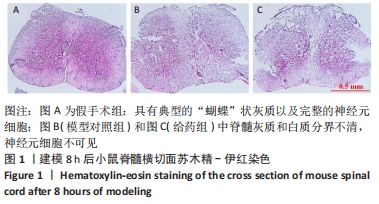
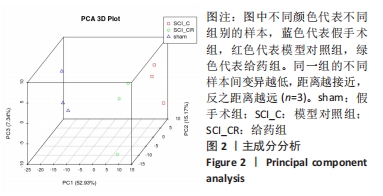
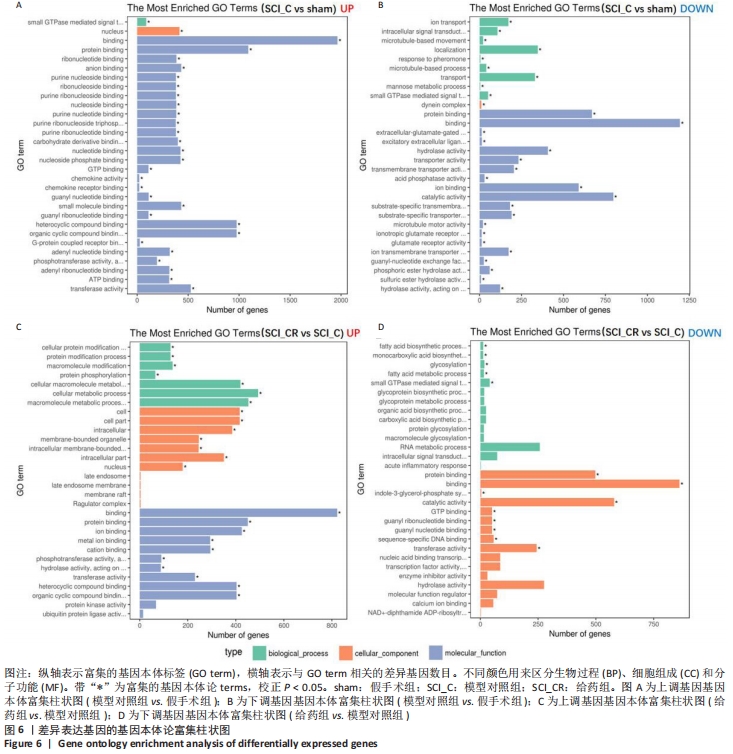
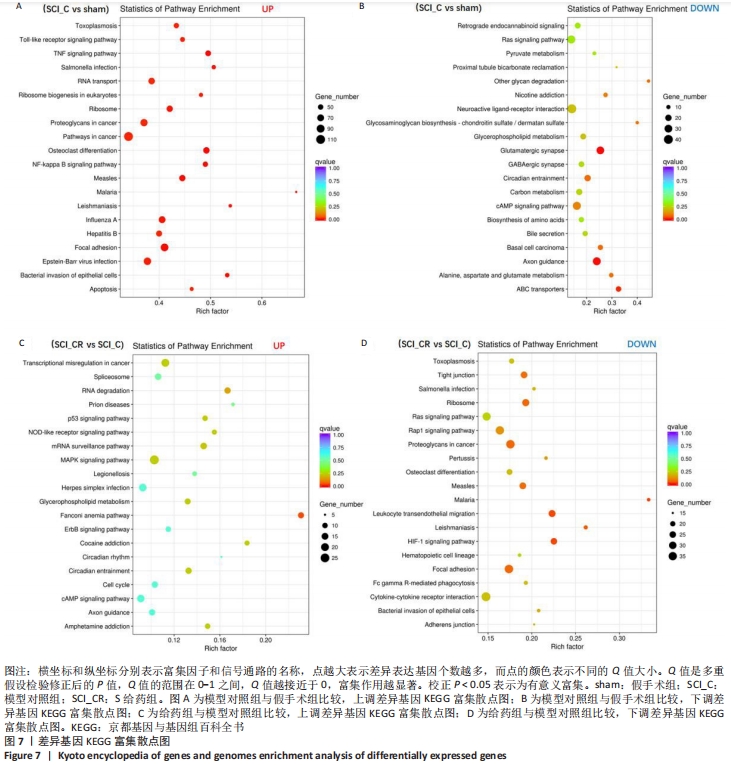
[1] GAO L, PENG Y, XU W, et al. Progress in Stem Cell Therapy for Spinal Cord Injury. Stem Cells Int. 2020;2020:2853650.
[2] YUAN S, SHI Z, CAO F, et al. Epidemiological Features of Spinal Cord Injury in China: A Systematic Review. Front Neurol. 2018;9:683.
[3] 程菡, 胡雪慧, 韩蕾, 等. 感恩对脊髓损伤患者心理资本和生活质量的影响[J]. 华南国防医学杂志,2020,34(11):805-809.
[4] 汪晶, 李伦兰, 丁杨, 等. 脊髓损伤患者住院医疗费用及其影响因素分析[J]. 中国病案,2021,22(4):50-54.
[5] GALEIRAS VR, FERREIRO VM, MOURELO FM, et al. Update on traumatic acute spinal cord injury. Part 1. Med Intensiva. 2017;41(4):237-247.
[6] AHMED A, PATIL AA, AGRAWAL DK. Immunobiology of spinal cord injuries and potential therapeutic approaches. Mol Cell Biochem. 2018; 441(1-2):181-189.
[7] 李鹏飞, 高枫. 脊髓损伤后神经修复与再生研究进展[J]. 延安大学学报(医学科学版),2021,19(1):92-95.
[8] 王赛男, 胡建国, 吕合作. 炎症小体活化对脊髓损伤局部免疫微环境的影响[J]. 中国免疫学杂志,2018,34(5):765-768.
[9] 何腾, 李何阳子, 王琳琳. 脊髓损伤后炎症小体在脊髓功能恢复中作用的研究进展[J]. 中华创伤杂志,2019,35(10):948-952.
[10] 高书涛, 荀传辉, 盛伟斌. NLRP3炎症小体在创伤性脊髓损伤中作用的研究进展[J]. 中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2019,29(11):1042-1045.
[11] MARTINON F, BURNS K, TSCHOPP J. The inflammasome: a molecular platform triggering activation of inflammatory caspases and processing of proIL-beta. Mol Cell. 2002;10(2):417-426.
[12] CHRISTGEN S, PLACE DE, KANNEGANTI TD. Toward targeting inflammasomes: insights into their regulation and activation. Cell Res. 2020;30(4):315-327.
[13] CHEN YQ, WANG SN, SHI YJ, et al. CRID3, a blocker of apoptosis associated speck like protein containing a card, ameliorates murine spinal cord injury by improving local immune microenvironment. J Neuroinflammation. 2020;17(1):255.
[14] ITO H, KANBE A, SAKAI H, et al. Activation of NLRP3 signalling accelerates skin wound healing. Exp Dermatol, 2018;27(1):80-86.
[15] 魏荣志, 王玉玞, 闫景龙. 大鼠脊髓损伤模型研究进展概述[J]. 神经损伤与功能重建,2020,15(5):274-277.
[16] 黄勇, 周英杰. 大鼠脊髓损伤模型研究进展[J]. 中华实验外科杂志, 2020,37(3):594-596.
[17] WENG J, LI DD, JIANG BG, et al. Temporal changes in the spinal cord transcriptome after peripheral nerve injury. Neural Regen Res. 2020; 15(7):1360-1367.
[18] ISMAEL S, NASOOHI S, ISHRAT T. MCC950, the Selective Inhibitor of Nucleotide Oligomerization Domain-Like Receptor Protein-3 Inflammasome, Protects Mice against Traumatic Brain Injury. J Neurotrauma. 2018;35(11):1294-1303.
[19] COLL RC, ROBERTSON AA, CHAE JJ, et al. A small-molecule inhibitor of the NLRP3 inflammasome for the treatment of inflammatory diseases. Nat Med. 2015;21(3):248-255.
[20] ISMAEL S, ZHAO L, NASOOHI S, et al. Inhibition of the NLRP3-inflammasome as a potential approach for neuroprotection after stroke. Sci Rep. 2018;8(1):5971.
[21] COCKRAM PE, KIST M, PRAKASH S, et al. Ubiquitination in the regulation of inflammatory cell death and cancer. Cell Death Differ. 2021;28(2):591-605.
[22] ZHANG W, JIA L, ZHAO B, et al. Quercetin reverses TNFalpha induced osteogenic damage to human periodontal ligament stem cells by suppressing the NFkappaB/NLRP3 inflammasome pathway. Int J Mol Med. 2021;47(4):39.
[23] MANES NP, NITA-LAZAR A. Molecular Mechanisms of the Toll-Like Receptor, STING, MAVS, Inflammasome, and Interferon Pathways. mSystems. 2021:e33621.
[24] SIVASINPRASASN S, WIKAN N, TOCHARUS J, et al. Pelargonic acid vanillylamide and rosuvastatin protect against oxidized low-density lipoprotein-induced endothelial dysfunction by inhibiting the NF-kappaB/NLRP3 pathway and improving cell-cell junctions. Chem Biol Interact. 2021:109572.
[25] LIU Z, LI J, LIN S, et al. PI3K regulates the activation of NLRP3 inflammasome in atherosclerosis through part-dependent AKT signaling pathway. Exp Anim. 2021;70(4):488-497.
[26] LI X, MEI W, HUANG Z, et al. Casticin suppresses monoiodoacetic acid-induced knee osteoarthritis through inhibiting HIF-1alpha/NLRP3 inflammasome signaling. Int Immunopharmacol. 2020;86:106745.
[27] FANG F, XIE Z, QUAN J, et al. Baicalin suppresses Propionibacterium acnes-induced skin inflammation by downregulating the NF-kappaB/MAPK signaling pathway and inhibiting activation of NLRP3 inflammasome. Braz J Med Biol Res. 2020;53(12):e9949.
[28] HEIM VJ, STAFFORD CA, NACHBUR U. NOD Signaling and Cell Death. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2019;7:208.
[29] ZHANG WJ, CHEN SJ, ZHOU SC, et al. Inflammasomes and Fibrosis. Front Immunol. 2021;12:643149.
[30] LISSNER D, SCHUMANN M, BATRA A, et al. Monocyte and M1 Macrophage-induced Barrier Defect Contributes to Chronic Intestinal Inflammation in IBD. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2015;21(6):1297-1305.
[31] ZHANG Y, SHAO L, ZHOU N, et al. Transcriptome Analysis of Porcine PBMCs Reveals the Immune Cascade Response and Gene Ontology Terms Related to Cell Death and Fibrosis in the Progression of Liver Failure. Can J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2018;2018:2101906.
[32] CHEN K, DENG S, LU H, et al. RNA-seq characterization of spinal cord injury transcriptome in acute/subacute phases: a resource for understanding the pathology at the systems level. PLoS One. 2013;8(8): e72567.
[33] SHI LL, ZHANG N, XIE XM, et al. Transcriptome profile of rat genes in injured spinal cord at different stages by RNA-sequencing. BMC Genomics. 2017;18(1):173.
[34] CHEN H, LI J, LIANG S, et al. Effect of hypoxia-inducible factor-1/vascular endothelial growth factor signaling pathway on spinal cord injury in rats. Exp Ther Med. 2017;13(3):861-866.
[35] XIONG Y, XIA Y, DENG J, et al. Direct Peritoneal Resuscitation with Pyruvate Protects the Spinal Cord and Induces Autophagy via Regulating PHD2 in a Rat Model of Spinal Cord Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2020;2020:4909103.
[36] LI Y, HAN W, WU Y, et al. Stabilization of Hypoxia Inducible Factor-1alpha by Dimethyloxalylglycine Promotes Recovery from Acute Spinal Cord Injury by Inhibiting Neural Apoptosis and Enhancing Axon Regeneration. J Neurotrauma. 2019;36(24):3394-3409.
[37] LI JH, SHI ZJ, LI Y, et al. Bioinformatic identification of key candidate genes and pathways in axon regeneration after spinal cord injury in zebrafish. Neural Regen Res. 2020;15(1):103-111.
[38] GRAHAM ZA, QIN W, HARLOW LC, et al. Focal adhesion kinase signaling is decreased 56 days following spinal cord injury in rat gastrocnemius. Spinal Cord. 2016;54(7):502-509.
[39] NOURSHARGH S, ALON R. Leukocyte migration into inflamed tissues. Immunity. 2014;41(5):694-707.
