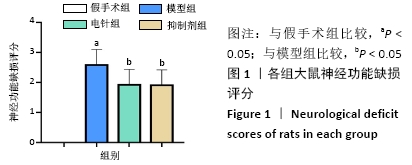
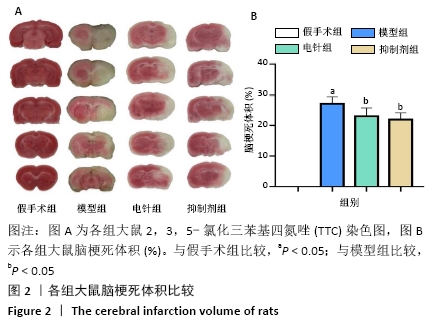
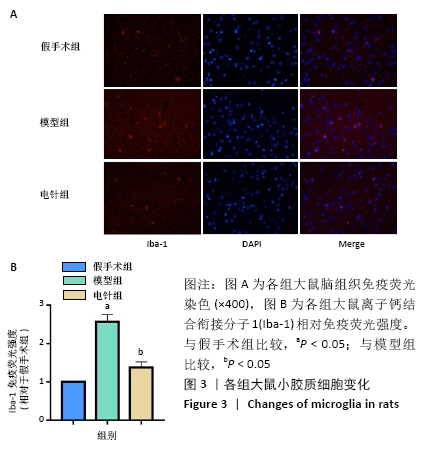
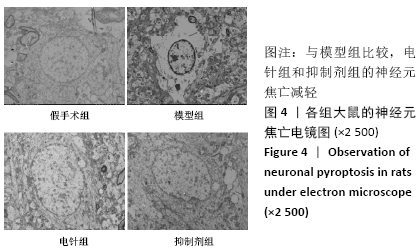
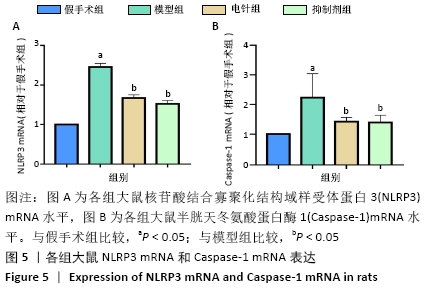
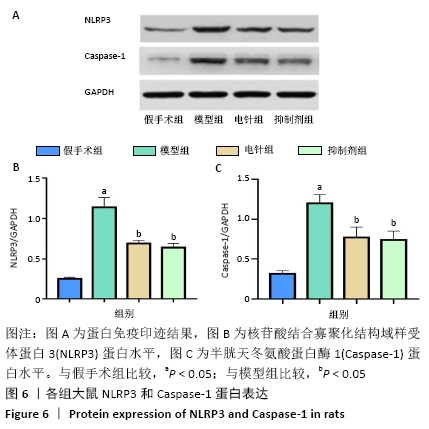
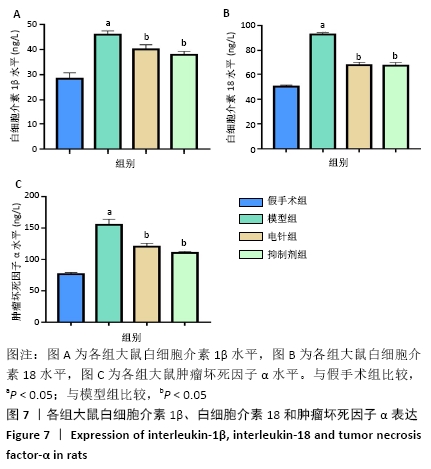
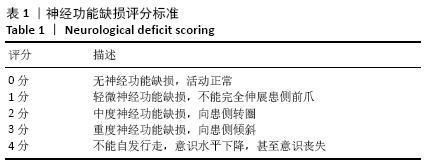
[1] 孙海欣, 王文志. 中国60万人群脑血管病流行病学抽样调查报告[J]. 中国现代神经疾病杂志,2018,18(2):83-88.
[2] 《中国脑卒中防治报告》编写组 .《中国脑卒中防治报告2019》概要[J]. 中国脑血管病杂志,2020,17(5):272-281.
[3] XIE W, ZHOU P, SUN Y, et al. Protective Effects and Target Network Analysis of Ginsenoside Rg1 in Cerebral Ischemia and Reperfusion Injury: A Comprehensive Overview of Experimental Studies. Cells. 2018;7(12):270.
