1.1 设计 细胞学实验,相关数据的分析采用t检验和单因素方差分析。
1.2 时间及地点 实验于2021年3-9月在河南省中医院河南中医药大学实验动物中心完成。
1.3 材料
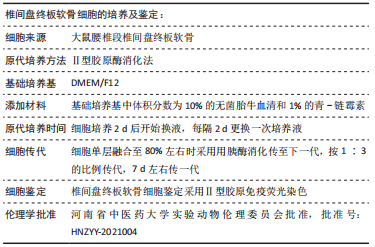
1.3.1 实验动物 选择50只清洁级SD雄性大鼠(1月龄),体质量(100±15) g,常规饲养,购自郑州大学实验动物中心,许可证号:SCXK(豫)2020-0008。实验过程遵循了国际兽医学编辑协会《关于动物伦理与福利的作者指南共识》和本地及国家法规。所有实验操作均经过河南省中医药大学实验动物伦理委员会批准(批准号:HNZYY-2021004)。
1.3.2 主要试剂与仪器 DMEM/F12培养基、青霉素-链霉素溶液、胎牛血清、0.25%胰蛋白酶消化液(美国gibco公司,货号:11320033,15140122,42G9150K,25200-056);H2O2购于上海威奥(WH1028-3);NC siRNA和Parkin siRNA由广州锐博生物合成;Parkin腺病毒过表达载体购自于汉恒生物;二甲基亚砜(德国WAK CHEMIE公司,货号:WAK-DMSO-50);Trizol、Lipo 3000 转染试剂(美国invitrogen公司,货号:257408,2209775),Ⅱ型胶原酶(广州赛国生物科技有限公司,货号:EZ4360324);CCK-8试剂盒、乳酸脱氢酶细胞毒性检测试剂盒、ATP检测试剂盒、超氧化物歧化酶(superoxide dismutase,SOD)检测试剂盒、脂质氧化丙二醛检测试剂盒、线粒体膜电位检测试剂盒(JC-1)、Annexin V-PE细胞凋亡检测试剂盒(上海碧云天生物技术有限公司,货号:C0037,C0016,S0026,S0101S,S0131S,C2006,C1065M);过氧化氢酶活性检测试剂盒(BC0205)、Ⅱ型胶原抗体(K009364P)购自北京索莱宝科技有限公司;Parkin、LC3、p62、GAPDH(美国
Cell Signaling Technology 公司,货号:4211T,3868T,48768T,5879S);生物素标记山羊抗兔免疫球蛋白IgG,生物素标记山羊抗小鼠 IgG(中国上海碧云天生物技术有限公司,货号:A0277,A0286)。
细胞培养箱(REVCO,RCO-3000-5),酶标仪(Molecular Devices,Spectra MaxM3),低温高速离心机(Eppdorf),CytoFLEX型流式细胞仪(美国贝克曼库尔特公司),荧光显微镜(Olympus,型号:BX41),基础电泳仪,转膜仪(美国 Bio-Rad 公司,型号:164-5050,170-3930)。
1.4 方法
1.4.1 药物的制备 黄芪桂枝五物汤中药饮片由河南省中医院提供。黄芪 9 g,芍药 9 g,桂枝 9 g,生姜 18 g,大枣 12枚加入8倍纯水浸泡,2 h后煎煮2次,每次30 min,将2次煎煮所得药液过滤并混合后浓缩至1 mL原液=2 g生药的水提物。将体积分数95%的乙醇缓慢加入到上述制备的水提物中,经过搅拌后进行密封,放置于4 ℃的冰箱中静置24 h。所得到混合物经过抽滤后获得水提醇沉物(1 mL水提醇沉物=2 g生药)。通过旋蒸的方式将水提醇沉物进行浓度设置(1 mL水提醇沉物=5 g生药),置于-80 ℃保存。使用时将其用完全培养基稀释至6.25,12.5,25 mg/mL。
1.4.2 大鼠椎间盘终板软骨细胞的分离和培养 参考文献[12]的方法分离出大鼠椎间盘终板软骨细胞。采用10%的戊巴比妥40 mg/kg腹腔注射麻醉大鼠,脊柱脱臼法处死,以体积分数75%的乙醇消毒液擦拭全身,无菌操作下取出大鼠腰椎段,剥离附着组织,仅保留椎间盘终板软骨,无菌PBS洗涤后剪碎研磨,0.25%胰蛋白酶消化液消化30 min,后加入3 mLⅡ型胶原酶消化2 h。待细胞游离状态时收集悬液,离心10 min(1 000 r/min,离心半径5 cm),去上清液,PBS洗涤后加入DMEM/F12完全培养基重悬为单细胞悬液,接种于培养皿中,于含有体积分数5%CO2的培养箱(37 ℃)中进行培养,第2天换液,此后每隔2 d换1次液,取长至80%以上的P3代软骨细胞进行实验。
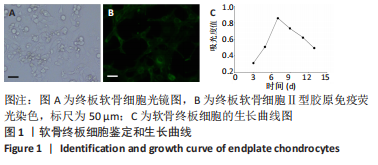
1.4.3 终板软骨细胞鉴定 细胞贴壁后,移去培养液后加入40 g/L多聚甲醛,在室温条件固定20 min,之后加入0.2%的Triton X-100进行透化15 min。透化完成后加入3%的BSA进行封闭(30 min),再加入Ⅱ型胶原一抗(1∶100),在4 ℃下过夜。最后加入荧光标记的二抗(1∶200),避光孵育1 h后在荧光显微镜下观察拍照。
1.4.4 分组及处理 ①为了研究黄芪桂枝五物汤对线粒体损伤、氧化应激和线粒体自噬蛋白表达的影响,将细胞分为正常组、模型组和黄芪桂枝五物汤低、中、高剂量组。其中黄芪桂枝五物汤各剂量组分别用含低(6.25 mg/mL)、中(12.5 mg/mL)、高(25 mg/mL)剂量黄芪桂枝五物汤的培养液培养细胞24 h,而正常组和模型组不添加药物。之后除正常组外,模型组和黄芪桂枝五物汤各剂量组中添加400 μmol/L的H2O2继续处理细胞2 h。②为了研究Parkin介导的线粒体自噬在调控细胞氧化应激和线粒体损伤中的作用,将细胞接种于6孔板,每孔细胞数为1×106个。待细胞生长至60%时按照说明书转染相对应的siRNA,24 h后收集细胞。将细胞分为NC siRNA组、NC siRNA+H2O2组、Parkin siRNA组、Parkin siRNA+H2O2组,继续用400 μmol/L 的H2O2处理2 h。NC siRNA的序列为:5’-UUC UGC GAA CGU GUC ACG UTT-3’,Parkin siRNA的序列为:5’-CCA ACU CCC UGA UUA AAG ATT-3’。
1.5 主要观察指标
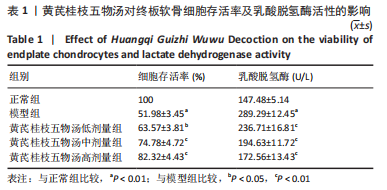
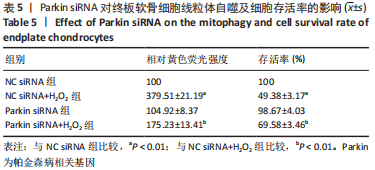
1.5.1 CCK-8法检测细胞存活率 将椎间盘终板软骨细胞以1×104个/孔的密度接种到96孔板中,按照1.4.4中的分组和方法进行相应处理,每组设置6个复孔,重复3次。处理完成后培养孔中加入CCK-8溶液10 μL,继续孵育2 h。使用酶标仪检测细胞在450 nm处的吸光度值。
