中国组织工程研究 ›› 2023, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (28): 4462-4467.doi: 10.12307/2023.576
• 组织构建实验造模 experimental modeling in tissue construction • 上一篇 下一篇
七十味珍珠丸干预脑梗死模型大鼠软脑膜微循环及胶质瘢痕的变化
马 辉,孙正启,李岩松
- 西藏民族大学医学院人体形态学教研室,陕西省咸阳市 712000
Effect of Ratnasampil on pia microcirculation and glial scar in a rat model of cerebral infarction
Ma Hui, Sun Zhengqi, Li Yansong
- Department of Human Morphology, Xizang Minzu University School of Medicine, Xianyang 712000, Shaanxi Province, China
摘要:
文题释义:
七十味珍珠丸:是藏药的一种,由珍珠、檀香、降香、九眼石、西红花、牛黄等组成,具有镇静安神、通络活血、开窍醒脑的作用。该药最早记载于藏医经典著作《四部医典》,主要用于治疗白脉病、癫痫、脑溢血、神经性障碍等疾病,目前,该药的药理研究多集中于抗惊厥、改善血液流变学和血流动力学。该药药效温和,不良反应较少。软脑膜微循环:微循环障碍主要表现为微血管结构、功能、微血流异常等。大部分的脑血管疾病均与软脑膜微循环异常联系密切。脑微循环具有维持脑中枢调节功能的作用,脑部微血管阻塞等会引起脑供血不足,引起一系列脑功能障碍。
背景:改善脑梗死微脑膜循环、抑制瘢痕形成可有效治疗脑梗死疾病,因此寻找安全有效的药物来改善脑微循环及瘢痕形成至关重要。
目的:探讨七十味珍珠丸对脑梗死大鼠软脑膜微循环、Janus激酶2(Janus Kinase2,JAK2)/转录激活因子3(signal transducer and activator transcription3,STAT3)蛋白表达及胶质瘢痕的影响。
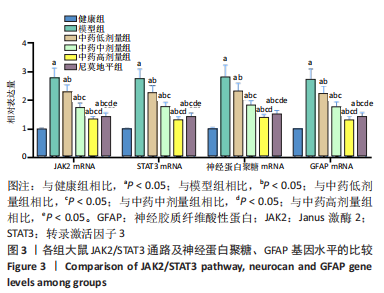
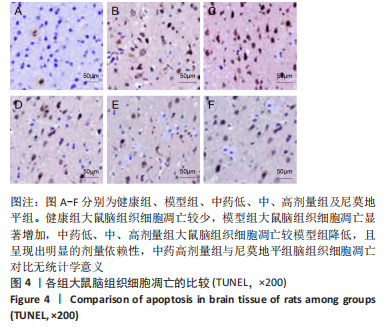
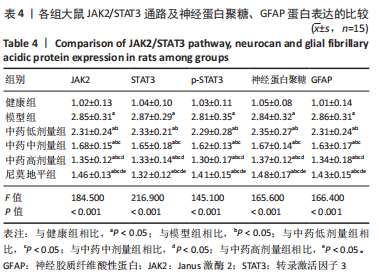
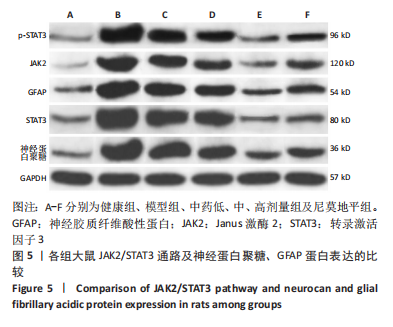
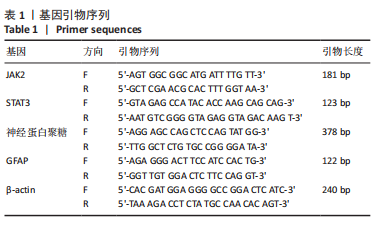
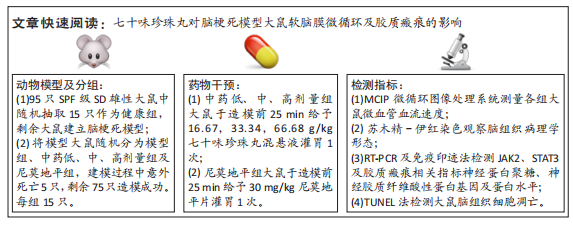
