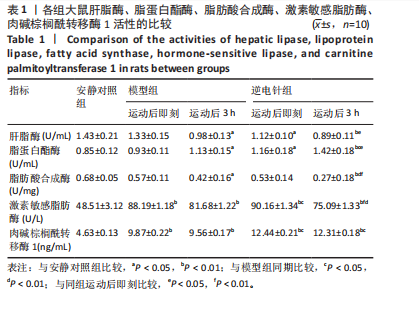
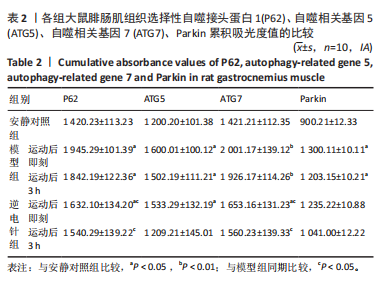
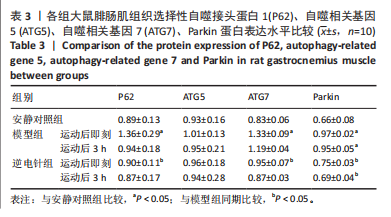
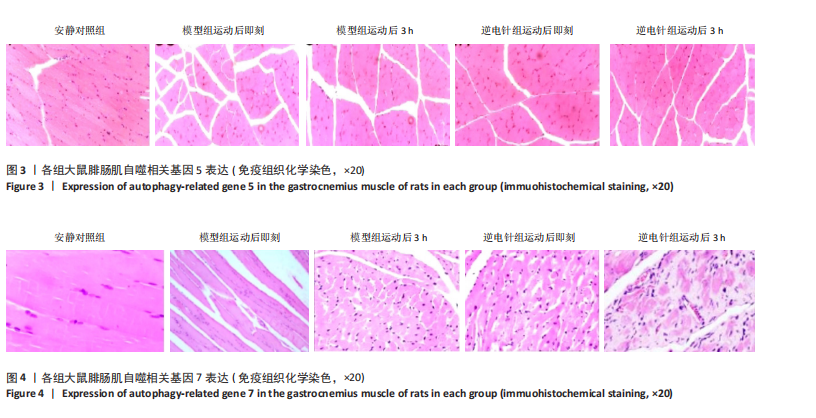
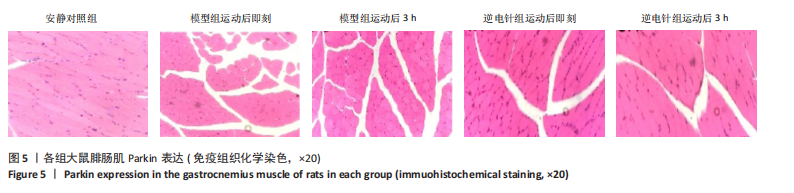
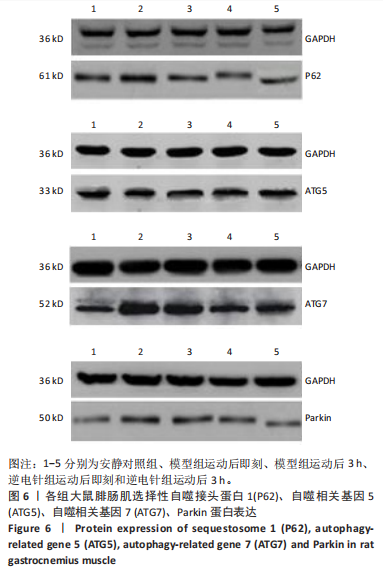
[1] 徐美玲, 苏东雪, 周建玲,等. 香芩解热颗粒对不同肥胖模型小鼠脂质代谢和慢性炎症的影响[J]. 中国中药杂志,2022,47(5): 1307-1315.
[2] HEATH V. Metabolism: Feel the burn--muscle metabolite cou‐ples exercise to heat production. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2014;10(4):188.
[3] KIRK B, FEEHAN J, LOMBARDI G, et al. Muscle, bone, and fat crosstalk: The biological role of myokines, osteokines, and adipokines. Curr Osteoporos Rep. 2020;18(4):388-400.
[4] 张一文, 喻松仁, 姚琦, 等.细胞自噬调控肥胖脂肪组织炎症状态的研究进展[J].江西中医药,2020,51(8):77-80.
[5] 王立宇, 刘淑云, 肖茂春, 等. 电针对急性后循环缺血豚鼠蜗神经核能量代谢功能重塑的影响及机制研究[J].听力学及言语疾病杂志,2023,31(1):39-43.
[6] 潘伟滨, 林晓敏, 范筱. 脊髓损伤后调控星形胶质细胞和小胶质细胞活化的电针技术[J].中国组织工程研究,2019,23(29): 4675-4680.
[7] 郭轩彤, 潘洪娣, 刘欣安, 等. 电针刺激合谷穴改善帕金森病模型小鼠运动障碍实验研究[J]. 湖北中医药大学学报,2022,24(6):5-8.
[8] 杨云昊, 陶春鹤, 庞芳, 等. 电针通过调节AMPK/mTOR/ULK1信号通路对衰老小鼠肝脏自噬与氧化应激的影响[J]. 针刺研究,2022, 47(1):7-14.
[9] GONG M, CAO C, CHEN F, et al. Electroacupuncture attenuates hepatic lipid accumulation via AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) activation in obese rats. Acupunct Med. 2015;34(3):209-214.
[10] BEDFORD TG, TIPTON CM, WILSON NC, et al. Maximum oxygen consumption of rats and its changes with various experimental procedures. J Appl Physiol. 1979;47(6):1278-1283.
[11] 闫清伟, 李亚楠, 赵娜, 等. 运动改善APP/PS1小鼠海马白质的机制研究[J]. 中国体育科技, 2020,56(11): 84-89.
[12] 高明, 杨华元, 刘堂义, 等. 手针与电针对急性运动大鼠骨骼肌线粒体的影响[J]. 中国针灸,2005,25(6):421-424.
[13] 黄东,李跃林,卜凯, 等.黄酮对运动大鼠脂肪代谢酶与ERRα表达的影响[J]. 广西师范大学学报(自然科学版),2016,34(1):168-173.
[14] 章媛. 有氧联合抗阻运动对绝经后血脂异常女性心血管剩余风险指标的影响[D]. 上海:上海体育学院,2022.
[15] 闫焕焕. 60min游泳运动对高脂膳食大鼠脂代谢紊乱的影响及作用机制的研究[D]. 扬州: 扬州大学,2010.
[16] KUHAJDA FP, JENNER K, WOOD FD, et al. Fatty acid synthesis: a potential selective target for antineoplastic therapy. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1994;91(14):6379-6383.
[17] 谢钰德,李志升,李圆,等.脂肪酸合成酶在乳腺癌治疗抵抗中的研究进展[J].广东医学,2023,44(4):519-524.
[18] 刘梨, 周巍, 黎铭玉, 等. 电针“足三里”“关元”穴对佐剂性关节炎大鼠滑膜细胞凋亡及相关凋亡蛋白表达的影响[J]. 针刺研究, 2022,47(8):696-702.
[19] 司原成, 任晨晨, 张二伟, 等. 电针对营养性肥胖小鼠脂肪因子及脂肪酸合成酶的影响[J]. 西部中医药,2023,36(6):10-13.
[20] VAUGHAN M, BERGER JE, STEINBERG D. Hormone-sensitive Lipase and Monoglyceride Lipase Activities in Adipose Tissue. J Biol Chem. 1964;239(2):401-409.
[21] 裴莎莎. HIIE/MICE对小鼠骨骼肌脂肪水解酶的激活作用[D].石家庄:河北师范大学,2020.
[22] 魏建翔, 何玉秀, 刘阳, 等. 急性高强度间歇运动后肥胖小鼠脂肪水解酶活性的变化[C]//中国体育科学学会. 第十二届全国体育科学大会论文摘要汇编——专题报告(运动生理生化分会). 2022.
[23] 梅佳顺. HIIT对肥胖小鼠不同部位脂肪组织脂肪水解酶类的激活作用[D].石家庄:河北师范大学,2019.
[24] 王洁. 运动、饮食干预对肥胖小鼠脂肪组织中Sirt1及其信号通路的影响[D].沈阳:沈阳体育学院,2020.
[25] 杨玲, 彭团辉, 徐晓阳,等.终生HIIT和MICT运动对自然衰老小鼠运动能力和脂代谢的影响[J]. 广州体育学院学报,2022,42(3): 23-33.
[26] 贺杰, 漆正堂,丁树哲.运动与肉碱棕榈酰转移酶-Ⅰ研究进展[J].中国运动医学杂志,2008(6):794-797.
[27] 沈友青, 黄国源, 王配才, 等. 大强度间歇运动对高脂喂养大鼠代谢表征和骨骼肌脂代谢基因表达的影响[J]. 中国体育科技,2016, 52(1):84-91+140.
[28] 李敏, 沈琴, 王晓萍, 等.单核/巨噬细胞自噬在肝病中的作用研究进展[J].药学研究,2021,40(5):319-323.
[29] PINTO AP, ROCHA AL,MARAFON BB, et al. Impact of Different Physical Exercises on the Expression of Autophagy Markersin Mice. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(5):2635.
[30] 尚画雨,付玉,夏志,等.针刺对运动性骨骼肌损伤大鼠骨骼肌线粒体自噬的影响[J].中国病理生理杂志,2017,33(11):2038-2046.
[31] 张欣,李俊平,王瑞元.针刺对运动性骨骼肌损伤大鼠细胞自噬及Omi/HtrA2通路的影响[J].中国运动医学杂志,2022,41(8):625-632.
[32] LAMARK T, SVENNING S, JOHANSEN T. Regulation of selec-tive autophagy: the p62/SQSTM1 paradigm. Essays Biochem. 2017;61(6): 609-624.
[33] 晏珺, 卢宗孝, 于雪, 等. 电针“委中”在大鼠腰多裂肌损伤修复过程中对自噬相关蛋白Beclin1, p62的影响[J].环球中医药,2018, 11(2):161-166.
[34] 王羽心, 孙忠人, 朱嘉民, 等. 针刺调控自噬保护脊髓损伤探析[J]. 针灸临床杂志,2023,39(3):1-5.
[35] 李梦影, 李灵杰, 马春伟,等. 不同低氧训练模式通过激活小鼠脂肪组织脂噬作用调节脂代谢[J]. 中国运动医学杂志,2022,41(11): 866-874.
[36] TANAKA G, KATO H, IZAWA T. Endurance exercise training induces fat depot-specific differences in basal autophagic activity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2015;266(3): 512-517.
[37] 田华,郭连军,刘富,等.葛根素下调Atg5, LC3Ⅰ/Ⅱ蛋白对缺血再灌注脑损伤小鼠的神经保护作用[J].中国临床药理学杂志, 2023,39(4):508-512.
[38] 吴梦佳, 唐成林, 赵丹丹, 等. 电针对失神经大鼠骨骼肌自噬相关基因表达的影响[J]. 中国康复理论与实践,2018,24(3):260-265.
[39] 孔海军,谌晓安.低氧运动预适应激活自噬调控Hippo/YAP/TAZ信号通路减轻急性低氧力竭运动大鼠骨骼肌损伤[J].山东体育学院学报,2023,39(3):89-98.
[40] 林大卫. 电针通过抑制自噬缓解脓毒症大鼠骨骼肌萎缩的研究[D]. 镇江: 江苏大学,2022.
[41] GUHA P, SNYDER SH. Noncatalytic functions of IPMKare essential for activation of autophagy and liver regeneration.Autophagy. 2019;15(8): 1473-1474.
[42] 姚俊鹏, 李瑛, 张林. 电针对食源性肥胖大鼠下丘脑自噬相关蛋白7表达的影响[J].广州中医药大学学报,2019,36(4):545-548.
[43] YANG Y, JING Y, LI XZ, et al. Dysfunction of Akt/FoxO3a/Atg7 regulatory loop magnifies obesity-regulated muscular mass decline[J]. Molecular Meta bolism. 2024;81(1):101892.
[44] 余辕耕. 电针通过调控肝脏SIRT1/ATG7改善胰岛素抵抗的机制研究[D]. 武汉:湖北中医药大学,2021.
[45] 花卫成,付鹏宇,张缨,等. 运动经FoxO1-脂噬通路缓解ApoE-/-小鼠高脂血症的研究[J].中国实验动物学报,2021,29(6):808-815.
[46] LIRA VA, OKUTSU M, ZHANG M, et al. Autophagy is required for exercise training-induced skeletal muscle adaptation and improvement of physical performance. Faseb J. 2013;27(10):4184-4193.
[47] WOHLGEMUTH SE, SEO AY, MARZETTI E, et al. Skeletal muscle autophagy and apoptosis during aging: effects of calorie restriction and life-long exercise. Exp Gerontol. 2010;45(2):138-148.
[48] 樊宗山,周艳杰,韩华凤.温阳活血益气汤联合电针治疗运动后神经肌肉损伤临床研究[J].新中医,2022,54(15):93-96.
[49] ROVERATO ND, SAILER C, CATONE N, et al. Parkin is an E3 ligase for the ubiquitin-like modifier FAT10,which inhibits Parkin activation and mitophagy. Cell Rep. 2021;34(11):108857.
[50] 肖琪,樊慧杰,李艳荣,等. PARK2介导的帕金森病中帕金蛋白对α-突触核蛋白的作用[J].中国老年学杂志,2024,44(4):999-1005.
[51] 张贵君,汪瑶,李军令,等.电针对帕金森病小鼠SIRT3/PINK1/Parkin通路介导的线粒体自噬的影响[J].针刺研究,2024,49(3): 221-230.
[52] HU YJ, LI YY, LI M, et al. Calcium supplementation attenuatesfluoridei nduced bone injury via PINK1/Parkin-mediated mitophagy and mitocho-ndrial apoptosis in mice. J Hazard Mater. 2024;465(1):133411-133411.
[53] 汪彦旭. 不同运动对大鼠主动脉血管平滑肌Parkin/Mfn2的影响机制研究[D]. 北京:首都体育学院,2022.
[54] 王彦春,何方,马骏,等.电针对帕金森病模型大鼠泛素-蛋白酶体系统的影响[J].中国针灸,2013,33(8):725-729.
[55] 方琼. AMPK在运动调控老年小鼠骨骼肌自噬中的作用[D]. 苏州: 苏州大学,2021.
[56] 吴姝雯,刘敏,楼毅杰,等.不同频率电针介导PINK1/Parkin通路治疗STC模型大鼠的机制研究[J].浙江中西医结合杂志,2023, 33(2):106-111.
[57] MING W, MENGQIAN Y, ZHONG YG, et al. The Effect of Electroacupuncture on Obesity through Browning of White Adipocytes and Mitochondrial Autophagy. Indian J Pharmaceutical Sci. 2020; 82(7):146. |