[40] ALON R, SHULMAN Z. Chemokine triggered integrin activation and actin remodeling events guiding lymphocyte migration across vascular barriers. Exp Cell Res. 2011;317(5):632-641.
[41] DEHNE N, FUHRMANN D, BRUNE B. Hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF) in hormone signaling during health and disease. Cardiovasc Hematol Agents Med Chem. 2013;11(2):125-135.
[42] RISBUD MV, SHAPIRO IM. Notochordal cells in the adult intervertebral disc: new perspective on an old question. Crit Rev Eukaryot Gene Expr. 2011;21(1):29-41.
[43] KIM DH, WIRTZ D. Focal adhesion size uniquely predicts cell migration. FASEB J. 2013;27(4):1351-1361.
[44] PRAGER-KHOUTORSKY M, LICHTENSTEIN A, KRISHNAN R, et al. Fibroblast polarization is a matrix-rigidity-dependent process controlled by focal adhesion mechanosensing. Nat Cell Biol. 2011;13(12):1457-1465.
[45] GEIGER B, SPATZ JP, BERSHADSKY AD. Environmental sensing through focal adhesions. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2009;10(1):21-33.
[46] PATLA I, VOLBERG T, ELAD N, et al. Dissecting the molecular architecture of integrin adhesion sites by cryo-electron tomography. Nat Cell Biol. 2010;12(9):909-915.
[47] CHEN J, CHEN YQ, SHI YJ, et al. VX-765 reduces neuroinflammation after spinal cord injury in mice. Neural Regen Res. 2021;16(9):1836-1847.
[48] BAKRI FG, MOLLIN M, BEAUMEL S, et al. Second Report of Chronic Granulomatous Disease in Jordan: Clinical and Genetic Description of 31 Patients From 21 Different Families, Including Families From Lybia and Iraq. Front Immunol. 2021;12:639226.
[49] WU Z, LU Z, OU J, et al. Inflammatory response and oxidative stress attenuated by sulfiredoxin1 in neuronlike cells depends on nuclear factor erythroid2related factor 2. Mol Med Rep. 2020;22(6): 4734-4742.
[50] BEDNAREK R, SELMI A, WOJKOWSKA D, et al. Functional inhibition of F11 receptor (F11R/junctional adhesion molecule-A/JAM-A) activity by a F11R-derived peptide in breast cancer and its microenvironment. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2020,179(2):325-335.
[51] ELZAKRA N, KIM Y. HIF-1alpha Metabolic Pathways in Human Cancer. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2021;1280:243-260.
[52] ZHENG J, CHEN P, ZHONG J, et al. HIF1alpha in myocardial ischemiareperfusion injury (Review). Mol Med Rep. 2021;23(5):352.
[53] JU Y, HE M, MAO B, et al. [Sequential changes of hypoxia-inducible factor 1 alpha in experimental spinal cord injury and its significance]. Hua Xi Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2002;33(1):43-45.
[54] SIDDIQ A, AMINOVA LR, TROY CM, et al. Selective inhibition of hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF) prolyl-hydroxylase 1 mediates neuroprotection against normoxic oxidative death via HIF- and CREB-independent pathways. J Neurosci. 2009;29(27):8828-8838.
[55] WANG X, MA J, FU Q, et al. Role of hypoxiainducible factor1alpha in autophagic cell death in microglial cells induced by hypoxia. Mol Med Rep. 2017;15(4):2097-2105.
[56] LEFORT C T, LEY K. Neutrophil arrest by LFA-1 activation. Front Immunol. 2012;3:157.
[57] BLIGHT BJ, GILL AS, SUMSION JS, et al. Cell Adhesion Molecules are Upregulated and May Drive Inflammation in Chronic Rhinosinusitis with Nasal Polyposis. J Asthma Allergy. 2021;14:585-593.
[58] CHAVAKIS T, PREISSNER KT, SANTOSO S. Leukocyte trans-endothelial migration: JAMs add new pieces to the puzzle. Thromb Haemost. 2003;89(1):13-17.
[59] YANG Z, LV Q, WANG Z, et al. Identification of crucial genes associated with rat traumatic spinal cord injury. Mol Med Rep. 2017;15(4):1997-2006.
[60] LI Y, CHEN Y, LI X, et al. RNA sequencing screening of differentially expressed genes after spinal cord injury. Neural Regen Res. 2019;14(9): 1583-1593.
[61] WANG T, WU B, ZHANG X, et al. Identification of gene coexpression modules, hub genes, and pathways related to spinal cord injury using integrated bioinformatics methods. J Cell Biochem. 2019. doi: 10.1002/jcb.27908.
[62] LI Z, SUN Y, HE M, et al. Differentially-expressed mRNAs, microRNAs and long noncoding RNAs in intervertebral disc degeneration identified by RNA-sequencing. Bioengineered. 2021;12(1):1026-1039.
[63] SHI Z, NING G, ZHANG B, et al. Signatures of altered long noncoding RNAs and messenger RNAs expression in the early acute phase of spinal cord injury. J Cell Physiol. 2019;234(6):8918-8927.
[64] BASSIOUNI W, ALI M, SCHULZ R. Multifunctional intracellular matrix metalloproteinases: implications in disease. FEBS J. 2021. doi: 10.1111/febs.15701.
[65] DE CASTRO R J, BURNS C L, MCADOO DJ, et al. Metalloproteinase increases in the injured rat spinal cord. Neuroreport. 2000;11(16): 3551-3554.
[66] LEE JY, CHOI HY, AHN HJ, et al. Matrix metalloproteinase-3 promotes early blood-spinal cord barrier disruption and hemorrhage and impairs long-term neurological recovery after spinal cord injury. Am J Pathol, 2014;184(11):2985-3000.
[67] LEE JY, NA WH, CHOI HY, et al. Jmjd3 mediates blood-spinal cord barrier disruption after spinal cord injury by regulating MMP-3 and MMP-9 expressions. Neurobiol Dis. 2016;95:66-81.
[68] PALSSON-MCDERMOTT EM, O’NEILL LA. Signal transduction by the lipopolysaccharide receptor, Toll-like receptor-4. Immunology. 2004; 113(2):153-162.
[69] XIA H, WANG D, GUO X, et al. Catalpol Protects Against Spinal Cord Injury in Mice Through Regulating MicroRNA-142-Mediated HMGB1/TLR4/NF-kappaB Signaling Pathway. Front Pharmacol. 2020;11:630222.
[70] CHEN D, PAN D, TANG S, et al. Administration of chlorogenic acid alleviates spinal cord injury via TLR4/NFkappaB and p38 signaling pathway antiinflammatory activity. Mol Med Rep. 2018;17(1):1340-1346.
[71] NI H, JIN W, ZHU T, et al. Curcumin modulates TLR4/NF-kappaB inflammatory signaling pathway following traumatic spinal cord injury in rats. J Spinal Cord Med, 2015;38(2):199-206.
[72] JEVNIKAR Z, OBERMAJER N, KOS J. LFA-1 fine-tuning by cathepsin X. IUBMB Life. 2011;63(9):686-693.
[73] ZHANG W, WANG H, SUN M, et al. CXCL5/CXCR2 axis in tumor microenvironment as potential diagnostic biomarker and therapeutic target. Cancer Commun (Lond). 2020;40(2-3):69-80.
[74] WANG LY, TU YF, LIN YC, et al. CXCL5 signaling is a shared pathway of neuroinflammation and blood-brain barrier injury contributing to white matter injury in the immature brain. J Neuroinflammation. 2016;13:6.
[75] LI BH, GARSTKA MA, LI ZF. Chemokines and their receptors promoting the recruitment of myeloid-derived suppressor cells into the tumor. Mol Immunol. 2020;117:201-215.
[76] ZITO G, BUSCETTA M, CIMINO M, et al. Cellular Models and Assays to Study NLRP3 Inflammasome Biology. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(12):4294.
[77] SAMPATH P, MOIDEEN K, RANGANATHAN UD, et al. Monocyte Subsets: Phenotypes and Function in Tuberculosis Infection. Front Immunol. 2018;9:1726.
[78] DETILLIEUX KA, SHEIKH F, KARDAMI E, et al. Biological activities of fibroblast growth factor-2 in the adult myocardium. Cardiovasc Res. 2003;57(1):8-19.
|