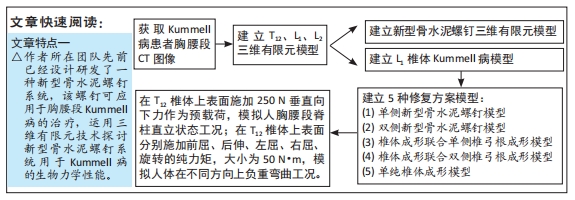
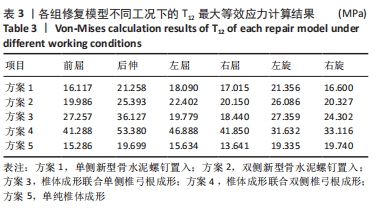
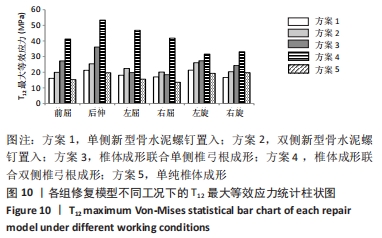
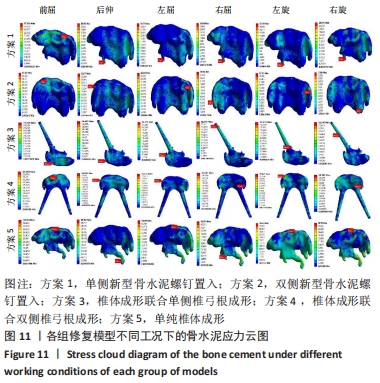
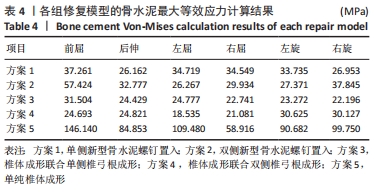
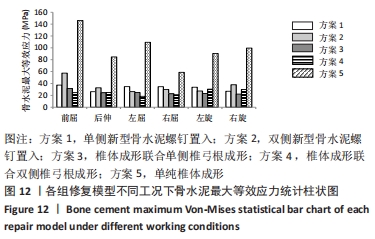
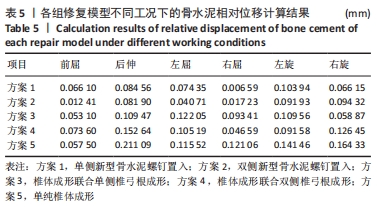
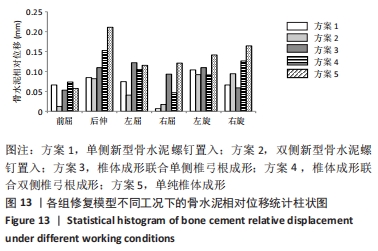
[1] CUI L, CHEN L, XIA W, et al. Vertebral fracture in postmenopausal Chinese women: a population-based study. Osteoporos Int. 2017; 28(9):2583-2590.
[2] RAJASEKARAN S, KANNA RM, SCHNAKE KJ, et al.Osteoporotic Thoracolumbar Fractures-How Are They Different?-Classification and Treatment Algorithm. J Orthop Trauma. 2017;31 Suppl 4:S49-S56.
[3] 王复案,陈允震.骨质疏松性椎体压缩性骨折诊疗现状及其对策[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2019,25(5):590-594,599.
[4] 吴斗,刘强.骨质疏松性骨折手术治疗策略[J].中国骨质疏松杂志, 2019,25(5):581-584.
[5] OSTERHOUSE MD, KETTNER NW. Delayed posttraumatic vertebral collapse with intravertebral vacuum cleft. J Manipulative Physiol Ther. 2002;25(4):270-275.
[6] YOUNG WF, BROWN D, KENDLER A, et al. Delayed post-traumatic osteonecrosis of a vertebral body (Kummell’s disease). Acta Orthop Belg. 2002;68(1):13-19.
[7] LIBICHER M, APPELT A, BERGER I, et al. The intravertebral vacuum phenomen as specific sign of osteonecrosis in vertebral compression fractures: results from a radiological and histological study. Eur Radiol. 2007;17(9):2248-2252.
[8] MATZAROGLOU C, GEORGIOU CS, ASSIMAKOPOULOS K, et al. Kümmell’s disease: pathophysiology, diagnosis, treatment andthe role of nuclear medicine. Rationale according to our experience. Hell J Nucl Med. 2011;14(3):291-299.
[9] FENG SW, CHANG MC, WU HT, et al. Are intravertebral vacuum phenomena benign lesions? Eur Spine J. 2011;20(8):1341-1348.
[10] 李良辰,何登伟,黄文君,等.Kummell病椎体裂隙征发生机制的研究进展[J].中华骨质疏松和骨矿盐疾病杂志,2015,8(4):363-366.
[11] YU CW, HSU CY, SHIH TT, et al. Vertebral osteonecrosis: MR imaging findings and related changes on adjacent levels. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2007;28(1):42-47.
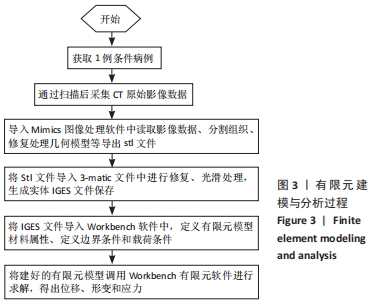
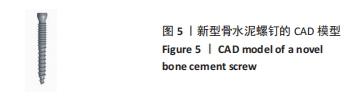
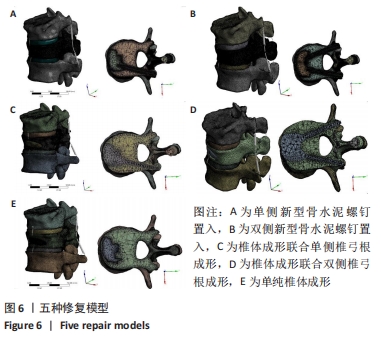
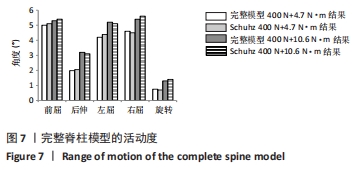
[12] 邵明昊,吕飞舟,马晓生,等. 腰椎皮质骨钉道螺钉在骨质疏松症患者中应用的三维有限元分析[J]. 中华老年骨科与康复电子杂志, 2015(2):1-6.
[13] KUMARESAN S, YOGANANDAN N, PINTAR FA. Finite element analysis of the cervical spine: a material property sensitivity study. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon). 1999;14(1):41-53.
[14] 蔡凯文,蒋国强,卢斌,等.椎间隙骨水泥渗漏的不同分型对邻椎相邻终板应力分布的影响:三维有限元研究[J].中华骨科杂志,2019, 39(6):364-373.
[15] STEEL HH. Kümmell’s disease. Am J Surg. 1951;81(2):161-167.
[16] CHEN L, DONG R, GU Y, et al. Comparison between Balloon Kyphoplasty and Short Segmental Fixation Combined with Vertebroplasty in the Treatment of Kümmell’s Disease. Pain Physician. 2015;18(4):373-381.
[17] NIU J, SONG D, ZHOU H, et al. Percutaneous Kyphoplasty for the Treatment of Osteoporotic Vertebral Fractures With Intravertebral Fluid or Air: A Comparative Study. Clin Spine Surg. 2017;30(8):367-373.
[18] WANG F, WANG D, TAN B, et al. Comparative Study of Modified Posterior Operation to Treat Kümmell’s Disease. Medicine (Baltimore). 2015;94(39):e1595.
[19] ZHANG X, HU W, YU J, et al. An Effective Treatment Option for Kümmell Disease With Neurological Deficits: Modified Transpedicular Subtraction and Disc Osteotomy Combined With Long-Segment Fixation. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2016;41(15):E923-E930.
[20] LIM J, CHOI SW, YOUM JY, et al. Posttraumatic Delayed Vertebral Collapse : Kummell’s Disease. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2018;61(1):1-9.
[21] PEH WC, GELBART MS, GILULA LA, et al. Percutaneous vertebroplasty: treatment of painful vertebral compression fractures with intraosseous vacuum phenomena. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2003; 180(5):1411-1417.
[22] MA R, CHOW R, SHEN FH. Kummell’s disease: delayed post-traumatic osteonecrosis of the vertebral body. Eur Spine J. 2010;19(7):1065-1070.
[23] LIU F, CHEN Z, LOU C, et al. Anterior reconstruction versus posterior osteotomy in treating Kümmell’s disease with neurological deficits: A systematic review. Acta Orthop Traumatol Turc. 2018;52(4):283-288.
[24] KRAUSS M, HIRSCHFELDER H, TOMANDL B, et al. Kyphosis reduction and the rate of cement leaks after vertebroplasty of intravertebral clefts. Eur Radiol. 2006;16(5):1015-1021.
[25] CHEN GD, LU Q, WANG GL, et al. Percutaneous Kyphoplasty for Kummell Disease with Severe Spinal Canal Stenosis. Pain Physician. 2015;18(6):E1021-1028.
[26] 陈峰,方文来.Kummell病的治疗进展[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志, 2013,28(1): 95-96.
[27] ZHANG J, FAN Y, HE X, et al. Is percutaneous kyphoplasty the better choice for minimally invasive treatment of neurologically intact osteoporotic Kümmell’s disease? A comparison of two minimally invasive procedures. Int Orthop. 2018;42(6):1321-1326.
[28] 王小刚,杨彬,王亚寒,等.单侧穿刺椎体成形术治疗Kummell病的疗效观察[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2019,27(1):86-88.
[29] LI HK, HAO DJ, YANG JS, et al. Percutaneous kyphoplasty versus posterior spinal fixation with vertebroplasty for treatment of Kümmell disease: A case-control study with minimal 2-year follow-up. Medicine (Baltimore). 2017;96(51):e9287.
[30] HUANG YS, HAO DJ, FENG H, et al. Comparison of Percutaneous Kyphoplasty and Bone Cement-Augmented Short-Segment Pedicle Screw Fixation for Management of Kümmell Disease. Med Sci Monit. 2018;24:1072-1079.
[31] HUANG YS, GE CY, FENG H, et al. Bone Cement-Augmented Short-Segment Pedicle Screw Fixation for Kümmell Disease with Spinal Canal Stenosis. Med Sci Monit. 2018;24:928-935.
[32] ZHANG GQ, GAO YZ, ZHENG J, et al. Posterior decompression and short segmental pedicle screw fixation combined with vertebroplasty for Kümmell’s disease with neurological deficits. Exp Ther Med. 2013; 5(2):517-522.
[33] DI HX, LIU FY, YANG SD, et al. Short-segment fixation with a cement-augmented pedicle screw for Kummell disease: Case report. Medicine (Baltimore). 2017;96(50):e8617.
[34] LEE K, ADSUL N, KIM HS, et al. Percutaneous Pedicle Screw Fixation with Bone Cement Augmentation Under Epidural Anesthesia for Treatment of Kümmell Disease in Extremely Old Age. World Neurosurg. 2018;119:506-510.
[35] ZHANG C, WANG G, LIU X, et al. Failed percutaneous kyphoplasty in treatment of stage 3 Kummell disease: A case report and literature review. Medicine (Baltimore). 2017;96(47):e8895.
[36] TSAI TT, CHEN WJ, LAI PL, et al. Polymethylmethacrylate cement dislodgment following percutaneous vertebroplasty: a case report. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2003;28(22):E457-460.
[37] Nagad P, Rawall S, Kundnani V, et al. Postvertebroplasty instability. J Neurosurg Spine. 2012;16(4):387-393.
[38] SEO DH, OH SH, YOON KW, et al. Risk Factors of New Adjacent Compression Fracture after Percutaneous Vertebroplasty: Effectiveness of Bisphosphonate in Osteoporotic or Osteopenic Elderly Patients. Korean J Neurotrauma. 2014;10(2):86-91.
[39] 葛云林,陶利江,卢一生.经皮球囊扩张椎体后凸成形术术后再发椎体骨折的危险因素和防治策略[J]. 颈腰痛杂志,2016,37(5):404-407.
[40] 陈新来,于志勇,黄春选,等.球囊扩张椎体后凸成形术后继发相邻节段椎体骨折的危险因素分析[J]. 中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2016, 31(1):51-53.
[41] WANG D, LI Y, YIN H, et al. Three-dimensional finite element analysis of optimal distribution model of vertebroplasty. Ann Palliat Med. 2020; 9(3):1062-1072.
[42] SU Y, REN D, JIANG M, et al. T1 finite element model of Kümmell’s disease shows changes in the vertebral stress distribution. Int J Clin Exp Med. 2015;8(11):20046-20055.
[43] ERDEM I, TRUUMEES E, VAN DER MEULEN MC. Simulation of the behaviour of the L1 vertebra for different material properties and loading conditions. Comput Methods Biomech Biomed Engin. 2013; 16(7):736-746.
|