1.5.2 乳酸脱氢酶活性的检测 将细胞按照1×106个/孔的密度接种于细胞6孔板中,分组及处理方法见1.4.4中①。处理完成后将椎间盘终板软骨细胞于冰上裂解后离心提取上清(4 ℃,12 000 r/min,离心5 min),根据乳酸脱氢酶测定试剂盒说明书进行操作,每组设3个复孔,试剂混匀后静置3 min,用酶标仪1 cm光径在440 nm处测定吸光度值。
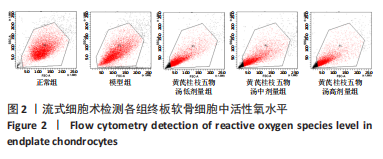
1.5.3 流式细胞术检测活性氧水平 将细胞接种于细胞12孔板中,椎间盘终板软骨细胞的分组及处理见1.4.4,无菌PBS洗涤2次,加入胰酶消化细胞。收集细胞再次使用无菌PBS洗涤,离心5 min(1 000 r/min,离心半径13.5 cm),丢弃上清液,加入稀释后的活性氧荧光探针染剂重复吹吸重悬,细胞培养箱内培养(每隔5 min吹吸重新1次),30 min后转移至FACS管中,立即放入流式细胞仪测量并进行分析。
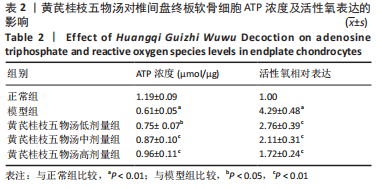
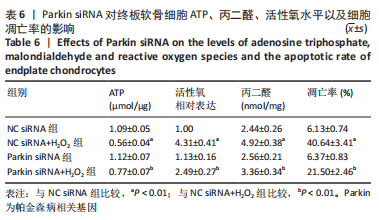
1.5.4 ATP含量的检测 将细胞接种于12孔板中(1×105个/孔)进行培养,具体分组见1.4.4,于冰上裂解后离心提取上清(4 ℃,12 000 r/min,5 min),根据试剂盒说明书进行操作,每个样品做3个复孔,随后用化学发光仪测定相对光单位值并分析ATP浓度。
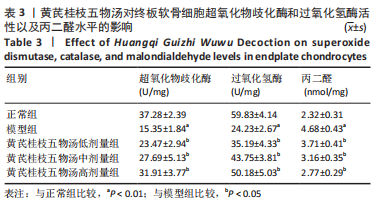
1.5.5 SOD和过氧化氢酶活性的检测 将细胞接种于12孔板中(1×105个/孔)进行培养,具体分组见1.4.4中①,于冰上裂解后离心提取上清(4 ℃,12 000 r/min,5 min),根据试剂盒说明书进行操作,每个样品做3个复孔,随后用酶标仪测定SOD和过氧化氢酶的吸光度值。
1.5.6 丙二醛含量的测定 将细胞接种于12孔板中(1×105个/孔)进行培养,椎间盘终板软骨细胞分组见14.4,操作步骤严格按照试剂盒的说明书进行。酶标仪在532 nm条件下来测定样品的吸光度值。
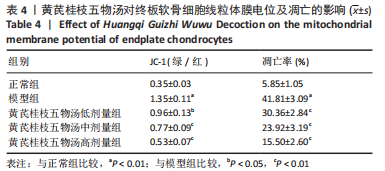
1.5.7 JC-1荧光探针检测线粒体膜电位 将细胞以1×105个/孔接种于12孔板培养板中,分组见1.4.4中①,经处理后丢弃培养基,加入JC-1荧光探针染液(二甲基亚砜配制,质量浓度1 g/mL),于37 ℃培养箱中放置20 min,后使用无菌PBS洗涤细胞3次,使用倒置荧光显微镜观察,并用Image J软件分析平均荧光强度。平均荧光强度=吸光度总和/荧光面积,线粒体去极化比例采用红绿荧光平均强度比值衡量。
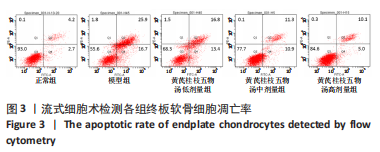
1.5.8 流式凋亡双染法检测细胞凋亡 以1×105个/孔接种于12孔板培养皿中,分组见1.4.4中①。处理完成后将各组细胞分别消化离心,制备单细胞悬浮液,加入Annexin-FITC,混合均匀后再加入PI混匀。反应10 min(37 ℃,避光)后加入Binding Buffer,吹打细胞悬浮液,过滤后使用流式细胞仪检测细胞凋亡情况。
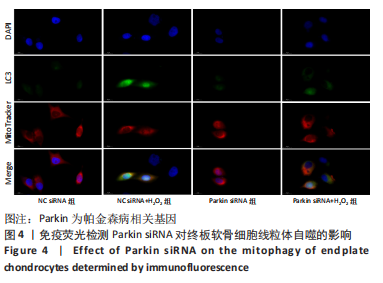
1.5.9 细胞线粒体自噬 将细胞按照2×105个/孔的密度接种于细胞6孔板中,分组见1.4.4中②,将无菌玻片裁剪后于浸泡于浓硫酸中过夜,纯水洗涤并烘干消毒,加入胰酶消化后计数,待细胞爬片后加入LC3抗体(1∶50)和TOMM20抗体(1∶100),4 ℃孵育过夜,染色后加入相应的二抗(1∶200),室温避光孵育1 h。使用荧光显微镜截取图像。使用Image-J软件测量每个视野中黄色(LC3B和TOMM20覆盖层)的相对荧光强度来评估线粒体自噬。
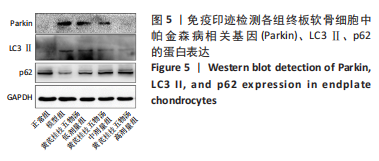
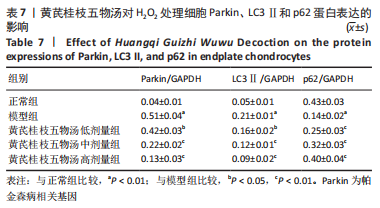
1.5.10 免疫印迹法检测相关蛋白表达 将细胞接种于12孔板中(1×105个/孔)进行培养,具体分组见1.4.4中①。处理完成后细胞内加RIPA裂解液于冰上裂解,100 ℃水浴锅内沸腾10 min,离心提取蛋白上清液。蛋白样品经凝胶电泳后转移至PVDF膜,5%脱脂奶粉封闭2 h(4 ℃),Parkin、LC3Ⅱ、p62和GAPDH抗体分别按1∶1 000、1∶2 000、1∶2 000、1∶5 000进行稀释,将转移后的PVDF膜放入并在4 ℃环境下孵育过夜,洗涤3次加入二抗室温孵育2 h(1∶1 000),放入曝光仪中PVDF膜滴加ECL显色液检测各组蛋白条带的吸光度值,Image J软件分析各组条带灰度值,记录蛋白表达水平。
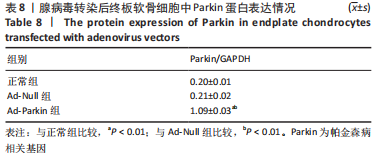
1.5.11 Parkin腺病毒过表达转染及处理 将细胞接种于6孔板中(密度为1×106个/孔),待细胞生长至50%-60%时,将腺病毒空载(pAd-Null)和Parkin腺病毒载体(pAd-Parkin)分别加入到细胞中(病毒滴度:1.47×1013 PFU/L)。加入DMEM/F12(不含血清)的培养基过夜培养,之后更换完全培养基继续培养48 h。免疫印迹检测转染效率。
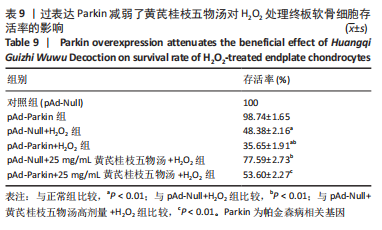
将细胞接种于96孔板(1×104个/孔)中,分别用pAd-Null和pAd-Parkin感染终板软骨细胞,其中黄芪桂枝五物汤和H2O2处理的剂量和时间见1.4.4。实验分为6组:即对照组(pAd-Null)、pAd-Parkin组、pAd-Null+H2O2组、pAd-Parkin+H2O2组、pAd-Null+25 mg/mL黄芪桂枝五物汤+ H2O2组、pAd-Parkin +25 mg/mL黄芪桂枝五物汤+ H2O2组。处理完成后进行CCK-8检测。
1.6 统计学分析 数据统计分析采用SPSS 21.0软件进行,所得结果用x±s表示。对于多组数据间的比较采用单因素方差分析;两两组间比较,对于方差齐的运用LSD法,而方差不齐的则使用Dunnett法。以P < 0.05为差异有显著性意义。文章统计学方法已经由河南省中医药大学的生物统计学专家审核。