方法:于95只雄性SD大鼠中随机抽取15只作为健康组,剩余大鼠建立脑梗死模型,将模型大鼠随机分为模型组、中药低、中、高剂量组以及尼莫地平组,在建模过程中意外死亡5只,剩余75只建模成功,每组15只。中药低、中、高剂量组分别于造模前25 min给予16.67,33.34,66.68 g/kg七十味珍珠丸混悬液灌胃1次,尼莫地平组于造模前25 min给予 30 mg/kg尼莫地平片灌胃1次。建模后运用MCIP微循环图像处理系统检测脑血流速度,苏木精-伊红染色观察脑组织病理学形态,RT-PCR检测JAK2、STAT3、神经蛋白聚糖、胶质纤维酸性蛋白基因水平,TUNEL技术检测脑组织细胞凋亡情况,免疫印迹检测JAK2、STAT3、p-STAT3、神经蛋白聚糖、胶质纤维酸性蛋白的蛋白表达。
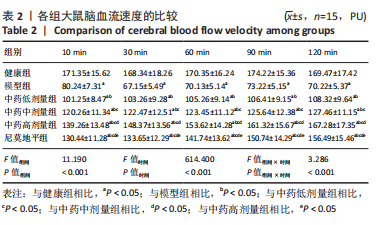
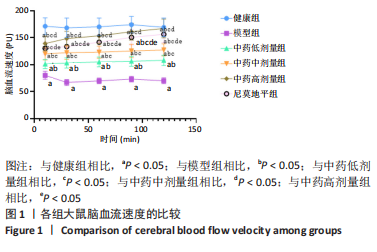
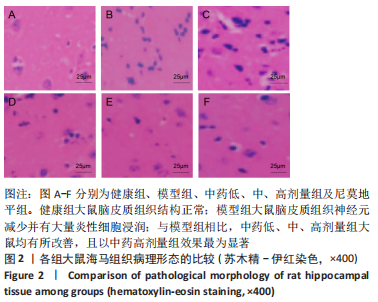
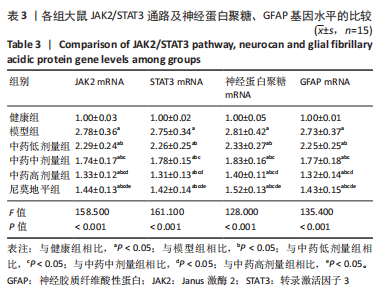
结果与结论:①与健康组相比,模型组不同时间点脑血流速度降低,JAK2、STAT3、p-STAT3、神经蛋白聚糖、胶质纤维酸性蛋白、神经元细胞凋亡率升高(P < 0.05);②与模型组相比,中药低剂量组不同时间点脑血流速度升高,JAK2、STAT3、磷酸化转录激活因子3、神经蛋白聚糖、胶质纤维酸性蛋白、神经元细胞凋亡率降低(P < 0.05);③与中药中剂量组相比,中药高剂量组与尼莫地平组不同时间点脑血流速度升高,JAK2、STAT3、p-STAT3、神经蛋白聚糖、胶质纤维酸性蛋白、神经元细胞凋亡率降低(P < 0.05);④与中药高剂量组相比,尼莫地平组不同时间点脑血流速度降低,JAK2、STAT3、p-STAT3、神经蛋白聚糖、胶质纤维酸性蛋白、神经元细胞凋亡率升高(P < 0.05);⑤健康组大鼠脑皮质组织结构正常;模型组脑皮质组织神经元减少,少数存活的神经元固缩,并有大量炎性细胞浸润;与模型组相比,中药低、中、高剂量组及尼莫地平组均有所改善,且以中药高剂量组效果显著;⑥提示七十味珍珠丸可能通过抑制胶质瘢痕标志蛋白神经蛋白聚糖、神经胶质纤维酸性蛋白水平影响胶质瘢痕的形成,还可改善脑梗死大鼠软脑膜微循环,并通过抑制JAK2/STAT3通路的激活,减少脑组织细胞的凋亡,从而发挥脑保护的作用。
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-6927-3013(马辉)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
中图分类号: