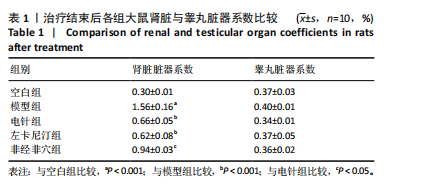
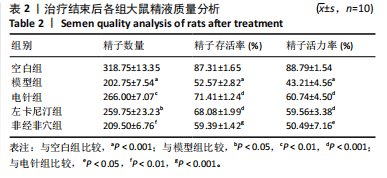
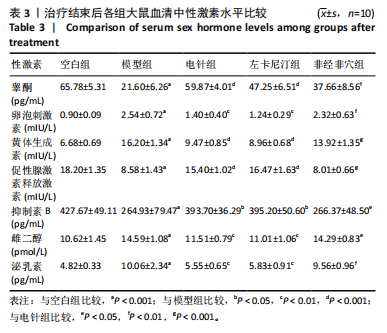
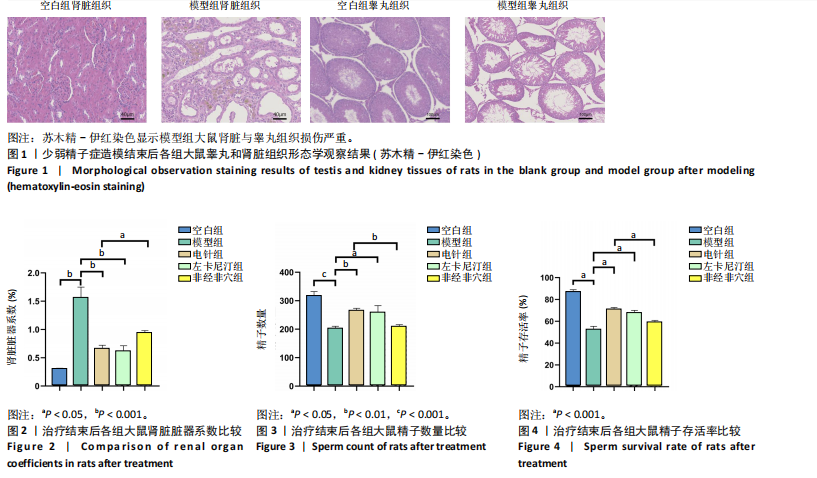
[1] 申玉行,陈广辉,王广建,等.基于“肾藏精”理论运用补肾填精法治疗少弱精子症的研究进展[J].中国性科学,2020,29(4):118-121.
[2] 孙自学,陈央娣,陈建设,等.益肾通络方治疗肾虚络阻型少弱精子症不育疗效观察[J].中华中医药学刊,2024,42(8):1-6.
[3] SHARMA A, JAYASENA CN, DHILLO WS. Regulation of the Hypothalamic-Pituitary-Testicular Axis: Pathophysiology of Hypogonadism. Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am. 2022;51(1):29-45.
[4] YANG Y, ZUO Z, YANG Z, et al. Nickel chloride induces spermatogenesis disorder by testicular damage and hypothalamic-pituitary-testis axis disruption in mice. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2021;225:112718.
[5] 黄念文,李海松,王彬,等.基于“肾主生殖”理论探讨少弱精子症的病机及龟鹿育麟汤组方思路[J].天津中医药大学学报,2024,43(3):285-288.
[6] 李威,叶佰盛,黄振,等.从“天癸竭,地道不通”谈绝经后骨质疏松症研究进展[J].中国中西医结合杂志,2024,44(5):623-626.
[7] 朱善意,高越颖,陈爽,等.颐和春口服液对肾阳虚大鼠睾丸功能的影响[J].中药新药与临床药理,2010,21(2):133-136.
[8] 柳强龙,李玉来,杨月,等.针药联合治疗少弱精症[J].亚太传统医药,2022, 18(8):136-139.
[9] 马亮.基于“肾藏精”理论针刺治疗肾虚精亏型少弱精症的临床研究[D].银川:宁夏医科大学,2023.
[10] ADACHI Y, SASAGAWA I, TATENO T, et al. Influence of adenine-induced chronic renal failure on testicular function in the rat. Andrologia. 1998;30(2):115-118.
[11] 罗芳芳,林木南,黄冬娥,等.电针疏密波、电针断续波、电针连续波在瘀血阻滞型膝骨关节炎中的应用对比[J].中国医药导报,2022,19(15):136-139.
[12] 陈赟,韩紫阳,孙志兴,等.基于全国名老中医徐福松教授“内肾外肾”理论浅析男性生殖 [J].中华男科学杂志,2024,30(2):163-166.
[13] 马东岳,王安民,杨九天,等.基于“脑-心-肾-精室”轴理论探讨早泄的生物学基础[J].中国实验方剂学杂志,2024,30(10):203-209.
[14] 吴霞,程华初,谭金曲,等.基于频数统计方法的“中极穴”主治病症的古代文献研究[J].中国医药导报,2021,18(13):104-107,111.
[15] 罗诗雨,徐福.《针灸大成》关元穴应用规律探析[J].浙江中医杂志,2023, 58(1):41-42.
[16] MBIYDZENYUY NE, QULU LA. Stress, hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis, hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal axis, and aggression. Metab Brain Dis. 2024;39(8): 1613-1636.
[17] 马晓杰,杨大鹏,陈少宇,等.性激素受体在双峰驼正常睾丸及隐睾的分布[J].云南农业大学学报(自然科学),2024,39(2):27-35.
[18] 吕银娟,龚健,萧闵.下丘脑Kiss1系统在产前应激诱导男性后代生殖功能异常中的潜在作用[J].中国现代医学杂志,2024,34(10):54-59.
[19] 马琳,李学智,姚太万,等.不同针灸疗法对老年雄性大鼠下丘脑-睾丸中生殖激素调控系统相关基因表达的影响[J].针刺研究,2019,44(3):200-204,219.
[20] GROSSMANN M, WITTERT GA. Dysregulation of the Hypothalamic-Pituitary-Testicular Axis due to Energy Deficit. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2021;106(12): e4861-e4871.
[21] SMITH BK, WARD M. The Role of Testosterone Therapy in Men’s Health. Nurs Clin North Am. 2023;58(4):525-539.
[22] ODUWOLE OO, HUHTANIEMI IT, MISRAHI M. The Roles of Luteinizing Hormone, Follicle-Stimulating Hormone and Testosterone in Spermatogenesis and Folliculogenesis Revisited. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(23):12735.
[23] 袁茜,徐晓英,董云华.血清生物标记物在非梗阻性和梗阻性无精子症鉴别诊断中的应用[J].临床医学进展,2023,13(6):10369-10375.
[24] 曾勇,宋明哲,赵明,等.性激素负反馈作用在男性不育诊疗中的应用[J].生殖医学杂志,2017,26(8):743-748.
[25] WANG CN, SANG MM, GONG SN, et al. Two resveratrol analogs, pinosylvin and 4,4’-dihydroxystilbene, improve oligoasthenospermia in a mouse model by attenuating oxidative stress via the Nrf2-ARE pathway. Bioorg Chem. 2020; 104:104295.
[26] GÖKALP ÖZKORKMAZ E, ÖZDEMIR BAŞARAN S, AFŞIN M, et al. Comparison of testosterone, FSH, LH and E2 hormone levels in infertility suspected males with COVID-19 infection. Medicine (Baltimore). 2023;102(43):e35256.
[27] JIAO W, SUN J, ZHANG X, et al. Improvement of Qilin pills on male reproductive function in tripterygium glycoside-induced oligoasthenospermia in rats. Andrologia. 2021;53(4):e13923.
[28] SPAGGIARI G, COSTANTINO F, GRANATA ARM, et al. Prolactin and spermatogenesis: new lights on the interplay between prolactin and sperm parameters. Endocrine. 2023;81(2):330-339.
[29] LIU Y, WANG G, ZHANG F, et al. Correlation between serum levels of reproductive hormones and testicular spermatogenic function in men with azoospermia. Andrologia. 2022;54(10):e14546.
[30] TERASAWA E. Neuroestradiol in regulation of GnRH release. Horm Behav. 2018; 104:138-145.
[31] RUSSELL N, GROSSMANN M. Mechanisms in endocrinology: Estradiol as a male hormone. Eur J Endocrinol. 2019;181(1):R23-R43.
[32] LEAVY M, TROTTMANN M, LIEDL B, et al. Effects of Elevated β-Estradiol Levels on the Functional Morphology of the Testis - New Insights. Sci Rep. 2017;7:39931.
[33] ANDREONE L, AMBAO V, PELLIZZARI EH, et al. Role of FSH glycan structure in the regulation of Sertoli cell inhibin production. Reproduction. 2017;154(5):711-721.
[34] NEGRI F, BOERI L, CILIO S, et al. The Importance of Discordant Follicle Stimulating Hormone and Inhibin B Levels in Primary Infertile Men: Findings from a Cross-Sectional Study. World J Mens Health. 2024.doi: 10.5534/wjmh.230298.
[35] LIU L, HUANG W, LUO K, et al. Relationship between semen parameters, serum InhB, and INSL-3 levels, and the degree of varicocele. Clinics (Sao Paulo). 2024; 79:100339.
[36] LI J, HU T, WANG Y, et al. Development a nomogram to predict fertilisation rate of infertile males with borderline semen by using semen parameters combined with AMH and INHB. Andrologia. 2021;53(9):e14182.
[37] YANG Q, SU S, LUO N, CAO G. Adenine-induced animal model of chronic kidney disease: current applications and future perspectives. Ren Fail. 2024;46(1): 2336128.
[38] BARATI E, NIKZAD H, KARIMIAN M. Oxidative stress and male infertility: current knowledge of pathophysiology and role of antioxidant therapy in disease management. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2020;77(1):93-113.
[39] HASSANIN HM, KAMAL AA, ISMAIL OI. Resveratrol ameliorates atrazine-induced caspase-dependent apoptosis and fibrosis in the testis of adult albino rats. Sci Rep. 2024;14(1):17743.
[40] ADACHI Y, SASAGAWA I, NAKADA T. Reproductive insufficiency in the male rat with adenine-induced chronic renal failure. Urol Int. 1993;51(4):228-230.
[41] MATEUS FG, MOREIRA S, MARTINS AD, et al. L-Carnitine and Male Fertility: Is Supplementation Beneficial? J Clin Med. 2023;12(18):5796.
[42] MA L, SUN Y. COMPARISON OF L-CARNITINE VS. Coq10 and Vitamin E for idiopathic male infertility: a randomized controlled trial. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2022;26(13):4698-4704. |