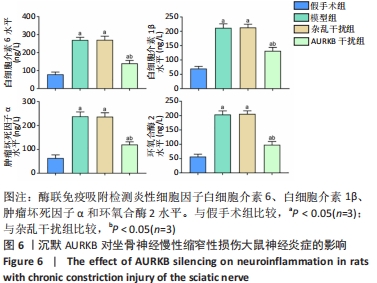
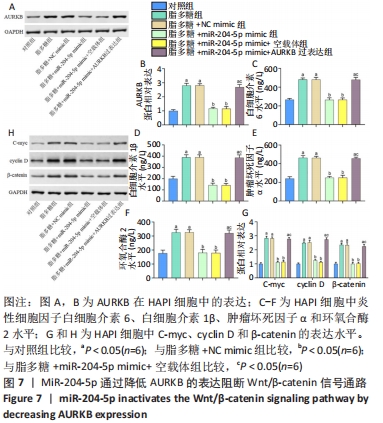
[1] 寿雯婷,张世红,陈忠.钠离子通道在神经病理性疼痛中的作用研究进展[J].浙江大学学报(医学版),2011,40(2):217-221.
[2] VAN HECKE O, AUSTIN SK, KHAN RA, et al. Neuropathic pain in the general population: a systematic review of epidemiological studies. Pain. 2014;155(4):654-662.
[3] LEMA MJ, FOLEY KM, HAUSHEER FH. Types and epidemiology of cancer-related neuropathic pain: the intersection of cancer pain and neuropathic pain. Oncologist. 2010;15 Suppl 2:3-8.
[4] JIANGPAN P, QINGSHENG M, ZHIWEN Y, et al. Emerging Role of microRNA in Neuropathic Pain. Curr Drug Metab. 2016;17(4):336-344.
[5] LÓPEZ-GONZÁLEZ MJ, LANDRY M, FAVEREAUX A. MicroRNA and chronic pain: From mechanisms to therapeutic potential. Pharmacol Ther. 2017;180:1-15.
[6] DAYER CF, LUTHI F, LE CARRÉ J, et al. Differences in the miRNA signatures of chronic musculoskeletal pain patients from neuropathic or nociceptive origins. PLoS One. 2019;14(7):e0219311.
[7] 梁冰,董铁立.miR-19a对慢性压迫性损伤大鼠神经病理性疼痛的影响及其机制[J].第三军医大学学报,2018,40(7):590-595.
[8] ZHANG X, CHEN Q, SHEN J, et al. miR-194 relieve neuropathic pain and prevent neuroinflammation via targeting FOXA1. J Cell Biochem. 2020;121(5-6):3278-3285.
[9] SHEN WS, LI CF, ZHOU ZS, et al. MicroRNA-204 silencing relieves pain of cervical spondylotic radiculopathy by targeting GDNF. Gene Ther. 2020;27(6):254-265.
[10] WANG Y, YE F, HUANG C, et al. Bioinformatic Analysis of Potential Biomarkers for Spinal Cord-injured Patients with Intractable Neuropathic Pain. Clin J Pain. 2018;34(9):825-830.
[11] MOURA DS, CAMPILLO-MARCOS I, VÁZQUEZ-CEDEIRA M, et al. VRK1 and AURKB form a complex that cross inhibit their kinase activity and the phosphorylation of histone H3 in the progression of mitosis. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2018;75(14):2591-2611.
[12] SHEN Y, DING Z, MA S, et al. Targeting aurora kinase B alleviates spinal microgliosis and neuropathic pain in a rat model of peripheral nerve injury. J Neurochem. 2020;152(1):72-91.
[13] 文苾蕊, 张志玲, 陈乃宏. Wnt信号通路在神经病理性疼痛中的作用及机制研究进展[J].药学学报,2020,55(2):35-41.
[14] HU C, ZHAO YT, CUI YB, et al. Wnt/beta-Catenin Signaling Contributes to Vincristine-Induced Neuropathic Pain. Physiol Res. 2020;69(4):701-710.
[15] SHEU ML, CHIANG CY, SU HL, et al. Intrathecal Injection of Dual Zipper Kinase shRNA Alleviating the Neuropathic Pain in a Chronic Constrictive Nerve Injury Model. Int J Mol Sci. 2018;19(8):2421.
[16] GUO D, HU X, ZHANG H, et al. Orientin and neuropathic pain in rats with spinal nerve ligation. Int Immunopharmacol. 2018;58:72-79.
[17] BOUHASSIRA D. Neuropathic pain: Definition, assessment and epidemiology. Rev Neurol (Paris). 2019;175(1-2):16-25.
[18] GRACE PM, STRAND KA, GALER EL, et al. Morphine paradoxically prolongs neuropathic pain in rats by amplifying spinal NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016;113(24): E3441-3450.
[19] NISHIHARA T, TANAKA J, SEKIYA K, et al. Chronic constriction injury of the sciatic nerve in rats causes different activation modes of microglia between the anterior and posterior horns of the spinal cord. Neurochem Int. 2020;134:104672.
[20] PFYFFER D, WYSS PO, HUBER E, et al. Metabolites of neuroinflammation relate to neuropathic pain after spinal cord injury. Neurology. 2020;95(7):e805-e814.
[21] LIANG YH, CHEN GW, LI XS, et al. Guanosine-5’-triphosphate cyclohydrolase 1 regulated long noncoding RNAs are potential targets for microglial activation in neuropathic pain. Neural Regen Res. 2021; 16(3):596-600.
[22] WU J, WANG C, DING H. LncRNA MALAT1 promotes neuropathic pain progression through the miR‑154‑5p/AQP9 axis in CCI rat models. Mol Med Rep. 2020;21(1):291-303.
[23] ZHANG X, ZHANG Y, CAI W, et al. MicroRNA-128-3p Alleviates Neuropathic Pain Through Targeting ZEB1. Neurosci Lett. 2020;729:134946.
[24] TIAN J, SONG T, WANG W, et al. miR-129-5p Alleviates Neuropathic Pain Through Regulating HMGB1 Expression in CCI Rat Models. J Mol Neurosci. 2020;70(1):84-93.
[25] 夏志强. miRNA-204-5p靶向RAB22A调控胶质瘤增殖、迁移与侵袭的机制分析[D].北京:北京协和医学院,2016.
[26] GAO J, WANG Y, ZHAO X, et al. MicroRNA-204-5p-Mediated Regulation of SIRT1 Contributes to the Delay of Epithelial Cell Cycle Traversal in Diabetic Corneas. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2015;56(3):1493-1504.
[27] LI H, WANG J, LIU X, et al. MicroRNA-204-5p suppresses IL6-mediated inflammatory response and chemokine generation in HK-2 renal tubular epithelial cells by targeting IL6R. Biochem Cell Biol. 2019;7(2): 109-117.
[28] Nie M, Wang Y, Yu Z, et al. AURKB promotes gastric cancer progression via activation of CCND1 expression. Aging (Albany NY). 2020;12(2): 1304-1321.
[29] HUANG D, HUANG Y, HUANG Z, et al. Relation of AURKB over-expression to low survival rate in BCRA and reversine-modulated aurora B kinase in breast cancer cell lines. Cancer Cell Int. 2019;19:166.
[30] LEE JY, CHOI HY, JU BG, et al. Estrogen alleviates neuropathic pain induced after spinal cord injury by inhibiting microglia and astrocyte activation. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2018;1864(7): 2472-2480.
[31] TSUDA M. Microglia-Mediated Regulation of Neuropathic Pain: Molecular and Cellular Mechanisms. Biol Pharm Bull. 2019;42(12): 1959-1968.
[32] TOZAKI-SAITOH H, TSUDA M. Microglia-neuron interactions in the models of neuropathic pain. Biochem Pharmacol. 2019;169:113614.
[33] 王菲菲, 韩光, 杜英杰,等.Wnt/β-catenin信号通路在高压氧治疗大鼠神经病理性痛中的作用[J].临床麻醉学杂志,2016,32(2):171-174.
[34] ITOKAZU T, HAYANO Y, TAKAHASHI R, et al. Involvement of Wnt/beta-catenin signaling in the development of neuropathic pain. Neurosci Res. 2014;79:34-40.
[35] FAN X, BIAN W, LIU M, et al. MiR-216b-5p attenuates chronic constriction injury-induced neuropathic pain in female rats by targeting MAL2 and inactivating Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Neurochem Int. 2020;28:104930.
[36] LUO Y, BARRIOS-RODILES M, GUPTA GD, et al. Atypical function of a centrosomal module in WNT signalling drives contextual cancer cell motility. Nat Commun. 2019;10(1):2356.
[37] LEE KB, JIN H, YE S, et al. Recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein-2 inhibits gastric cancer cell proliferation by inactivating Wnt signaling pathway via c-Myc with aurora kinases. Oncotarget. 2016; 7(45):73473-73485.
[38] SUBRAMANIYAN B, KUMAR V, MATHAN G. Effect of sodium salt of Butrin, a novel compound isolated from Butea monosperma flowers on suppressing the expression of SIRT1 and Aurora B kinase-mediated apoptosis in colorectal cancer cells. Biomed Pharmacother. 2017;90:402-413.
|