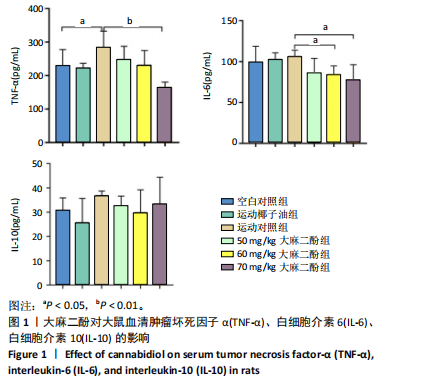
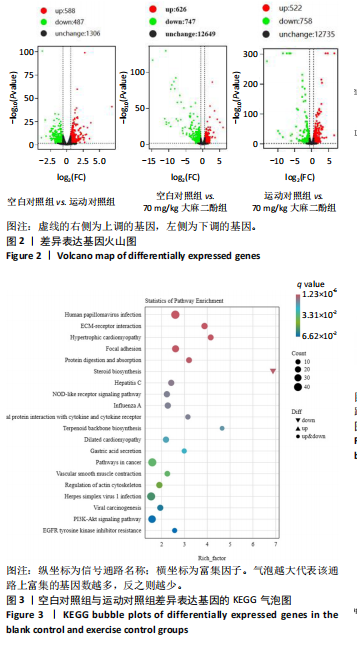
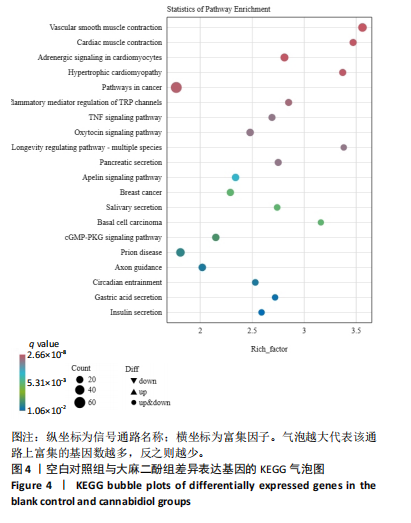
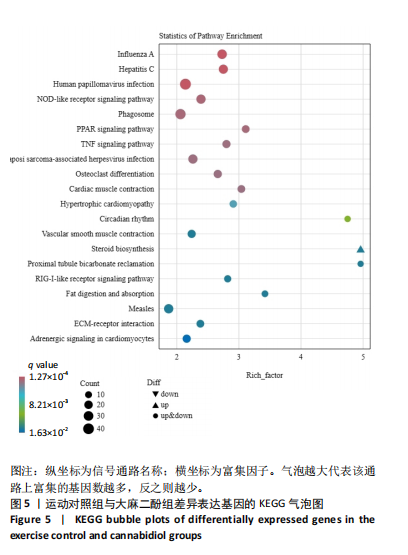
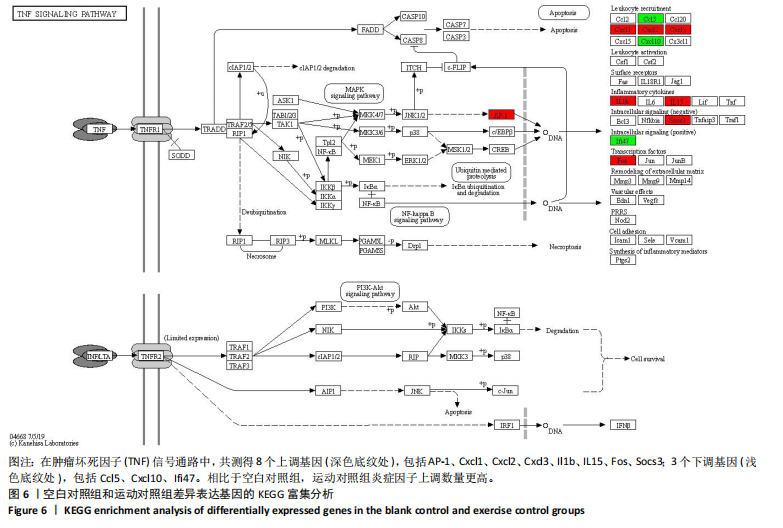
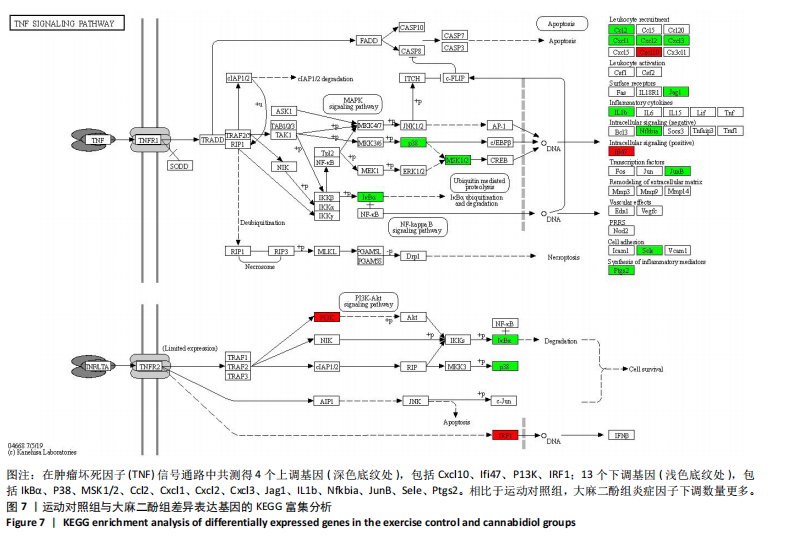
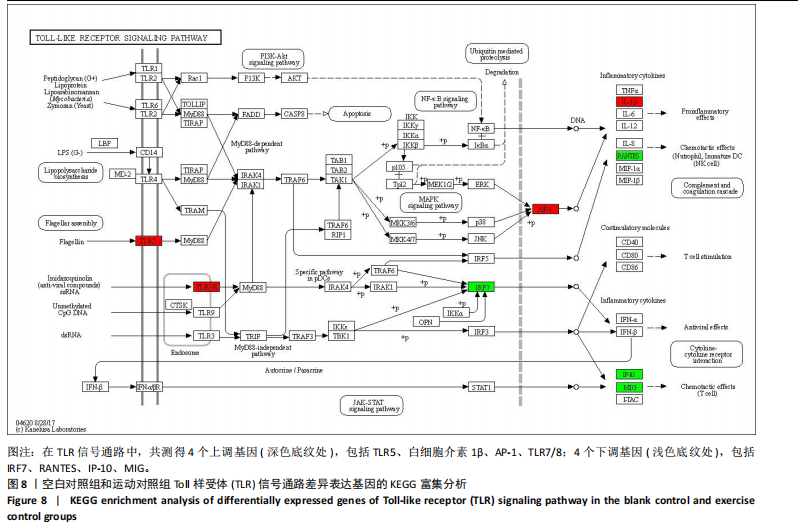
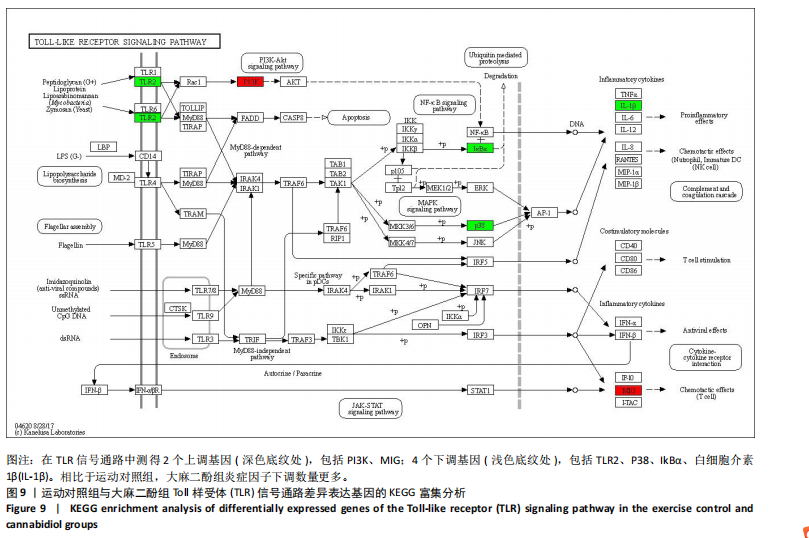
[1] DA ROCHA AL, PINTO AP, KOHAMA EB, et al. The proinflammatory effects of chronic excessive exercise. Cytokine. 2019;119:57-61.
[2] CERQUEIRA E, MARINHO DA, NEIVA HP, et al. Inflammatory Effects of High and Moderate Intensity Exercise-A Systematic Review. Front Physiol. 2020;10:1550.
[3] MCCARTNEY D, BENSON MJ, DESBROW B, et al. Cannabidiol and Sports Performance: a Narrative Review of Relevant Evidence and Recommendations for Future Research. Sports Med Open. 2020;6(1):27.
[4] BURSTEIN S. Cannabidiol (CBD) and its analogs: a review of their effects on inflammation. Bioorg Med Chem. 2015;23(7):1377-1385.
[5] ZUARDI AW, RODRIGUES JA, CUNHA JM. Effects of cannabidiol in animal-models predictive of antipsychotic activity. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 1991;104(2):260-264.
[6] LEWEKE FM, SCHNEIDER U, RADWAN M, et al. Different effects of nabilone and cannabidiol on binocular depth inversion in man. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2000;66(1):175-181.
[7] DEVINSKY O, MARSH E, FRIEDMAN D, et al. Cannabidiol in patients with treatment-resistant epilepsy: an open-label interventional trial. Lancet Neurol. 2016;15(3):270-278.
[8] BLESSING EM, STEENKAMP MM, MANZANARES J, et al. Cannabidiol as a Potential Treatment for Anxiety Disorders. Neurotherapeutics. 2015;12(4): 825-836.
[9] BORRELLI F, AVIELLO G, ROMANO B, et al. Cannabidiol, a safe and non-psychotropic ingredient of the marijuana plant Cannabis sativa, is protective in a murine model of colitis. J Mol Med (Berl). 2009;87(11):1111-1121.
[10] WEISS L, ZEIRA M, REICH S, et al. Cannabidiol arrests onset of autoimmune diabetes in NOD mice. Neuropharmacology.2008;54(1):244-249.
[11] ARRUZA L, PAZOS MR, MOHAMMED N, et al. Cannabidiol reduces lung injury induced by hypoxic-ischemic brain damage in newborn piglets. Pediatr Res. 2017;82(1):79-86.
[12] DE FILIPPIS D, ESPOSITO G, CIRILLO C, et al. Cannabidiol Reduces Intestinal Inflammation through the Control of Neuroimmune Axis. PLoS One. 2011; 6(12):e28159.
[13] LI HB, KONG WM, CHAMBERS CR, et al. The non-psychoactive phytocannabinoid cannabidiol (CBD) attenuates pro-inflammatory mediators, T cell infiltration, and thermal sensitivity following spinal cord injury in mice. Cell Immunol. 2018;329:1-9.
[14] DOPKINS N, MIRANDA K, WILSON K, et al. Effects of Orally Administered Cannabidiol on Neuroinflammation and Intestinal Inflammation in the Attenuation of Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2022;17(1-2):15-32.
[15] ZHANG J, LUO ZH, ZHANG Z, et al. Protective effect and mechanism of cannabidiol on myocardial injury in exhaustive exercise training mice. Chem Biol Interact. 2022;365:110079.
[16] 侯莉娟, 刘晓莉, 乔德才. 大鼠游泳运动疲劳模型建立的研究[J]. 实验动物科学与管理,2005(1):1-3.
[17] QIAO X, ZHANG W, ZHAO W. Role of CXCL10 in Spinal Cord Injury. Int J Med Sci. 2022;19(14):2058-2070.
[18] ARIAS AY, KOLISHETTI N, VASHIST A, et al. Anti-inflammatory effects of CBD in human microglial cell line infected with HIV-1.Sci Rep. 2023;13(1):7376.
[19] KURET T, KREFT M E, ROMIH R, et al. Cannabidiol as a Promising Therapeutic Option in IC/BPS: In Vitro Evaluation of Its Protective Effects against Inflammation and Oxidative Stress. Int J Mol Sci. 2023;24(5):5055.
[20] WANG Y, CHE M, XIN J, et al. The role of IL-1 beta and TNF-alpha in intervertebral disc degeneration. Biomed Pharmacother. 2020;131:110660.
[21] GARCIA-MORALES L, CASTILLO AM, RAMIREZ JT, et al. CBD Reverts the Mesenchymal Invasive Phenotype of Breast Cancer Cells Induced by the Inflammatory Cytokine IL-1 beta. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(7):2429.
[22] LEWIS ND, MUTHUKUMARANA A, FOGAL SE, et al. CCR1 Plays a Critical Role in Modulating Pain through Hematopoietic and Non-Hematopoietic Cells.PLoS One. 2014;9(8):e105883.
[23] CHEN YY, LIU SY, WU LL, et al. Epigenetic regulation of chemokine (CC-motif) ligand 2 in inflammatory diseases. Cell Prolif. 2023;56(7):e13428.
[24] MA H, XU F, LIU C, et al. A Network Pharmacology Approach to Identify Potential Molecular Targets for Cannabidiol’s Anti-Inflammatory Activity. Cannabis Cannabinoid Res. 2021;6(4):288-299.
[25] SEDGER LM, MCDERMOTT MF. TNF and TNF-receptors: From mediators of cell death and inflammation to therapeutic giants - past, present and future. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2014;25(4):453-472.
[26] JANG DI, LEE AH, SHIN HY, et al. The Role of Tumor Necrosis Factor Alpha (TNF-alpha) in Autoimmune Disease and Current TNF-alpha Inhibitors in Therapeutics. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(5):2719.
[27] CHEN CY, HUNG YF, TSAI CY, et al. Transcriptomic Analysis and C-Terminal Epitope Tagging Reveal Differential Processing and Signaling of Endogenous TLR3 and TLR7. Front Immunol. 2021;12:686060.
[28] Rinaldi B, Cuzzocrea S, Donniacuo M,et al. Hyperbaric oxygen therapy reduces the toll-like receptor signaling pathway in multiple organ failures. Intensive Care Med. 2011;37(7):1110-1119.
[29] MASUDA S, TANAKA M, INOUE T, et al. Chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand 1 is a myokine induced by palmitate and is required for myogenesis in mouse satellite cells. Acta Physiol (Oxf). 2018;222(3). doi: 10.1111/apha.12975.
[30] HOGAN KA, CHO DS, ARNESON PC, et al. Tumor-derived cytokines impair myogenesis and alter the skeletal muscle immune microenvironment. Cytokine. 2018;107:9-17.
[31] COMPTON T, POELLINGER N, STRUVE J, et al. Non-thermal Infrared Light Treatment of Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury and Subsequent Analysis of Macrophage Differentiation. J Vis Exp. 2021;(178). doi: 10.3791/62908.
[32] MACHADO TR, MACHADO TR, PASCUTTI PG. The p38 MAPK Inhibitors and Their Role in Inflammatory Diseases. Chemistryselect. 2021;6(23):5729-5742.
[33] UENO M, MAESHIGE N, HIRAYAMA Y, et al. Pulsed ultrasound prevents lipopolysaccharide-induced muscle atrophy through inhibiting p38 MAPK phosphorylation in C2C12 myotubes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2021;570:184-190.
[34] MACIEJEWSKA-SKRENDO A, TARNOWSKI M, KOPYTKO P, et al. CCL2 Gene Expression and Protein Level Changes Observed in Response to Wingate Anaerobic Test in High-Trained Athletes and Non-Trained Controls.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022;19(16):9947.
[35] ZHAO LL, LIU XG, ZHANG J, et al. Hydrogen Sulfide Alleviates Skeletal Muscle Fibrosis via Attenuating Inflammation and Oxidative Stress. Front Physiol. 2020;11:533690.
[36] PATEL H, YONG C, NAVI A, et al. Toll-like receptors 2 and 6 mediate apoptosis and inflammation in ischemic skeletal myotubes. Vasc Med. 2019;24(4): 295-305.
[37] KIM JW, SHIN SK, KWON EY. Luteolin Protects Against Obese Sarcopenia in Mice with High-Fat Diet-Induced Obesity by Ameliorating Inflammation and Protein Degradation in Muscles. Mol Nutr Food Res. 2023;67(6):e2200729.
|