中国组织工程研究 ›› 2022, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (1): 84-89.doi: 10.12307/2022.014
• 干细胞培养与分化 stem cell culture and differentiation • 上一篇 下一篇
DNA拓扑异构酶Ⅱ在ICR小鼠神经干细胞中的表达及意义
孙孟军1,郭建美2,周更苏3,董泽飞4,郑春贵3,曹翠丽5
- 邢台医学高等专科学校,1公共教学部,2基础医学部,3护理系,4口腔医学系,河北省邢台市 054000;5河北医科大学基础医学院神经生物研究室,河北省石家庄市 050017
Expression and significance of DNA topoisomerase II in neural stem cells of ICR mice
Sun Mengjun1, Guo Jianmei2, Zhou Gengsu3, Dong Zefei4, Zheng Chungui3, Cao Cuili5
- 1Public Teaching Department, 2Department of Basic Medicine, 3Department of Nursing, 4Department of Stomatology, Xingtai Medical College, Xingtai 054000, Hebei Province, China; 5Department of Neurobiology, Basic Medical College, Heibei Medical University, Shijiazhuang 050017, Hebei Province, China
摘要:
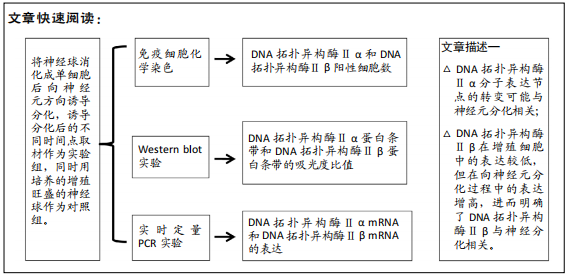
文题释义:
神经干细胞:是指有自我更新能力且可以发挥持续增殖以及多潜能分化功能的一类细胞,它们对于脑组织完整细胞结构的维持和正常功能的发挥具有重要作用。DNA拓扑异构酶Ⅱ:是一类广泛存在于生物体内的核蛋白,主要功能是调节核酸结构动态变化,在DNA复制、修复、转录、重组以及染色体分离等生命活动中发挥重要作用。DNA拓扑异构酶Ⅱ有2种同工酶,DNA拓扑异构酶Ⅱα主要分布于增殖细胞中,与细胞有丝分裂中期(G2/M期)染色体DNA双链的解聚与恢复有关,DNA拓扑异构酶Ⅱβ与间期细胞核内DNA构筑和代谢以及rRNA转录有关,主要分布于增殖不典型的细胞。
背景:胚胎期的神经干细胞可向神经元和神经胶质细胞分化,而实际应用中希望神经干细胞更多地分化成神经元。因此,研究神经干细胞向神经元的定向分化机制至关重要。DNA拓扑异构酶Ⅱ是一类广泛存在于生物体内的核蛋白,在DNA复制、修复、转录、重组以及染色体分离等生命活动中发挥重要作用。
目的:探讨神经干细胞及其向神经元定向分化过程中DNA拓扑异构酶Ⅱ的表达及意义。
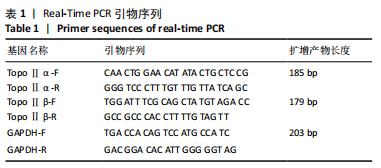
方法:从ICR小鼠(E12.5 d)大脑皮质中分离培养神经干细胞,将神经干细胞球消化成单细胞后,以5×108 L-1密度接种于用Matrigel铺底的培养皿上,加入含B27、N2、10 μg/L胶质细胞源性神经营养因子的成神经诱导分化条件培养液,诱导培养1,2,3 d采用免疫细胞化学、Western blot、实时定量PCR检测DNA拓扑异构酶Ⅱα和β的表达。
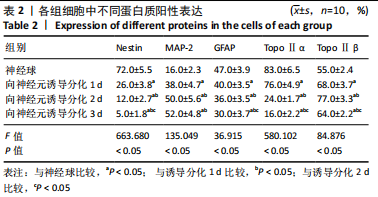
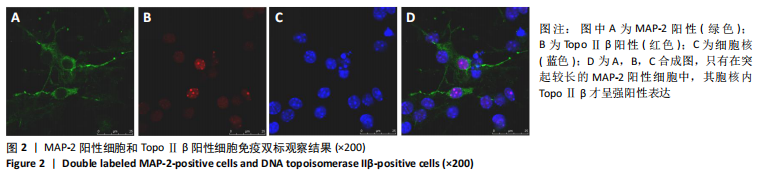
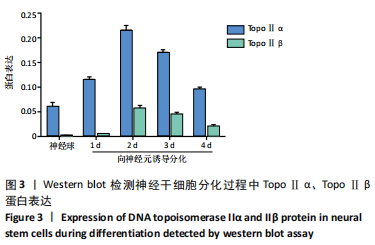
结果与结论:①DNA拓扑异构酶Ⅱα阳性细胞在神经球内数量较多,且均匀分布,在向神经元诱导分化后阳性细胞有所减少;DNA拓扑异构酶Ⅱβ阳性细胞在神经球内数量较少,主要分布在神经球中央,在向神经元诱导分化后强表达的阳性细胞开始增多,在诱导分化2 d达到高峰,之后呈减少趋势;②在神经球中DNA拓扑异构酶Ⅱα蛋白和mRNA表达较高,在向神经元诱导分化后逐渐降低;在神经球中DNA拓扑异构酶Ⅱβ蛋白和mRNA表达较低,在向神经元诱导分化后显著增高;③通过实验得出DNA拓扑异构酶Ⅱβ参与神经干细胞向神经元的定向分化。
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-6326-5159(曹翠丽);https://orcid.org/0000-0002-1930-1431(孙孟军)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
中图分类号: