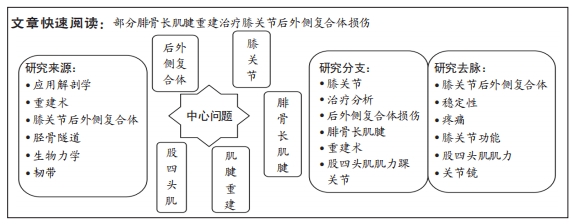
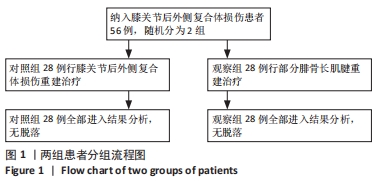
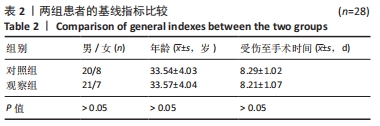
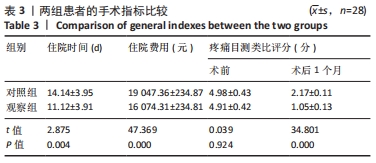
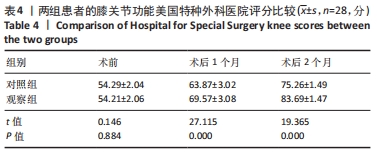
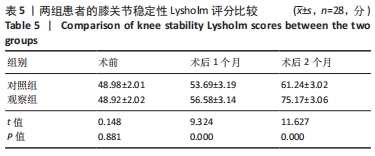
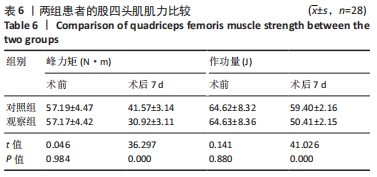
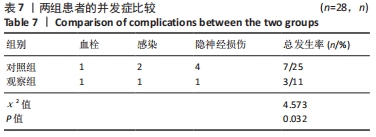
[1] 代朋乙,黄昌林.关节镜下一期修复重建膝关节多发韧带损伤的疗效观察[J]. 解放军医学杂志,2019,44(1):57-62.
[2] 杨洋,冯青,李冕,等. 膝关节多韧带损伤与胫骨平台骨折分型系统的相关性研究[J]. 中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2020,17(2):140-146.
[3] 周鹏,刘俊才,邓翔天,等. 改良Laprade术式重建膝关节后外侧复合体联合关节镜下重建后交叉韧带的早期疗效分析[J]. 华西医学,2019,10(78):624-628.
[4] 仲鹤鹤,孙鹏鹏,桑鹏,等. 模拟重建膝关节后外侧复合体核心韧带后膝关节稳定性评估[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2021,10(6):1241-1243.
[5] 王辉,邹宏,沈建平,等. 膝关节对角线损伤中后外侧复合体损伤一期手术疗效观察[J]. 中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2019,15(10):654-658.
[6] 周利,唐吉平,林春阳,等. 微创接骨术配合“续骨活血汤”治疗胫骨平台前内侧塌陷骨折合并膝关节后外侧复合体损伤的疗效分析[J]. 中国中西医结合外科杂志,2020,26(2):130-135.
[7] 刘仕杰,史福东,左金增. 双侧腓骨长肌腱与双侧腘绳肌腱重建膝关节前后交叉韧带的近期疗效观察[J]. 重庆医学,2019,48(2):158-160.
[8] 余浩,邓晚秋,桑鹏,等. 关节镜下自体同侧腓骨长肌腱重建膝关节前交叉韧带[J]. 中国修复重建外科杂志,2020,10(7):843-847.
[9] 张新伟,陶日东,凌耀光,等. 自体腓骨长肌腱重建膝前交叉韧带的疗效[J]. 中国临床研究,2019,32(2):223-225.
[10] WEILER A, FROSCH KH, GWINNER C, et al. The Posterolateral Instability Score (PoLIS) of the knee joint: a guideline for standardized documentation, classification, and surgical decision-making. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2020;14(3):2014-2018.
[11] 王怀东,张富军,裴海波,等. 关节镜下单束和双束重建前交叉韧带对膝关节退变及膝关节稳定性的影响研究[J]. 陕西医学杂志, 2019,48(5):108-111.
[12] 周鹏.改良Laprade术式重建膝关节后外侧复合体联合关节镜下重建后交叉韧带的早期疗效分析[J]. 华西医学,2019,12(47):621-625.
[13] 李岳,张辉,冯华. 腘肌腱再张力化手术和重建术治疗急性膝关节后外旋转不稳定的临床疗效[J]. 中华骨科杂志,2020,40(7):417-423.
[14] MENZDORF L, DRENCK T, AKOTO R, et al. Clinical results after surgical treatment of posterolateral tibial plateau fractures (“apple bite fracture”) in combination with ACL injuries. Eur J Trauma Emerg Surg. 2020;46(8):53-56.
[15] 李佳岱,牛玉军. 磁共振检查对膝关节前外侧韧带与外侧稳定结构损伤的相关性分析[J]. 陕西医学杂志,2020,49(9):71-75.
[16] 张钟,张凯博,毛贝尼,等. 膝关节前外侧韧带的研究进展[J]. 中国修复重建外科杂志,2020,34(5):108-115.
[17] 郝林杰,马涛,宋伟,等. 膝外翻患者外侧入路膝关节置换并髌骨置换对髌骨轨迹及膝前痛的影响[J]. 中国骨与关节杂志,2020, 10(2):88-93.
[18] 饶根云,谢友军, 雷祥进. 自体腓骨长肌腱膝前交叉韧带单束重建的近期疗效观察[J]. 中国骨与关节损伤杂志, 2019, 34(4):419-421.
[19] 陈军,鄂刚,马震胜,等. 膝关节前交叉韧带重建术后恢复不良患者应用复元活血汤对临床效果,膝关节疼痛和膝关节功能的影响[J]. 临床误诊误治,2020,33(3):68-72.
[20] 石伟发,郭志民,邓辉云,等. 腓骨长肌腱和腘绳肌腱重建前交叉韧带的系统评价[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2020,24(5):161-170.
[21] 王洪江,连纪文,翟永喜,等. 部分腓骨长肌腱重建治疗膝关节后外侧复合体损伤[J]. 创伤外科杂志,2021,23(3):209-211.
[22] 郭文骏,刘毅. 膝关节后外侧复合体损伤机制及治疗的研究进展[J]. 山东医药,2016,56(37):107-109.
[23] 周利,唐吉平,林春阳,等. 微创接骨术配合“续骨活血汤”治疗胫骨平台前内侧塌陷骨折合并膝关节后外侧复合体损伤的疗效分析[J]. 中国中西医结合外科杂志,2020,26(2):338-343.
[24] 陈杰波,徐才祺,燕晓宇,等. 膝关节前外侧复合体及其损伤重建研究进展[J]. 中华骨与关节外科杂志,2020,13(7):612-616.
[25] 叶梓鹏,徐俊杰,董士奎,等. 膝关节后外侧结构损伤研究进展[J]. 国际骨科学杂志,2020,41(5):275-279.
[26] 兰敏,聂思,廖新根,等. 早期关节镜辅助一期重建膝关节多韧带损伤的重要性[J]. 中国内镜杂志,2020,26(3):13-16.
[27] 万宏来. 不同时机膝关节镜下前交叉韧带重建术治疗前交叉韧带损伤临床效果比较[J]. 临床军医杂志,2020,48(12):1475-1476.
[28] 邵嘉艺,张家豪,刘平,等. 传统单束前交叉韧带重建手术中钻制胫骨骨道对外侧半月板前角附着部损伤的解剖学研究[J]. 中国运动医学杂志,2020,39(6):470-475.
[29] 李岳,张辉,冯华. 腘肌腱再张力化手术和重建术治疗急性膝关节后外旋转不稳定的临床疗效[J]. 中华骨科杂志,2020,40(7):417-423.
[30] 郑峒,冯华,张辉,等. 前十字韧带重建术中修复外侧半月板后根部损伤的早期疗效[J]. 中华骨科杂志,2020,40(7):424-432.
[31] NASU H, NIMURA A, YAMAGUCHI K, et al. Morphology of the anterolateral ligament: a complex of fibrous tissues spread to the anterolateral aspect of the knee joint. Anat Sci Int. 2020;95(4):324-329.
[32] 徐慰凯,肖雁萍,李泽龙,等. 关节镜下一期重建修复膝关节多韧带损伤[J]. 临床骨科杂志,2020,23(2):212.
[33] 臧业峰,赵希春,王俐滢,等. 高压氧联合富血小板血浆应用于膝关节前交叉韧带重建术的疗效观察[J]. 中华航海医学与高气压医学杂志,2020,27(1):60-63.
[34] LANDREAU P, CATTEEUW A, HAMIE F, et al. Anatomic Study and Reanalysis of the Nomenclature of the Anterolateral Complex of the Knee Focusing on the Distal Iliotibial Band. Orthop J Sports Med. 2019; 7(1):621-625.
[35] 李韬,熊燕,张钟,等. 降低膝关节多发韧带损伤脱位致残率的分期分型诊治方法和疗效回顾性分析[J]. 中国骨伤,2020,33(12): 1134-1141.
[36] 姚望,潘剑英,曾春. 保残重建前交叉韧带对膝关节运动学特征的影响[J]. 中华关节外科杂志,2020,14(1):24-32.
[37] 张博,王志为,曲铁兵,等. 初次全膝关节置换术中内侧副韧带损伤的处理及随访研究[J]. 首都医科大学学报,2020,41(4):603-607.
[38] 刘彩龙,吴李闯,叶奕亨,等. 游离腓骨长肌腱联合半腱肌腱单束解剖鞘内重建前十字韧带股骨端损伤[J]. 中华骨科杂志,2020, 40(2):73-81.
[39] 毛云鹤,唐婕晞,李箭,等. 穿骨原位缝合修复前交叉韧带技术在膝关节多发韧带损伤脱位中的应用[J]. 中国修复重建外科杂志, 2020,34(2):190-195.
[40] 张钟,张凯博,毛贝尼,等. 膝关节前外侧韧带的研究进展[J]. 中国修复重建外科杂志,2020,34(5):643-650.
[41] CLEMENT CP, GUBERMAN R, LEE E, et al. Use of Cadaveric Graft in Reconstruction of Peroneus Brevis Rupture and Lateral Ankle Instability- A Case Report. J Am Podiatr Med Assoc. 2019;109(1):1121-1132.
[42] 宋猛,张正,闫理想,等. 关节镜下微骨折术联合自体骨软骨移植治疗膝关节股骨髁大面积软骨损伤[J]. 中国修复重建外科杂志, 2020,34(3):330-334.
[43] 余浩,邓晚秋,桑鹏,等. 关节镜下自体同侧腓骨长肌腱重建膝关节前交叉韧带[J]. 中国修复重建外科杂志,2020,34(7):843-847.
[44] NISHIKAWA D, DUARTE FA, SAITO GH, et al. Minimally Invasive Approach for the Reconstruction of the Peroneal Brevis Tendon Using Semitendinosus Autograft: An Alternative Technique to Avoid Soft Tissue Complications. Tech Foot Ankle Surg. 2020;19(4):55-60.
|