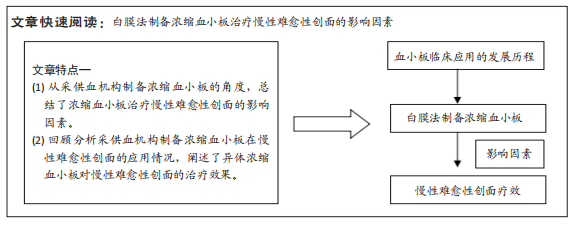
[1] RAVES N, PHILLIPS CJ, HARDING K. A narrative review of the epidemiology and economics of chronic wounds. Br J Dermatol. 2022;187(2):141-148.
[2] TIAN J, LEI XX, XUAN L, et al. The effects of aging, diabetes mellitus, and antiplatelet drugs on growth factors and anti-aging proteins in platelet-rich plasma. Platelets. 2019;30(6):773-792.
[3] SETHI D, MARTIN KE, SHROTRIYA S, et al. Systematic literature review evaluating evidence and mechanisms of action for platelet-rich plasma as an antibacterial agent. J Cardiothorac Surg. 2021;16(1):277.
[4] ANITUA E, ZALDUENDO M, TROYA M, et al. Platelet-Rich Plasma as an Alternative to Xenogeneic Sera in Cell-Based Therapies: A Need for Standardization. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(12):6552.
[5] MASTROGIACOMO M, NARDINI M, COLLINA MC, et al. Innovative Cell and Platelet Rich Plasma Therapies for Diabetic Foot Ulcer Treatment: The Allogeneic Approach. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022;10:869408.
[6] HAJDU SI. A note from history: The discovery of blood cells. Ann Clin Lab Sci. 2003;33(2):237-238.
[7] STASSEN JM, NYSTRÖM A. A historical review of hemostasis, thrombosis, and antithrombotic therapy. Ann Plast Surg. 1997;39(3):317-329.
[8] ION H, CARMEN D, LILIANA HL, et al. Platelet derivatives with dental medicine applications. J Oral Rehabil. 2020;12:142-152.
[9] MOŚCICKA P, PRZYLIPIAK A. History of autologous platelet-rich plasma: A short review. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2021;20(9):2712-2714.
[10] KHAN FA, PARAYARUTHOTTAM P, ROSHAN G, et al. Platelets and Their Pathways in Dentistry: Systematic Review. J Int Soc Prev Community Dent. 2017;7(Suppl 2):S55-S60.
[11] SÁNCHEZ-GONZÁLEZ DJ, MÉNDEZ-BOLAINA E, TREJO-BAHENA NI. Platelet-rich plasma peptides: key for regeneration. Int J Pept. 2012; 2012:532519.
[12] GHANAATI S, HERRERA-VIZCAINO C, AL-MAAWI S, et al. Fifteen Years of Platelet Rich Fibrin in Dentistry and Oromaxillofacial Surgery: How High is the Level of Scientific Evidence? J Oral Implantol. 2018;44(6):471-492.
[13] 单桂秋,林放,张爽,等.血小板拓展应用研究的认识与思考[J].中国输血杂志,2016,29(6):555-557.
[14] 杨彪,刘克,李世超,等.富血小板血浆在慢性难愈性创面中的研究进展[J].实用骨科杂志,2019,25(4):338-343.
[15] QIAN LW, FOURCAUDOT AB, YAMANE K, et al. Exacerbated and prolonged inflammation impairs wound healing and increases scarring. Wound Repair Regen. 2016;24(1):26-34.
[16] AKBARZADEH S, MCKENZIE MB, RAHMAN MM, et al. Allogeneic Platelet-Rich Plasma: Is It Safe and Effective for Wound Repair? Eur Surg Res. 2021; 62(1):1-9.