[4] L L, X W, Z Y. Ischemia-reperfusion Injury in the Brain: Mechanisms and Potential Therapeutic Strategies. Biochem Pharmacol (Los Angel). 2016;5(4):213.
[5] PATEL A, APAIAJAI N, CHATTIPAKORN N, et al. The Protective and Reparative Role of Colony Stimulating Factors in the Brain with Cerebral Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury. Neuroendocrinology. 2020. doi: 10.1159/000512367.
[6] 袁钰萍, 蒋霞, 刘璐, 等. 二甲双胍调节细胞自噬和焦亡发挥脑缺血再灌注损伤保护作用的机制研究[J]. 中国药学杂志,2021,56(5): 359-367.
[7] 佘颜, 胡雨琴, 张荆, 等. 细胞焦亡参与脑缺血再灌注损伤的初步研究[J]. 中国病理生理杂志,2019,35(8):1379-1386.
[8] TAN G, HUANG C, CHEN J, et al. HMGB1 released from GSDME-mediated pyroptotic epithelial cells participates in the tumorigenesis of colitis-associated colorectal cancer through the ERK1/2 pathway. J Hematol Oncol. 2020;13(1): 149.
[9] YU P, ZHANG X, LIU N, et al. Pyroptosis: mechanisms and diseases. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2021;6(1):128.
[10] XIANG H, GUO F, TAO X, et al. Pancreatic ductal deletion of S100A9 alleviates acute pancreatitis by targeting VNN1-mediated ROS release to inhibit NLRP3 activation. Theranostics. 2021;11(9):4467-4482.
[11] CASE CL. Regulating caspase-1 during infection: roles of NLRs, AIM2, and ASC. Yale J Biol Med. 2011;84(4):333-343.
[12] PULLI B, CHEN JW. Imaging Neuroinflammation - from Bench to Bedside. J Clin Cell Immunol. 2014;5:226.
[13] SIDOROV E, SANGHERA DK, VANAMALA J. Biomarker for Ischemic Stroke Using Metabolome: A Clinician Perspective. J Stroke. 2019;21(1):31-41.
[14] ZHANG H, PARK JH, MAHARJAN S, et al. Sac-1004, a vascular leakage blocker, reduces cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury by suppressing blood-brain barrier disruption and inflammation. J Neuroinflammation. 2017;14(1):122.
[15] 刘刚, 刘再然, 刘佳, 等. 电针傍刺经筋结点治疗缺血性脑卒中急性期上肢偏瘫的临床研究[J]. 中国中医急症,2020,29(2):249-252.
[16] 宋兆瑛, 刘俊双, 刘兢, 等. 头针联合电针治疗缺血性脑卒中后失语症临床研究[J]. 中国中医药信息杂志,2018,25(7):21-24.
[17] 华兴邦, 周浩良. 大鼠穴位图谱的研制[J]. 实验动物与动物实验, 1991,2(1):1-5.
[18] 李忠仁. 实验针灸学[M]. 北京:中国中医药出版社,2003.
[19] JIA Y, YI L, LI Q, et al. LncRNA MALAT1 aggravates oxygen-glucose deprivation/reoxygenation-induced neuronal endoplasmic reticulum stress and apoptosis via the miR-195a-5p/HMGA1 axis. Biol Res. 2021; 54(1):8.
[20] WANG J, WEN CY, CUI CC, et al. Effect of activation of the Ca(2+)-permeable acid-sensing ion channel 1a on focal cerebral ischemia in diabetic rats. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015;8(10):13255-13260.
[21] ZHANG LN, HAO L, GUO YS, et al. Are glutamate transporters neuroprotective or neurodegenerative during cerebral ischemia? J Mol Med (Berl). 2019;97(3):281-289.
[22] WU X, LIU X, HUANG H, et al. Effects of major ozonated autoheamotherapy on functional recovery, ischemic brain tissue apoptosis and oxygen free radical damage in the rat model of cerebral ischemia. J Cell Biochem. 2019;120(4):6772-6780.
[23] ZHENG L, DING J, WANG J, et al. Effects and Mechanism of Action of Inducible Nitric Oxide Synthase on Apoptosis in a Rat Model of Cerebral Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury. Anat Rec (Hoboken). 2016;299(2):246-255.
[24] WU C, LI C, ZHOU G, et al. Effects of electroacupuncture on the cortical extracellular signal regulated kinase pathway in rats with cerebral ischaemia/reperfusion. Acupunct Med. 2017;35(6):430-436.
[25] WANG HL, LIU FL, LI RQ, et al. Electroacupuncture improves learning and memory functions in a rat cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury model through PI3K/Akt signaling pathway activation. Neural Regen Res. 2021;16(6):1011-1016.
[26] 许秀洪, 周国平, 李春, 等. 表里经配穴法对脑缺血再灌注损伤大鼠海马细胞凋亡及JNK信号通路的影响[J]. 广州中医药大学学报, 2015,32(1):76-80.
[27] WU C, WANG J, LI C, et al. Effect of Electroacupuncture on Cell Apoptosis and ERK Signal Pathway in the Hippocampus of Adult Rats with Cerebral Ischemia-Reperfusion. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2015;2015:414965.
[28] LAN X, ZHANG X, ZHOU GP, et al. Electroacupuncture reduces apoptotic index and inhibits p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathway in the hippocampus of rats with cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury. Neural Regen Res. 2017;12(3):409-416.
[29] 龙漫, 郑洲, 陈泽斌. 电针预处理防治大鼠脑缺血再灌注损伤的研究进展[J]. 中国临床研究,2020,33(1):124-126.
[30] 李丹, 陈泽斌, 殷妮娜, 等. “标本配穴”电针预处理抗脑缺血再灌注损伤的效应研究[J]. 湖北中医药大学学报,2019,21(1):14-18.
[31] 杨小钰, 杨仁义, 黄海红, 等. 基于阴阳理论与生物信息学方法探讨抗脑缺血再灌注损伤后炎症反应的思路与方法[J]. 中医药学报, 2020,48(12):1-6.
[32] 奚马利. 全经针刺法配合刺络拔罐治疗脑卒中恢复期上肢痉挛的临床观察[D]. 长沙:湖南中医药大学,2016.
[33] WANG LQ, ZHENG YY, ZHOU HJ, et al. LncRNA-Fendrr protects against the ubiquitination and degradation of NLRC4 protein through HERC2 to regulate the pyroptosis of microglia. Mol Med. 2021;27(1):39.
[34] HE Y, AMER AO. Microbial modulation of host apoptosis and pyroptosis. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2014;4:83.
[35] WANG Y, MENG C, ZHANG J, et al. Inhibition of GSK-3beta alleviates cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury in rats by suppressing NLRP3 inflammasome activation through autophagy. Int Immunopharmacol. 2019;68:234-241.
[36] 王艳丽. NLRP3炎症小体活化对肺腺癌细胞A549增殖、迁移、侵袭的影响及其作用机制[D]. 南京:南京医科大学,2015.
[37] 丁杨, 胡容. NLRP3炎症小体激活及调节机制的研究进展[J]. 药学进展,2018,42(4):294-302.
[38] 卓荦, 刘永娟, 李小民. 脓毒症中细胞焦亡的相关研究进展[J]. 中华急诊医学杂志,2019,28(11):1449-1450.
[39] WANG Y, GAO W, SHI X, et al. Chemotherapy drugs induce pyroptosis through caspase-3 cleavage of a gasdermin. Nature. 2017;547(7661): 99-103.
[40] O’LOUGHLIN E, MADORE C, LASSMANN H, et al. Microglial Phenotypes and Functions in Multiple Sclerosis. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2018;8(2):a28993.
[41] ZHANG L, CAI Q, LIN S, et al. Qingda granule exerts neuroprotective effects against ischemia/reperfusion-induced cerebral injury via lncRNA GAS5/miR-137 signaling pathway. Int J Med Sci. 2021;18(7):1687-1698.
[42] BARCA C, WIESMANN M, CALAHORRA J, et al. Impact of hydroxytyrosol on stroke: tracking therapy response on neuroinflammation and cerebrovascular parameters using PET-MR imaging and on functional outcomes. Theranostics. 2021;11(9):4030-4049.
[43] 申婷, 肖纯, 向彬, 等. 脑缺血再灌注损伤后小胶质细胞异常活化的生物标志物研究进展[J]. 云南中医中药杂志,2017,38(7):85-87. |