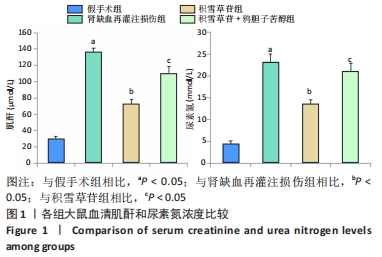
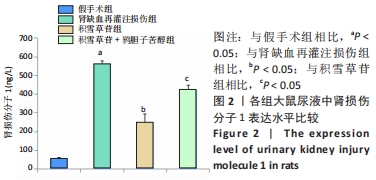
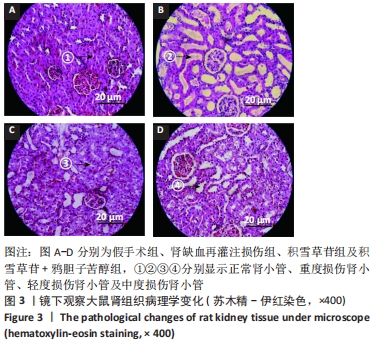
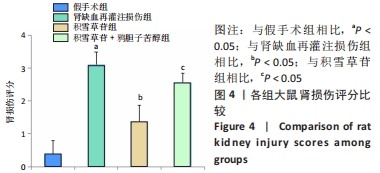
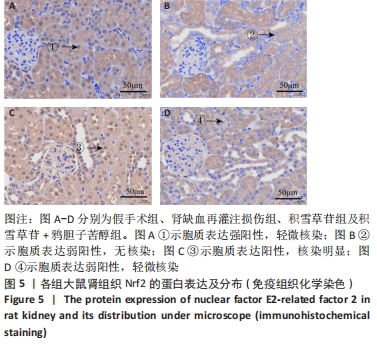
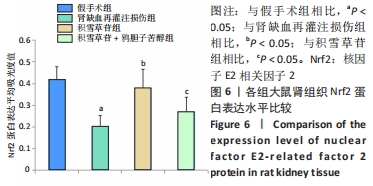
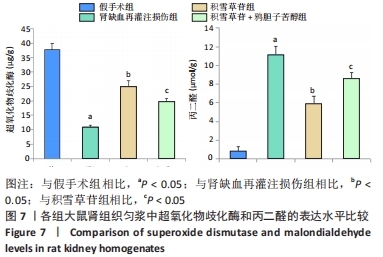
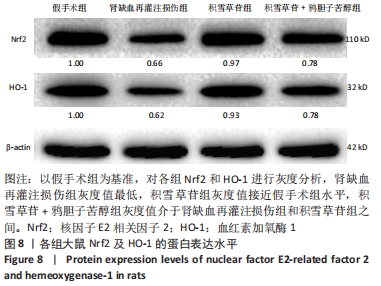
[1] XIE Y, XIAO J, FU C, et al. Ischemic Preconditioning Promotes Autophagy and Alleviates Renal Ischemia/reperfusion Injury. Biomed Res Int. 2018;2018:8353987.
[2] DIAO C,CHEN Z,QIU T, et al. Inhibition of Prmt5 Attenuates Oxidative Stress-induced Pyroptosis Via Activation of the Nrf2/ho-1 Signal Pathway in a Mouse Model of Renal Ischemia-reperfusion Injury. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2019;2019: 2345658.
[3] 谢敏慧,谷翠芝,李凤霞,等. 背入式腹膜后双肾蒂夹闭制作肾缺血再灌注损伤模型的技术方法[J]. 中国比较医学杂志,2018,28(6):106-110.
[4] GOLD R, KAPPOS L, ARNOLD DL, et al. Placebo-controlled Phase 3 Study of Oral Bg-12 for Relapsing Multiple Sclerosis. New Eng J Med. 2012;367(12):1098-1107.
[5] 余晓东,廖波,邓显忠,等. 一种新型实用的大鼠肾缺血再灌注损伤模型的建立[J]. 重庆医学,2011,40(13):1283-1284,1353-1354.
[6] DIALYNAS G, SHRESTHA OK, PONCE JM, et al. Myopathic Lamin Mutations Cause Reductive Stress and Activate the Nrf2/keap-1 Pathway. Plos Genet. 2015;11(5):1005231.
[7] CEBULA M, SCHMIDT EE, ARNÉR ES. Trxr1 as a Potent Regulator of the Nrf2-keap1 Response System. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2015;23(10):823-853.
[8] ITOH K, CHIBA T, TAKAHASHI S, et al. An Nrf2/small Maf Heterodimer Mediates the Induction of Phase Ii Detoxifying Enzyme Genes Through Antioxidant Response Elements. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1997;236(2):313-322.
[9] ZHANG G, WANG Q, ZHOU Q, et al. Protective Effect of Tempol on Acute Kidney Injury Through Pi3k/akt/nrf2 Signaling Pathway. Kidney Blood Press Res. 2016;41(2):129-138.
[10] ZHANG G, ZOU X, HUANG Y, et al. Mesenchymal Stromal Cell-derived Extracellular Vesicles Protect Against Acute Kidney Injury Through Anti-oxidation By Enhancing Nrf2/are Activation in Rats. Kidney Blood Press Res. 2016;41(2):119-128.
[11] LOBODA A,DAMULEWICZ M,PYZA E, et al. Role of Nrf2/ho-1 System in Development, Oxidative Stress Response and Diseases: an Evolutionarily Conserved Mechanism. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2016;73(17):3221-3247.
[12] 李季,崔兵兵,曲远均. 积雪草药理活性及新制剂研究进展[J]. 辽宁中医药大学学报,2020,22(12):200-204.
[13] 项佳媚,肖伟,许利嘉,等.积雪草的研究进展[J]. 中国现代中药,2016, 18(2):233-238,258.
[14] WANG H,WEI W,LAN X, et al. Neuroprotective Effect of Swertiamain on Cerebral Ischemia/reperfusion Injury By Inducing the Nrf2 Protective Pathway. Acs Chem Neurosci. 2019;10(5):2276-2286.
[15] NIGRO P, ABE J, BERK BC. Flow Shear Stress and Atherosclerosis: a Matter of Site Specificity. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2011;15(5):1405-1414.
[16] FERENBACH DA, KLUTH DC, HUGHES J. Hemeoxygenase-1 and Renal Ischaemia-reperfusion Injury. Nephron Experimental Nephrol. 2010;115(3):33-37.
[17] SHEN Y,LIU X,SHI J, et al. Involvement of Nrf2 in Myocardial Ischemia and Reperfusion Injury. Int J Biol Macromol. 2019;125:496-502.
[18] 孙光涛,戚询中,邹春颖,等. 基于Nrf2-ARE信号通路探析己酮可可碱对癫痫大鼠脑内氧化应激的影响[J]. 医学研究生学报,2020,33(2):144-148.
[19] XUE S, HE W, ZENG X, et al. Hypothermic Machine Perfusion Attenuates Ischemia/reperfusion Injury Against Rat Livers Donated After Cardiac Death By Activating the Keap1/nrf2?are Signaling Pathway. Mol Med Rep. 2018;18(1):815-826.
[20] KOIZUMI S. Human Heme Oxygenase‐1 Deficiency: a Lesson on Serendipity in the Discovery of the Novel Disease. Pediatr Int. 2007;49(2):125-132.
[21] SUBHASHINI B,ABOLFAZL Z,ANUPAM A. Heme Oxygenase 1 as a Therapeutic Target in Acute Kidney Injury. Am J Kidney Dis. 2017;69(4):531-545.
[22] 黄新宇,刘永林. 白藜芦醇激活Nrf2/ARE信号通路降低心肌缺血再灌注损伤大鼠炎症和氧化应激[J]. 中华中医药学刊,2017,35(6):1516-1520.
[23] LU M,JI J,JIANG Z, et al. The Keap1–nrf2–are Pathway as a Potential Preventive and Therapeutic Target: an Update. Med Res Rev. 2016;36(5):924-963.
[24] YAMAMOTO M, KENSLER TW, MOTOHASHI H. The KEAP1-NRF2 System: a Thiol-Based Sensor-Effector Apparatus for Maintaining Redox Homeostasis. Physiol Rev. 2018;98(3):1169-1203.
[25] KANSANEN E, KUOSMANEN SM, LEINONEN H, et al. The Keap1-Nrf2 pathway: Mechanisms of activation and dysregulation in cancer. Redox Biol. 2013;1(1):45-49.
[26] FAN Z, WIRTH AK, CHEN D, et al. Nrf2-Keap1 pathway promotes cell proliferation and diminishes ferroptosis. Oncogenesis. 2017;6(8):e371.
[27] ICHIMURA Y, WAGURI S, SOU YS, et al. Phosphorylation of p62 activates the Keap1-Nrf2 pathway during selective autophagy. Mol Cell. 2013;51(5):618-631.
[28] TU W, WANG H, LI S, et al. The Anti-Inflammatory and Anti-Oxidant Mechanisms of the Keap1/Nrf2/ARE Signaling Pathway in Chronic Diseases. Aging Dis. 2019;10(3):637-651.
[29] RENAUD CO, ZIROS PG, CHARTOUMPEKIS DV, et al. Keap1/Nrf2 Signaling: A New Player in Thyroid Pathophysiology and Thyroid Cancer. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2019;10:510.
|