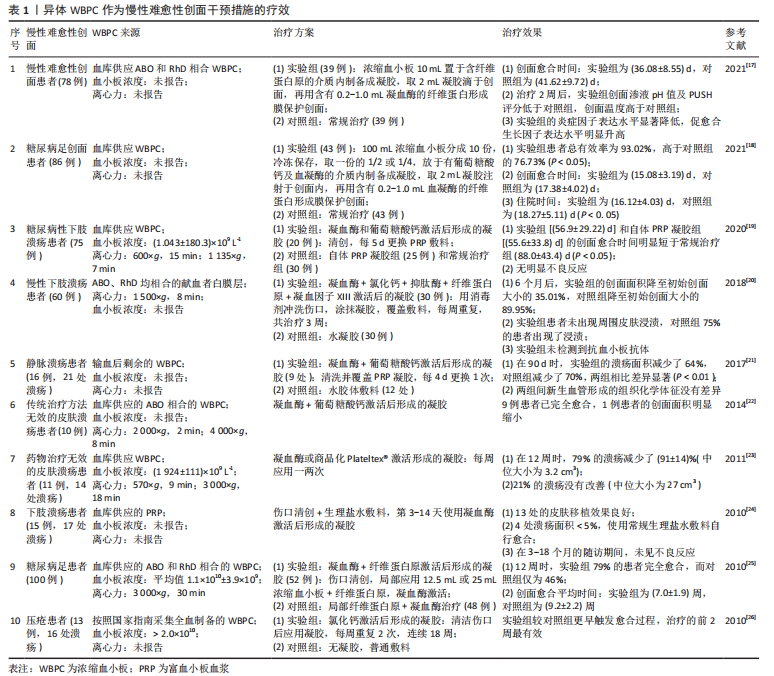
[17] 刘鸿雁,黄文炼,李竺憬,等.同种异体富血小板血浆凝胶治疗慢性难愈性创面的疗效分析[J].中国美容整形外科杂志,2021,32(12):741-744,755.
[18] 刘鸿雁,黄文炼,李竺憬,等.同种异体富血小板对糖尿病足创面的愈合再生情况分析[J].中国输血杂志,2021,34(4):358-361.
[19] HE M, GUO X, LI T, et al. Comparison of Allogeneic Platelet-rich Plasma With Autologous Platelet-rich Plasma for the Treatment of Diabetic Lower Extremity Ulcers. Cell Transplant. 2020;29:963689720931428.
[20] SEMENIČ D, CIRMAN T, ROŽMAN P, et al. Regeneration of chronic wounds with allogeneic platelet gel versus hydrogel treatment: a prospective study. Acta Clin Croat. 2018;57(3):434-442.
[21] OLIVEIRA MG, ABBADE LPF, MIOT HA, et al. Pilot study of homologous platelet gel in venous ulcers. An Bras Dermatol. 2017;92(4):499-504.
[22] ASADI M, ALAMDARI DH, RAHIMI HR, et al. Treatment of life-threatening wounds with a combination of allogenic platelet-rich plasma, fibrin glue and collagen matrix, and a literature review. Exp Ther Med. 2014;8(2): 423-429.
[23] GREPPI N, MAZZUCCO L, GALETTI G, et al. Treatment of recalcitrant ulcers with allogeneic platelet gel from pooled platelets in aged hypomobile patients. Biologicals. 2011;39(2):73-80.
[24] CHEN TM, TSAI JC, BURNOUF T. A novel technique combining platelet gel, skin graft, and fibrin glue for healing recalcitrant lower extremity ulcers. Dermatol Surg. 2010;36(4):453-460.
[25] JEONG SH, HAN SK, KIM WK. Treatment of diabetic foot ulcers using a blood bank platelet concentrate. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2010;125(3):944-952.
[26] SCEVOLA S, NICOLETTI G, BRENTA F, et al. Allogenic platelet gel in the treatment of pressure sores: a pilot study. Int Wound J. 2010;7(3):184-190.
[27] MURPHY S. Platelets from pooled buffy coats: an update. Transfusion. 2005;45(4):634-639.
[28] PHILIP J, SAMANTHA K, CHATTERJEE T, et al. Evaluation of Random Donor Platelets Produced from Buffy Coat Stored for 24 h at Ambient Temperature: Should This be Implemented in India? Indian J Hematol Blood Transfus. 2015;31(2):264-268.
[29] 傅雪梅,洪缨,李荫,等.中国血液成分制备现状与展望[A]//载何涛,耿鸿武,付涌水. 输血服务蓝皮书:中国输血行业发展报告(2019)[M].武汉:社会科学文献出版社,2019:94-108.
[30] VAN DER MEER PF, CANCELAS JA, VASSALLO RR, et al. Evaluation of the overnight hold of whole blood at room temperature, before component processing: platelets (PLTs) from PLT-rich plasma. Transfusion. 2011;51 Suppl 1:45S-49S.
[31] LU FQ, KANG W, PENG Y, et al. Characterization of blood components separated from donated whole blood after an overnight holding at room temperature with the buffy coat method. Transfusion. 2011;51(10):2199-2207.
[32] 周静.全血采集后即时制备与贮存过夜后制备的浓缩血小板质量比较[J].中国输血杂志,2020,33(5):526-528.
[33] 刘凤君,蒋秋容,王泽蓉,等.白膜放置时间对制备手工浓缩血小板质量的影响[J].中国输血杂志,2012,26(2):120-122.
[34] 卢发强,康炜,彭昱,等.全血(22±2)℃保存24 h对白膜法分离血小板体外激活和血浆凝血因子活性的影响[J].中国输血杂志,2012,26(6): 551-553.
[35] 连晓征,陈玉燕,陈惠民.不同血小板含量血液在不同静置时间对浓缩血小板第2次分离回收率影响分析[J].医学理论与实践,2019,32(9): 1408-1410.
[36] 陈永婷.室温静置对制备血小板方法的影响[J].中国输血杂志,2019, 32(9):887-889.
[37] 徐国胜,黄可君,范斌,等.白膜袋放置不同时间制备手工浓缩血小板比较[J].深圳中西医结合杂志,2017,27(10):125-126.
[38] 刁荣华,王泽蓉,王世春,等.不同方式放置白膜制备浓缩血小板质量指标比较[J].临床输血与检验,2019,21(1):24-27.
[39] TAMBELLA AM, ATTILI AR, DUPRÉ G, et al. Platelet-rich plasma to treat experimentally-induced skin wounds in animals: A systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS One. 2018;13(1):e0191093.
[40] MURPHY S, HEATON WA, REBULLA P. Platelet production in the Old World--and the New. Transfusion. 1996;36(8):751-754.
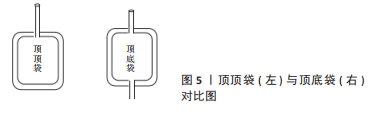
[41] CERELLI E, NOCERA M, DI BARTOLOMEO E, et al. Effect of adhesive properties of buffy coat on the quality of blood components produced with Top & Top and Top & Bottom bags. Blood Transfus. 2015;13(2):265-273.
[42] 罗曼华,康美艳,李津,等.改良白膜层离心装罐方法提高浓缩血小板质量的效果观察[J].中国输血杂志,2023,36(2):193-195.
[43] 熊志高,刘昕晨,杨小罗,等.新改良白膜法制备浓缩血小板的应用效果探讨[J].中国临床新医学,2022,15(8):717-721.
[44] 王承琳,王丽鸽,崔靖怡,等.浓缩血小板离心参数与装罐方法的标准化研究[J].中国输血杂志,2020,33(9):972-974.
[45] 王泽蓉,刁荣华,王世春,等.六联采血袋制备浓缩血小板制剂的质量分析[J].中国输血杂志,2012(S1):50.
[46] 肖达玲,杨坤,韦家寿,等.调整优化采血联袋后制备浓缩血小板的质量分析[J].中国输血杂志,2021,34(5):535-537.
[47] 余凤秀,周载鑫,沈秋,等.两种血袋白膜法制备浓缩血小板质量研究[J].实用临床医药杂志,2020,24(22):87-89,92.
[48] 阎兵,邹元国,谈维.应用顶底袋保留白膜法制备浓缩血小板[J].临床输血与检验,2014,16(2):182-185.
[49] BHARDWAJ G, TIWARI AK, AGGARWAL G, et al. Evaluation of quality matrix when practice changed from triple bags to quadruple (top and bottom) bags: In vitro analysis of blood components! Asian J Transfus Sci. 2021;15(1):30-36.
[50] LOTENS A, NAJDOVSKI T, CELLIER N, et al. New approach to ‘top-and-bottom’ whole blood separation using the multiunit TACSI WB system: quality of blood components. Vox Sang. 2014;107(3):261-268.
[51] PAPAIT A, CANCEDDA R, MASTROGIACOMO M, et al. Allogeneic platelet-rich plasma affects monocyte differentiation to dendritic cells causing an anti-inflammatory microenvironment, putatively fostering wound healing. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2018;12(1):30-43. |