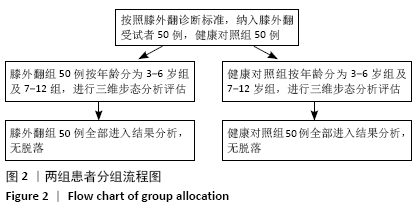
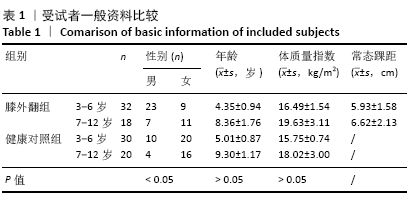
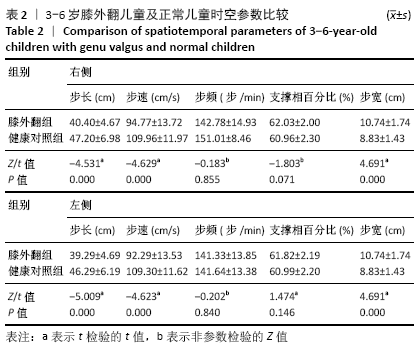
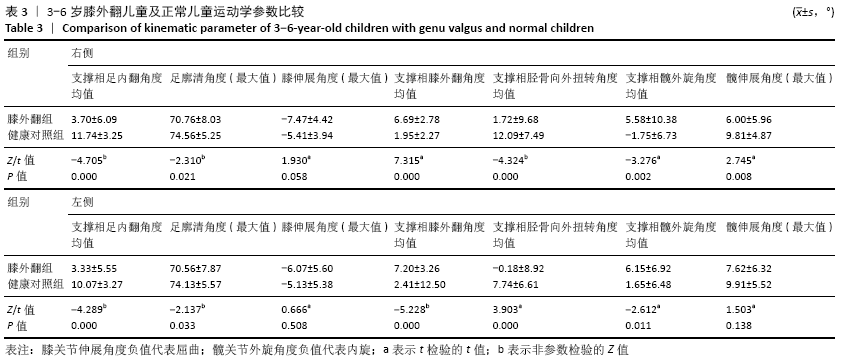
[1] HARDGRIB N, GOTTLIEBSEN M, RAHBEK O, et al. Correlation of radiological and clinical measurement of genu valgum in children. Danish Med J. 2018; 65(5):A5479.
[2] 张剑坤,覃佳强. 重度膝外翻的外科治疗进展[J]. 现代医药卫生,2014, 30(15):2287-2289.
[3] CHENG JCY, CHAN PS, CHIANG SC, et al. Angular and Rotational Profile of the Lower Limb in 2630 Chinese Children. J Pediatr Orthop. 1991;11(2):154-161.
[4] KASPIRIS A, ZAPHIROPOULOU C, VASILIADIS E. Range of variation of genu valgum and association with anthropometric characteristics and physical activity: comparison between children aged 3-9 years. J Pediatr Orthop B. 2013;22(4):296-305.
[5] WALKER JL, HOSSEINZADEH P, WHITE H, et al. Idiopathic genu valgum and its association with obesity in children and adolescents. J Pediatr Orthop. 2019;39(7):347-352.
[6] FABRY G. Clinical practice: the hip from birth to adolescence. Eur J Pediatr. 2010;169(2):143-148.
[7] LIN CJ, LIN SC, HUANG W, et al. Physiological knock-knee in preschool children: prevalence, correlating factors, gait analysis, and clinical significance. J Pediatr Orthop. 1999;19(5):650-654.
[8] NISSIM M, RAM-TSUR R, ZION M, et al. Effects of aquatic motor activities on early childhood cognitive and motor development. Open J Soc Sci. 2014; 2(12):24-39.
[9] MCC C, PINTO CN, FDC G, et al. Prevalence of genu valgum in public elementary schools in the city of SANTOS (SP), Brazil. Revista Paulista De Pediatria. 2017;35(4):443-447.
[10] 胡永波,劳永锵,史瑞超,等.计算机导航模板在儿童膝内外翻的初步应用[J].中国数字医学,2020,15(1):134-138.
[11] KADABA MP, RAMAKRISHNAN HK, WOOTTEN ME. Measurement of lower extremity kinematics during level walking. J Orthop Res.1990;8(3):383-392.
[12] SALAMON J, DIECKHOFF J, JUNG C, et al. Effects of genu varum deformity on postural stability. Int J Sports Med. 2012;33(6):469-473.
[13] EVANS AM. Mitigating clinician and community concerns about children’s flatfeet, intoeing gait, knock knees or bow legs. J Paediatr Child Health. 2017;53(11):1050-1053.
[14] UEKI Y, SAKUMA E, WADA I. Pathology and management of flexible flat foot in children. J Orthop Sci. 2019;24(1):9-13.
[15] KIM EK, KIM JS. The effects of short foot exercises and arch support insoles on improvement in the medial longitudinal arch and dynamic balance of flexible flatfoot patients. J Phys Ther Sci. 2016;28(11):3136-3139.
[16] FARR S, KRANZL A, PABLIK E, et al. Functional and radiographic consideration of lower limb malalignment in children and adolescents with idiopathic genu valgum. J Orthop Res. 2014;32(10):1362-1370.
[17] PERRY J, BURNFIELD JM. Gait Analysis: Normal and Pathological Function. Slack. 2010.
[18] HOCH MC, WEINHANDL JT. Effect of valgus knee alignment on gait biomechanics in healthy women. J Electromyogr Kinesiol. 2017;35:17-23.
[19] BARRIOS JA, HEITKAMP CA, SMITH BP, et al. Three-dimensional hip and knee kinematics during walking, running, and single-limb drop landing in females with and without genu valgum. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon). 2015;31:7-11.
[20] OKAMURA K, KANAI S, OKI S, et al. Does the weakening of intrinsic foot muscles cause the decrease of medial longitudinal arch height? J Phys Ther Sci. 2017;29(6):1001-1005.
[21] GANESAN B, FONG KNK, LUXIMON A, et al. Kinetic and kinematic analysis of gait pattern of 13 year old children with unilateral genu valgum. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2016;20(15):3168-3171.
[22] PRETKIEWICZ-ABACJEW E. Knock knee and the gait of six-year-old children. J Sports Med Phys Fitness. 2003;43(2):156-164.
[23] STEVENS PM, MACWILLIAMS B, MOHR RA. Gait analysis of stapling for genu valgum. J Pediatr Orthop. 2004;24(1):70-74.
[24] 施诚仁,金先庆,李仲智. 小儿外科学[M].4 版.北京:人民卫生出版社, 2000:475-477.
[25] 杨景.中医推拿、蜡疗配合矫形器治疗X型腿、O型腿100例疗效观察[J].临床医药文献电子杂志,2018,5(9):54-56.
[26] HALL M, DIAMOND LE, LENTON GK, et al. Immediate effects of valgus knee bracing on tibiofemoral contact forces and knee muscle forces. Gait Posture. 2019;68:55-62.
[27] HAN K, BAE K, LEVINE N, et al. Biomechanical effect of foot orthoses on rearfoot motions and joint moment parameters in patients with flexible flatfoot. Med Sci Monit. 2019;25:5920-5928.
|