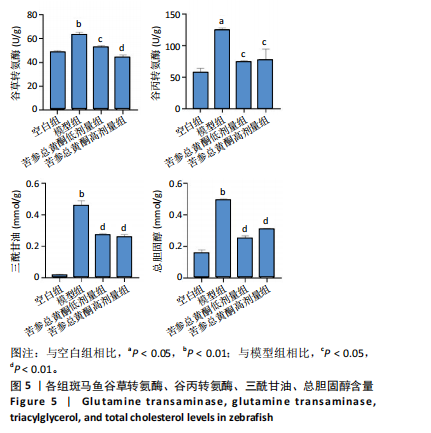
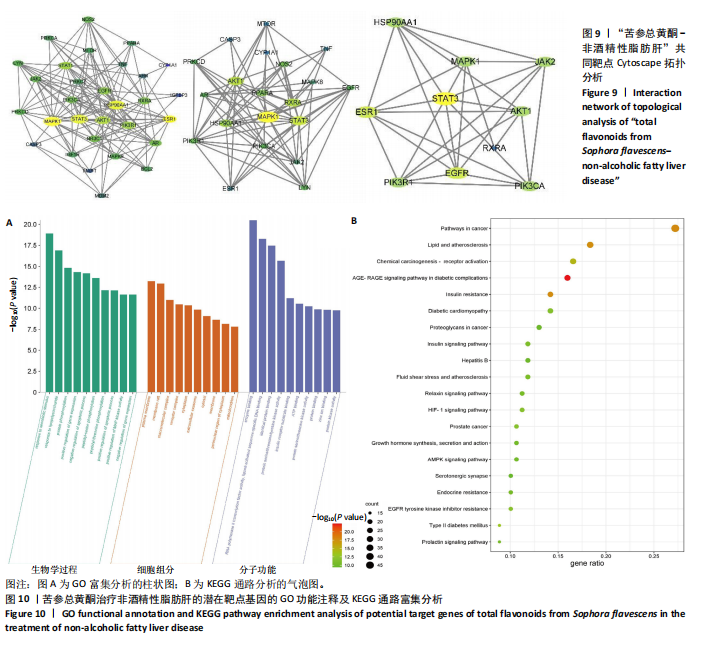
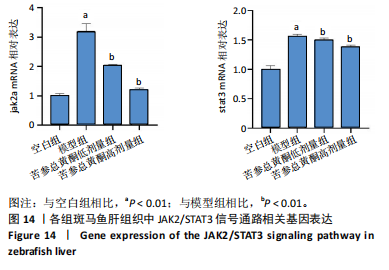
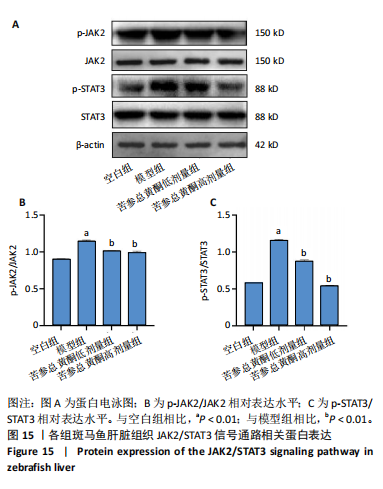
结果与结论:①苦参总黄酮能够改善非酒精性脂肪肝斑马鱼肝脏脂质累积,显著抑制斑马鱼脂质和转氨酶水平的升高(P < 0.05);调节炎症和脂代谢相关基因的表达;②网络药理学中获得168个共同靶点,cytoscape拓扑分析综合筛选出排名前10的核心基因分别为HSP90AA1、STAT3、PIK3R1、MAPK1、AKT1、RXRA、PIK3CA、EGFR、JAK2、ESR1;GO和KEGG分析通路主要集中在胰岛素抵抗、脂质与动脉粥样硬化方面;生物信息分析共获得59个“苦参总黄酮-非酒精性脂肪肝” 差异表达基因,受试者操作特征曲线分析及验证集验证得到6个核心靶点在健康人与非酒精性脂肪肝患者间有显著差异(P < 0.01);③RT-qPCR和Western blot实验结果表明苦参总黄酮能够抑制非酒精性脂肪肝斑马鱼JAK2/STAT3信号通路的激活。以上结果表明,苦参总黄酮通过调节JAK2/STAT3信号通路减轻炎性反应,抑制脂质累积从而改善非酒精性脂肪肝。
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-1635-4105(刘怡)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
中图分类号: