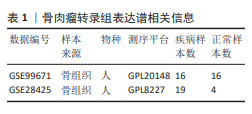
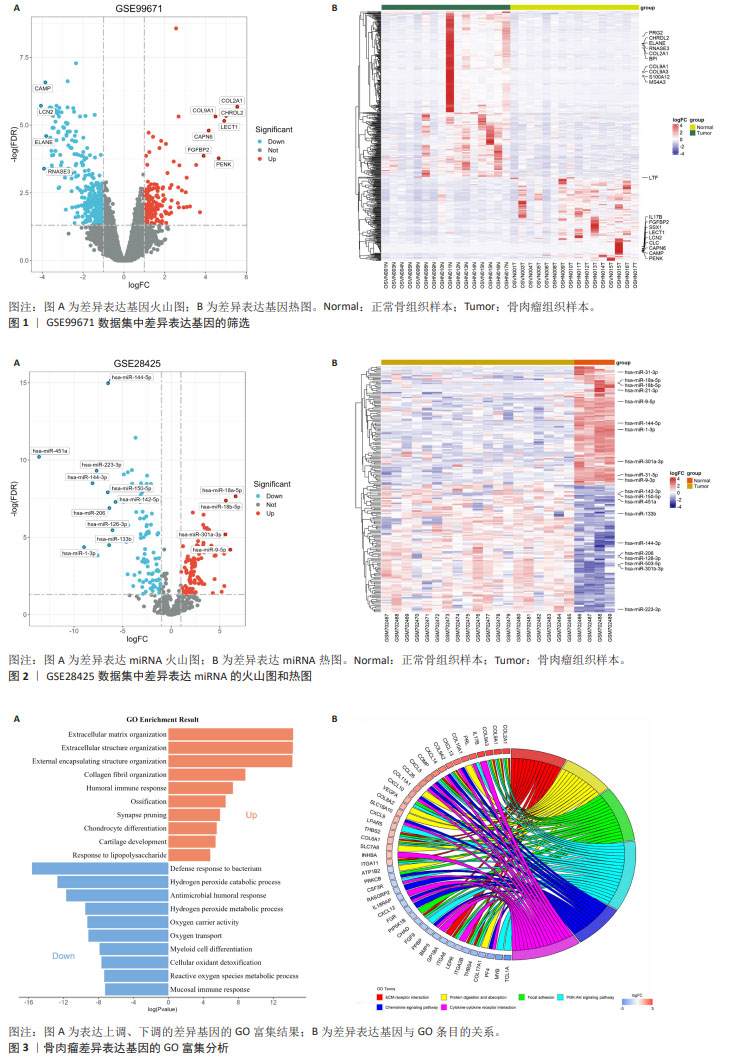
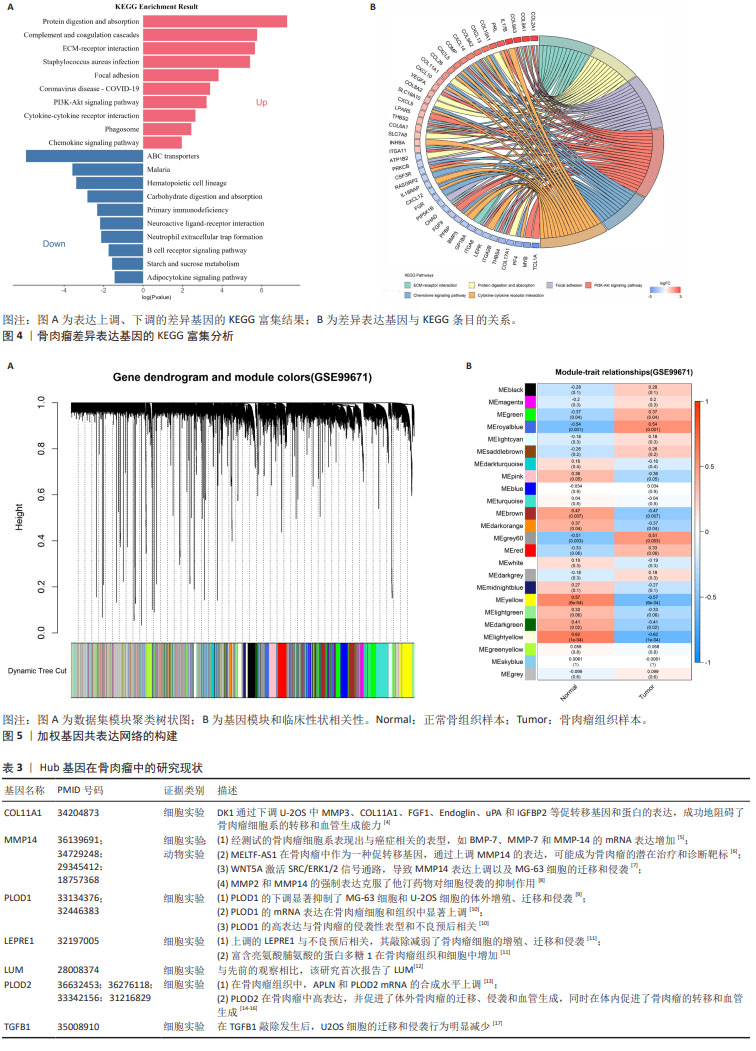
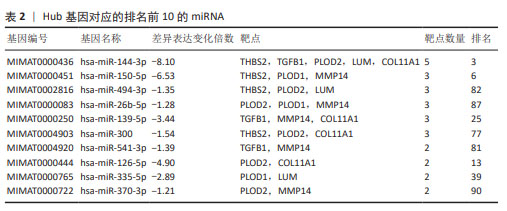
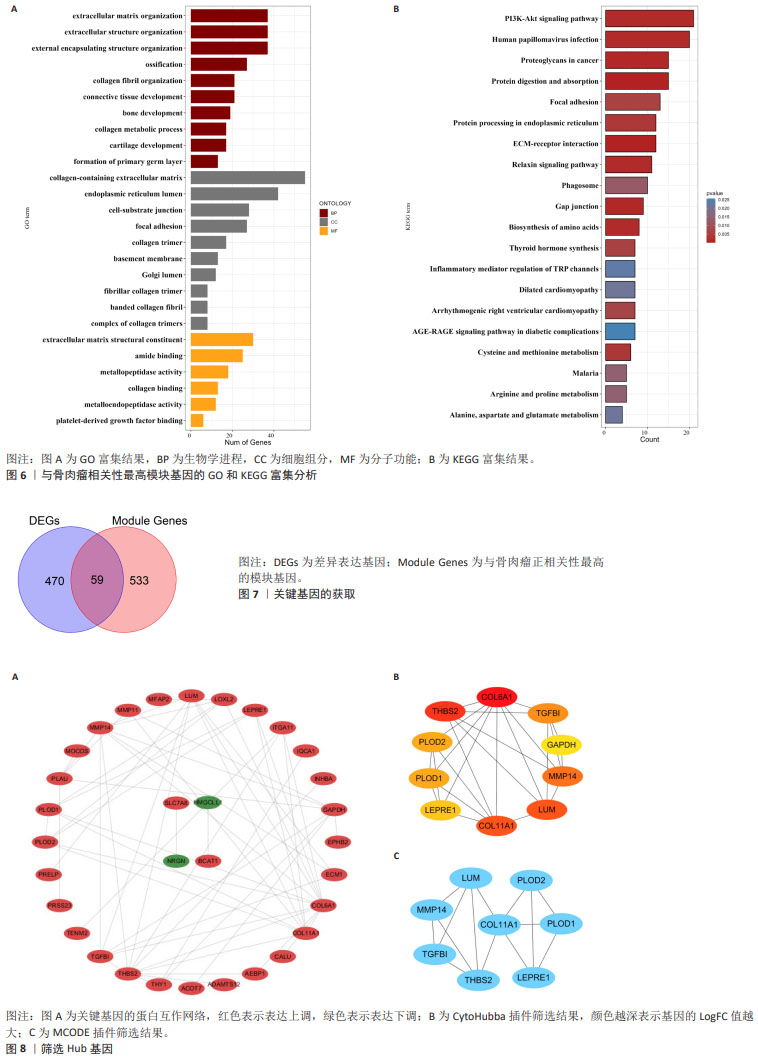
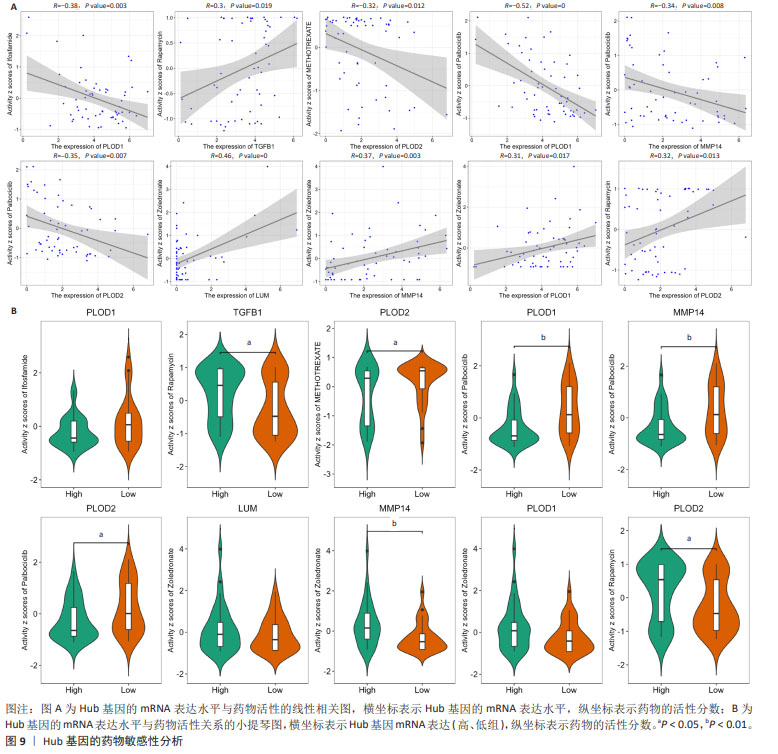
[1] CHEN Y, LIU R, WANG W, et al. Advances in targeted therapy for osteosarcoma based on molecular classification. Pharmacol Res. 2021;169:105684.
[2] 李帅,郑振中,张宇鹏,等.骨肉瘤关键基因及免疫浸润的生物信息分析[J].中国医学科学院学报,2022,44(1):110-117.
[3] ANGULO P, KAUSHIK G, SUBRAMANIAM D, et al. Natural compounds targeting major cell signaling pathways: a novel paradigm for osteosarcoma therapy. J Hematol Oncol. 2017;10(1):10.
[4] AZIZ MNM, RAHIM NFC, HUSSIN Y, et al. Anti-Metastatic and Anti-Angiogenic Effects of Curcumin Analog DK1 on Human Osteosarcoma Cells In Vitro. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2021;14(6):532.
[5] SIKORA M, KRAJEWSKA K, MARCINKOWSKA K, et al. Comparison of Selected Non-Coding RNAs and Gene Expression Profiles between Common Osteosarcoma Cell Lines. Cancers (Basel). 2022;14(18):4533.
[6] DING L, LIU T, QU Y, et al. lncRNA MELTF-AS1 facilitates osteosarcoma metastasis by modulating MMP14 expression. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2021;26:787-797.
[7] WANG X, ZHAO X, YI Z, et al. WNT5A promotes migration and invasion of human osteosarcoma cells via SRC/ERK/MMP-14 pathway. Cell Biol Int. 2018;42(5):598-607.
[8] FROMIGUÉ O, HAMIDOUCHE Z, MARIE PJ. Blockade of the RhoA-JNK-c-Jun-MMP2 cascade by atorvastatin reduces osteosarcoma cell invasion. J Biol Chem. 2008;283(45):30549-30556.
[9] JIANG H, GUO W, YUAN S, et al. PLOD1 Is a Prognostic Biomarker and Mediator of Proliferation and Invasion in Osteosarcoma. Biomed Res Int. 2020; 2020:3418398.
[10] WU X, XIANG H, CONG W, et al. PLOD1, a target of miR-34c, contributes to cell growth and metastasis via repressing LATS1 phosphorylation and inactivating Hippo pathway in osteosarcoma. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2020;527(1):29-36.
[11] HUANG Z, WANG Q, WANG Y, et al. Upregulated LEPRE1 correlates with poor outcome and its knockdown attenuates cells proliferation, migration and invasion in osteosarcoma. Anticancer Drugs. 2020; 31(4):326-332.
[12] WANG G, ZHANG Z, YANG M, et al. Comparative proteomics analysis of human osteosarcoma by 2D DIGE with MALDI-TOF/TOF MS. J Bone Oncol. 2016; 5(4):147-152.
[13] TRANG NTN, LAI CY, TSAI HC, et al. Apelin promotes osteosarcoma metastasis by upregulating PLOD2 expression via the Hippo signaling pathway and hsa_circ_0000004/miR-1303 axis. Int J Biol Sci. 2023;19(2):412-425.
[14] WANG Z, FAN G, ZHU H, et al. PLOD2 high expression associates with immune infiltration and facilitates cancer progression in osteosarcoma. Front Oncol. 2022;12:980390.
[15] CAO F, KANG XH, WANG DF, et al. Mechanism of lncRNA-SRLR induced invasion and metastasis in U2OS osteosarcoma cells. Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi. 2020;42(12):1007-1013.
[16] CAO F, KANG XH, CUI YH, et al. Upregulation of PLOD2 promotes invasion and metastasis of osteosarcoma cells. Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi. 2019;41(6):435-440.
[17] YEH LT, LIN CW, LU KH, et al. Niclosamide Suppresses Migration and Invasion of Human Osteosarcoma Cells by Repressing TGFBI Expression via the ERK Signaling Pathway. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(1):484.
[18] TEWARI D, PATNI P, BISHAYEE A, et al. Natural products targeting the PI3K-Akt-mTOR signaling pathway in cancer: A novel therapeutic strategy. Semin Cancer Biol. 2022;80:1-17.
[19] CZARNECKA AM, SYNORADZKI K, FIRLEJ W, et al. Molecular Biology of Osteosarcoma. Cancers (Basel). 2020; 12(8):2130.
[20] LIU M, ZHANG J, DONG H, et al. Nimotuzuma restrains proliferation and induces apoptosis in human osteosarcoma cells by regulation of EGFR/PI3K/AKT signal pathway. J Cell Physiol. 2019;234(11): 20879-20887.
[21] JIANG H, WANG X, MIAO W, et al. CXCL8 promotes the invasion of human osteosarcoma cells by regulation of PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. APMIS. 2017;125(9): 773-780.
[22] YUAN B, SHI K, ZHA J, et al. Nuclear receptor modulators inhibit osteosarcoma cell proliferation and tumour growth by regulating the mTOR signaling pathway. Cell Death Dis. 2023;14(1):51.
[23] WU C, GONG S, DUAN Y, et al. A tumor microenvironment-based prognostic index for osteosarcoma. J Biomed Sci. 2023; 30(1):23.
[24] DEMIRCIOGLU F, WANG J, CANDIDO J, et al. Cancer associated fibroblast FAK regulates malignant cell metabolism. Nat Commun. 2020;11(1):1290.
[25] ZHOU J, YI Q, TANG L. The roles of nuclear focal adhesion kinase (FAK) on Cancer: a focused review. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2019;38(1):250.
[26] CHEN X, CLEMENT M, HICKS MJ, et al. LOX upregulates FAK phosphorylation to promote metastasis in osteosarcoma. Genes Dis. 2022;10(1):254-266.
[27] QI Y, XU R. Roles of PLODs in Collagen Synthesis and Cancer Progression. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2018;6:66.
[28] DU H, PANG M, HOU X, et al. PLOD2 in cancer research. Biomed Pharmacother. 2017;90:670-676.
[29] SHI W, CHEN Z, LIU H, et al. COL11A1 as an novel biomarker for breast cancer with machine learning and immunohistochemistry validation. Front Immunol. 2022;13:937125.
[30] PIETRASZEK-GREMPLEWICZ K, KARAMANOU K, NIANG A, et al. Small leucine-rich proteoglycans and matrix metalloproteinase-14: Key partners? Matrix Biol. 2019;75-76:271-285.
[31] ABDEL MOUTI M, PAUKLIN S. TGFB1/INHBA Homodimer/Nodal-SMAD2/3 Signaling Network: A Pivotal Molecular Target in PDAC Treatment. Mol Ther. 2021;29(3): 920-936.
[32] KARAMANOU K, PERROT G, MAQUART FX, et al. Lumican as a multivalent effector in wound healing. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2018; 129:344-351.
[33] VARENNA M, CROTTI C, BONATI MT, et al. A novel mutation in collagen gene COL1A2 associated with transient regional osteoporosis. Osteoporos Int. 2022;33(1): 299-303.
[34] HOSHINO A, KIM HS, BOJMAR L, et al. Extracellular Vesicle and Particle Biomarkers Define Multiple Human Cancers. Cell. 2020; 182(4):1044-1061.e18.
[35] LIU JF, CHEN PC, CHANG TM, et al. Thrombospondin-2 stimulates MMP-9 production and promotes osteosarcoma metastasis via the PLC, PKC, c-Src and NF-κB activation. J Cell Mol Med. 2020;24(21): 12826-12839.
[36] PERSHA HE, KATO S, DE P, et al. Osteosarcoma with cell-cycle and fibroblast growth factor genomic alterations: case report of Molecular Tumor Board combination strategy resulting in long-term exceptional response. J Hematol Oncol. 2022;15(1):119.
[37] LU KH, LU EW, LIN CW, et al. New insights into molecular and cellular mechanisms of zoledronate in human osteosarcoma. Pharmacol Ther. 2020;214:107611. |