[1] MARCHAND S, STETZKOWSKI-MARDEN F, CARTAUD J. Differential targeting of components of the dystrophin complex to the postsynaptic membrane: Targeting of the dystrophin complex. Eur J Neurosci. 2001;13(2):221-229.
[2] FUSTER JM. Memory in the Cerebral Cortex (Second Edition). Publisher: MIT Press.1999.
[3] BADDELEY A. Working Memory. Current Biology.2010;(20):136-114
[4] FUSTER JM, ALEXANDER GE.Neuron Activity Related to Short-Term Memory. Science. 1971;173(3997):652-654.
[5] ZHOU YD, FUSTER JM. Mnemonic neuronal activity in somatosensory cortex.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1996;93(19):10533-10537.
[6] WIMMER K, NYKAMP DQ, CONSTANTINIDIS C, et al. Bump attractor dynamics in prefrontal cortex explains behavioral precision in spatial working memory. Nat Neurosci. 2014;17(3):431-439.
[7] STOKES MG, KUSUNOKI M, SIGALA N, et al. Dynamic Coding for Cognitive Control in Prefrontal Cortex. Neuron. 2013;78(2):364-375.
[8] GOTO Y, YANG CR, OTANI S.Functional and Dysfunctional Synaptic Plasticity in Prefrontal Cortex: Roles in Psychiatric Disorders. Biol Psychiatry. 2010;67(3):199-207.
[9] HENSTRIDGE CM, PICKETT E, SPIRES-JONES TL. Synaptic pathology: a shared mechanism in neurological disease. Ageing Res Rev. 2016;28:72-84.
[10] TERRY RD, MASLIAH E, SALMON DP, et al. Physical basis of cognitive alterations in alzheimer’s disease: Synapse loss is the major correlate of cognitive impairment. Ann Neurol. 1991;30(4):572-580.
[11] LISTON C, MALTER COHEN M, TESLOVICH T, et al. A typical Prefrontal Connectivity in Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder: Pathway to Disease or Pathological End Point?. Biol Psychiatry. 2011;69(12):1168-1177.
[12] BELLUCCI A, MERCURI NB, VENNERI A, et al. Parkinson’s disease: From synaptic loss to connectome dysfunction. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol. 2016;42(1):77-94.
[13] 刘涵慧, 李会杰. 老化认知神经科学:研究现状与未来展望[J].中国科学:生命科学,2021,51(6):743-763.
[14] HALSEY G , WU Y, GUO L. Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation//Guo L. (Ed.). Neural Interface Engineering: Linking the Physical World and the Nervous System. Springer International Publishing, Cham. 2020:49-65.
[15] ZHANG D, LI H, SUN J, et al. Antidepressant-Like Effect of Low-Intensity Transcranial Ultrasound Stimulation.IEEE Trans Biomed Eng. 2019;66(2): 411-420.
[16] THUT G, PASCUAL-LEONE A. A Review of Combined TMS-EEG Studies to Characterize Lasting Effects of Repetitive TMS and Assess Their Usefulness in Cognitive and Clinical Neuroscience. Brain Topogr. 2010;22(4):219-232.
[17] PEREIRA LS, MÜLLER VT, DA MOTA GOMES M, et al. Safety of repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation in patients with epilepsy: A systematic review. Epilepsy Behav. 2016;57(Pt A):167-176.
[18] 黄俐杰,何琼,王锐,等.功能超声成像技术及其应用研究进展[J].生物医学工程学杂志,2022,39(5):7.
[19] GRIFFITH TN, DOCTER TA, LUMPKIN EA. Tetrodotoxin-Sensitive Sodium Channels Mediate Action Potential Firing and Excitability in Menthol-Sensitive Vglut3-Lineage Sensory Neurons. J Neurosci. 2019;39(36): 7086-7101.
[20] OH SJ, LEE JM, KIM HB, et al. Ultrasonic Neuromodulation via Astrocytic TRPA1. Curr Biol. 2019;29(20):3386-3401.e8.
[21] BATTS A, JI R, KLINE-SCHODER A, et al. Transcranial Theranostic Ultrasound for Pre-Planning and Blood-Brain Barrier Opening: A Feasibility Study Using an Imaging Phased Array In Vitro and In Vivo. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng. 2022;69(4):1481-1490.
[22] PIPER RJ, HUGHES MA, MORAN CM, et al. Focused ultrasound as a non-invasive intervention for neurological disease: a review. Br J Neurosurg. 2016;30(3):286-293.
[23] NORTON SJ. Can ultrasound be used to stimulate nerve tissue?.Biomed Eng Online. 2003;2:6.
[24] 张帅, 许家悦, 李梦迪, 等. 基于皮层神经元模型的经颅磁声电刺激神经网络放电活动仿真分析[J]. 电工技术学报,2021,36(18): 3851-3859.
[25] 张帅, 王艺潇, 武健康, 等. 经颅磁声电刺激对老年小鼠电压门控钠钾离子通道的影响[J].中国组织工程研究,2023,27(26):4200-4207.
[26] YUAN YI, CHEN YD, LI XL. A new brain stimulation method: Noninvasive transcranial magneto–acoustical stimulation. Chinese Physics B. 2016; 25(8):084301
[27] 张帅, 崔琨, 史勋, 等. 经颅磁声电刺激参数对神经元放电模式的影响分析[J]. 电工技术学报,2019,34(18):3741-3749.
[28] ZHOU X, LIU S, WANG Y, et al. High-Resolution Transcranial Electrical Simulation for Living Mice Based on Magneto-Acoustic Effect. Front Neurosci. 2019;13:1342.
[29] WANG Y, FENG L, LIU S, et al. Transcranial Magneto-Acoustic Stimulation Improves Neuroplasticity in Hippocampus of Parkinson’s Disease Model Mice. Neurotherapeutics. 2019;16(4):1210-1224.
[30] FRIES P. A mechanism for cognitive dynamics: neuronal communication through neuronal coherence. Trends Cogn Sci. 2005;9(10):474-480.
[31] SACKS DD, SCHWENN PE, MCLOUGHLIN LT, et al. Phase-Amplitude Coupling, Mental Health and Cognition: Implications for Adolescence. Front Hum Neurosci. 2021;15:622313.
[32] STORZER L, BÜRGERS S, HIRSCHMANN J. Are Beta Phase-Coupled High-Frequency Oscillations and Beta Phase-Locked Spiking Two Sides of the Same Coin? . J Neurosci. 2015;35(5):1819-1820.
[33] MARZETTI L, BASTI A, CHELLA F, et al. Brain Functional Connectivity Through Phase Coupling of Neuronal Oscillations: A Perspective From Magnetoencephalography. Front Neurosci. 2019;13:964.
[34] CANOLTY RT, KNIGHT RT. The functional role of cross-frequency coupling. Trends Cogn Sci. 2010;14(11):506-515.
[35] ENGEL AK, FRIES P. Beta-band oscillations-signalling the status quo? Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2010;20(2):156-165.
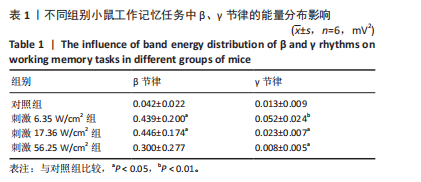
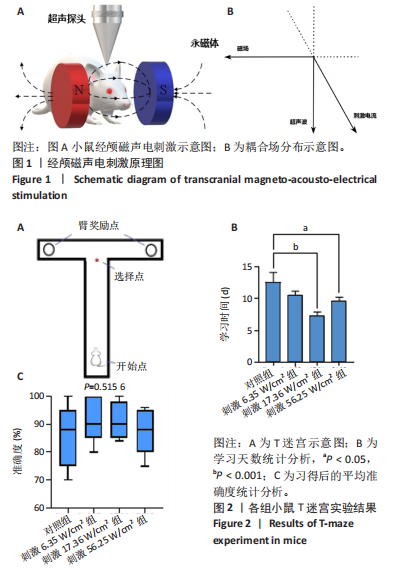
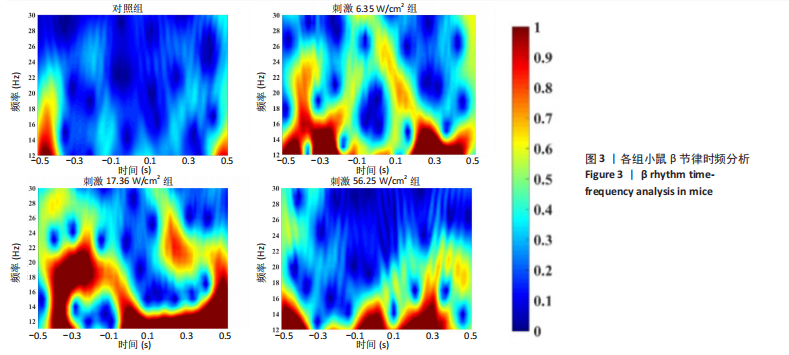
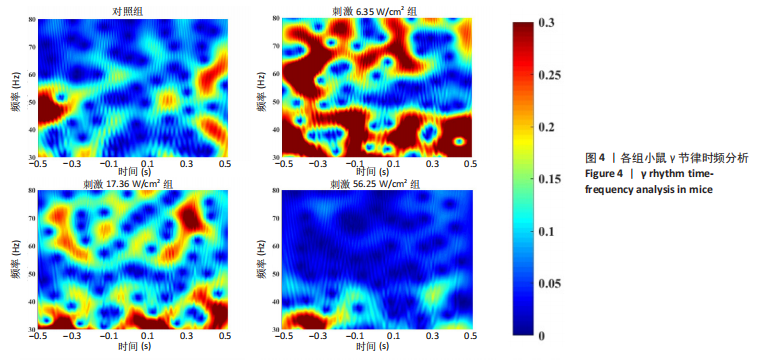
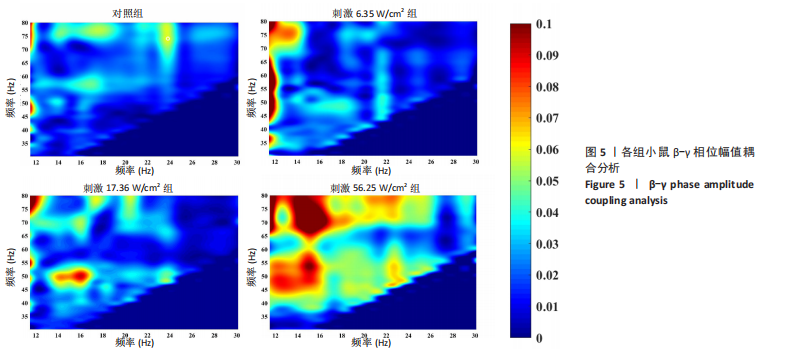
[36] 张帅, 党君武, 焦立鹏, 等. 经颅磁声电刺激对大鼠工作记忆局部场电位gamma节律的影响[J].中国生物医学工程学报,2021,40(5): 540-549.
[37] VAN DER MEIJ R, KAHANA M, MARIS E. Phase–Amplitude Coupling in Human Electrocorticography Is Spatially Distributed and Phase Diverse.J Neurosci. 2012;32(1):111-123.
[38] ENGEL AK, FRIES P, SINGER W. Dynamic predictions: Oscillations and synchrony in top-down processing. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2001;2(10):704-716.
[39] 高昕宇. 经颅磁声电刺激对新皮质神经元局部场电位影响的研究[D]. 天津:河北工业大学,2020.
[40] The Lancet Neurology. The Human Brain Project: mutiny on the flagship. Lancet Neurol. 2014;13(9):855.
[41] MONTALIBET A, JOSSINET J, MATIAS A, et al. Electric current generated by ultrasonically induced Lorentz force in biological media. Med Biol Eng Comput. 2001;39(1):15-20.
[42] CARVALHO TP, BUONOMANO DV. A novel learning rule for long-term plasticity of short-term synaptic plasticity enhances temporal processing. Front Integr Neurosci. 2011;5:20.
[43] PFISTER JP, GERSTNER W. Triplets of Spikes in a Model of Spike Timing-Dependent Plasticity. J Neurosci. 2006;26(38):9673-9682.
[44] KARMARKAR UR, BUONOMANO DV. A Model of Spike-Timing Dependent Plasticity: One or Two Coincidence Detectors?. J Neurophysiol. 2002;88(1):507-513.
[45] SENN W, MARKRAM H, TSODYKS M. An Algorithm for Modifying Neurotransmitter Release Probability Based on Pre- and Postsynaptic Spike Timing. Neural Comput. 2001;13(1):35-67.
[46] WANG Y, MARKRAM H, GOODMAN PH, et al. Heterogeneity in the pyramidal network of the medial prefrontal cortex. Nat Neurosci. 2006;9(4):534-542.
[47] VASILAKI E, GIUGLIANO M. Emergence of Connectivity Motifs in Networks of Model Neurons with Short- and Long-Term Plastic Synapses. PLoS One. 2014;9(1):e84626.
[48] VASILAKI E, GIUGLIANO M. Emergence of Connectivity Patterns from Long-Term and Short-Term Plasticities. Springer-Verlag. 2012. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-33269-2_25
[49] ESPOSITO U, GIUGLIANO M, VASILAKI E. Adaptation of short-term plasticity parameters via error-driven learning may explain the correlation between activity-dependent synaptic properties, connectivity motifs and target specificity. Front Comput Neurosci. 2015;8:175.
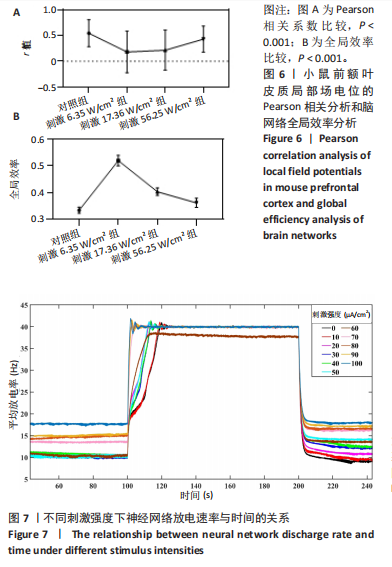
[50] 张帅, 武健康, 许家悦, 等. 经颅磁声电刺激对前额叶皮层神经集群钙信号的影响[J]. 生物医学工程学杂志,2022,39(1):19-27.
[51] BARAK O, TSODYKS M. Working models of working memory. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2014;25:20-24.
[52] 袁洁,蔡时青. 衰老过程中行为和认知功能退化的调控机制研究[J]. 遗传,2021,43(6):545-570.
[53] DUBEY A, MARKOWITZ DA, PESARAN B. Top-down control of exogenous attentional selection is mediated by beta coherence in prefrontal cortex. Neuron. 2023;111(20):3321-3334.e5.
[54] GĄGOL A, MAGNUSKI M, KROCZEKET B, et al. Delta-gamma coupling as a potential neurophysiological mechanism of fluid intelligence. Intelligence. 2018;66:54-63.
[55] DONG X, ZHANG X, WANG F, et al. Simultaneous calcium recordings of hippocampal CA1 and primary motor cortex M1 and their relations to behavioral activities in freely moving epileptic mice. Exp Brain Res. 2020;238:1479-1488.
[56] FAN XX, YANG L, XIANG B, et al. Recent Research Progress of Ca2+ Permeable Channels. Progress in Biochemistry and Biophysics. 2016; 43:1129-1138.
[57] SKOWROŃSKA K, OBARA-MICHLEWSKA M, CZARNECKA A, et al. Persistent Overexposure to N-Methyl-d-Aspartate (NMDA) Calcium-Dependently Downregulates Glutamine Synthetase, Aquaporin 4, and Kir4.1 Channel in Mouse Cortical Astrocytes. Neurotox Res. 2019; 35(1):271-280.
[58] COLLEDGE M, SNYDER EM, CROZIER RA, et al. Ubiquitination Regulates PSD-95 Degradation and AMPA Receptor Surface Expression. Neuron. 2003;40(3):595-607.
[59] COMPANS B, CAMUS C, KALLERGI E, et al. NMDAR-dependent long-term depression is associated with increased short term plasticity through autophagy mediated loss of PSD-95. Nat Commun. 2021;12(1):2849.
[60] YANG Y, CHEN J, CHEN X, et al. Endophilin A1 drives acute structural plasticity of dendritic spines in response to Ca2+/calmodulin.J Cell Biol. 2021;220(6):e202007172. |