中国组织工程研究 ›› 2022, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (22): 3450-3454.doi: 10.12307/2022.269
• 纳米生物材料 nanobiomaterials • 上一篇 下一篇
一种新型安全近红外发光纳米粒的制备及成像实验
许馨之1,张 悦1,金 颖2,金春香1
- 1吉林大学中日联谊医院超声科,吉林省长春市 130033;2吉林大学第一医院乳腺外科,吉林省长春市 130012
Preparation and imaging experiment of a new type of safe near-infrared luminescent nanoparticles
Xu Xinzhi1, Zhang Yue1, Jin Ying2, Jin Chunxiang1
- 1Department of Ultrasound, China-Japan Union Hospital, Jilin University, Changchun 130033, Jilin Province, China; 2Department of Breast Surgery, the First Hospital of Jilin University, Changchun 130012, Jilin Province, China
摘要:
文题释义:
近红外发光碳点:碳点制备简便、成本低、安全性高,是理想的体内示踪剂,但是目前制备的碳点多以蓝绿发光为主,组织穿透性差且无法进行实时追踪,而实验所使用的近红外发光碳点完美解决了上述问题,兼具安全性,且组织穿透性强,是理想的成像剂。
有机-无机杂化介孔二氧化硅:无机二氧化硅虽然具有体表面积大、制备简便、易于修饰等优点,但是其在体内不易降解,可能会造成不必要的循环负担。而将有机、无机硅源结合在一起,制备具有二硫键的杂化二氧化硅纳米粒,不仅具有无机二氧化硅纳米粒的优点,而且显著提高了其生物安全性。
背景:近红外发光碳点具备有蓝绿发光碳点不具备的组织穿透性,是理想的成像剂,但是由于其在体内易降解而无法到达靶点组织,实验将其与纳米粒相结合,使其能通过循环系统到达相应靶点,达到实时成像的目的。
目的:制备具有成像能力且安全性高的近红外成像载碳点介孔有机-无机杂化二氧化硅纳米粒(mesoporous organosilica nanocapsules-carbon nanodots,MON-CDs)。
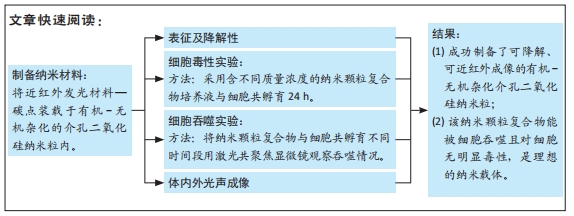
方法:利用胶束/前体共模板组装策略,以原硅酸四乙酯和双[3-(三乙氧基甲硅烷基)丙基]四硫化物为原材料、十六烷基三甲基氯化铵为模板剂、三乙醇胺为碱性催化剂成功制备了有机-无机杂化介孔二氧化硅纳米粒子,并将碳点加入到整个体系中制备MON-CDs。利用透射电镜与荧光光谱仪检测纳米粒的结构、形貌及其加载的荧光强度;利用光声成像仪、扫描激光共聚焦显微镜验证其体外成像能力,并在小鼠乳腺癌模型体内证明其体内光声成像能力;利用CCK-8实验检测不同质量浓度MON-CDs溶液的生物安全性。
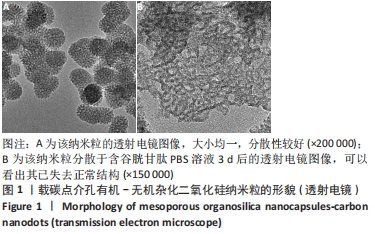
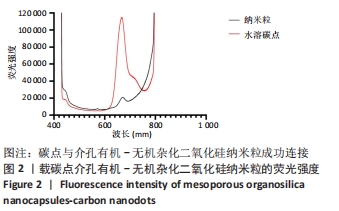
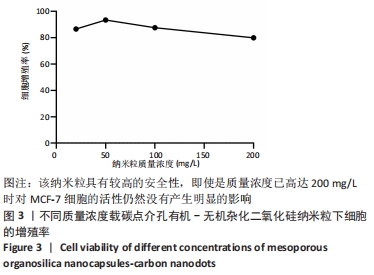
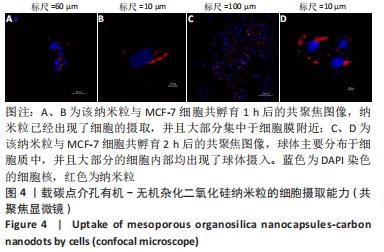
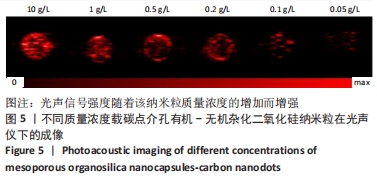
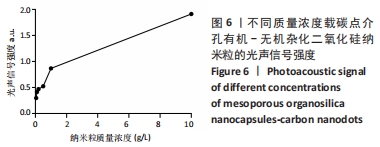
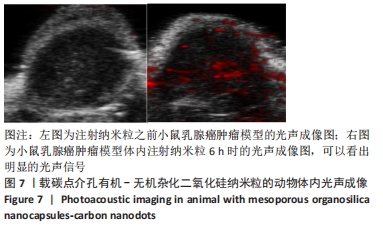
结果与结论:①透射电镜显示,MON-CDs的粒径为(50.0±4.6) nm,呈球形,大小均一且具备良好的分散性,孔道清晰可见,碳点参杂其中;荧光检测显示碳点与介孔有机-无机杂化二氧化硅纳米粒子成功连接;②CCK-8检测显示,当MON-CDs溶液的质量浓度在200 mg/L以内时无明显的细胞毒性;③扫描激光共聚焦显微镜显示,当MON-CDs与MCF-7细胞共孵育1 h时,纳米粒已出现了细胞摄取,并且大部分集中于细胞膜附近;共孵育2 h时,纳米粒累积进入细胞内的量增加,纳米粒主要分布于细胞质中,并且大部分细胞内部均出现了纳米粒的摄入;④光声成像检测显示,随着MON-CDs溶液质量浓度的增加,体外光声信号强度增强;经尾静脉注射MON-CDs溶液6 h后,在乳腺癌小鼠肿瘤组织处观察到了明显的光声信号;⑤结果表明,MON-CDs具有很好的生物安全性且拥有近红外发光,在光声成像仪及激光共聚焦下展现了良好的成像能力。
缩略语:载碳点介孔有机-无机杂化二氧化硅纳米粒:mesoporous organosilica nanocapsules-carbon nanodots,MON-CDs
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-7054-1406 (许馨之)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:生物材料;骨生物材料; 口腔生物材料; 纳米材料; 缓释材料; 材料相容性;组织工程
中图分类号: