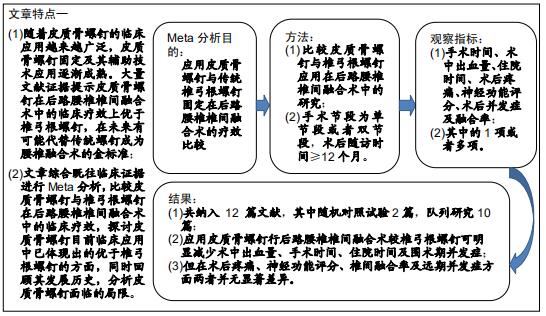
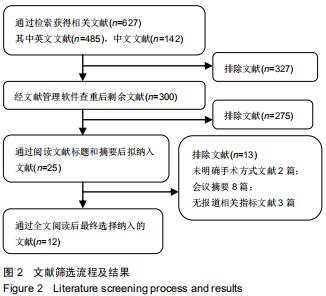
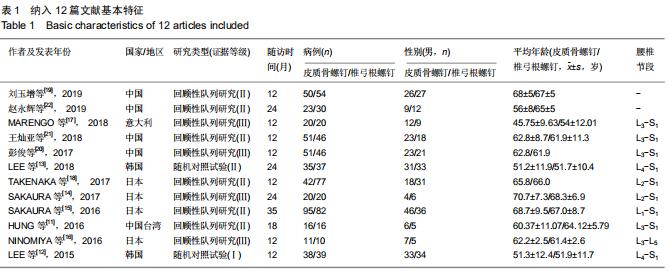
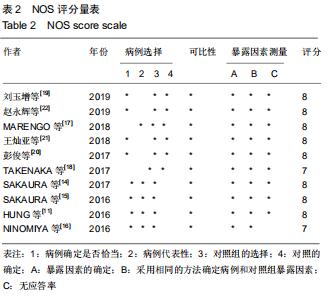
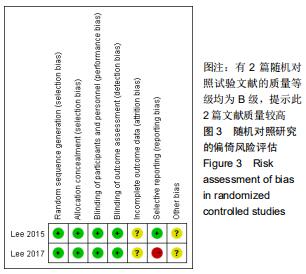
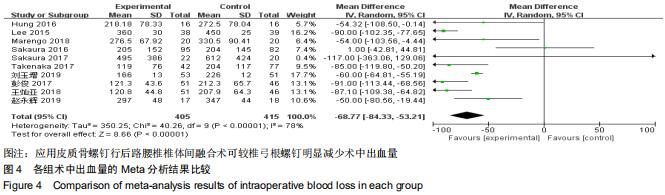
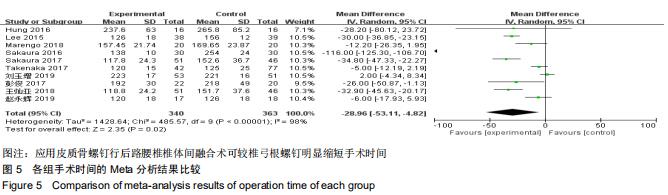
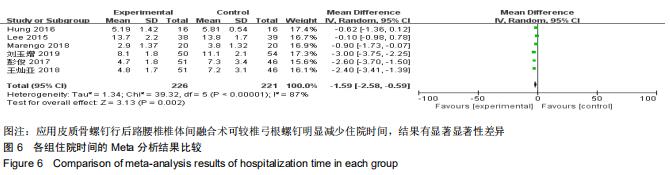
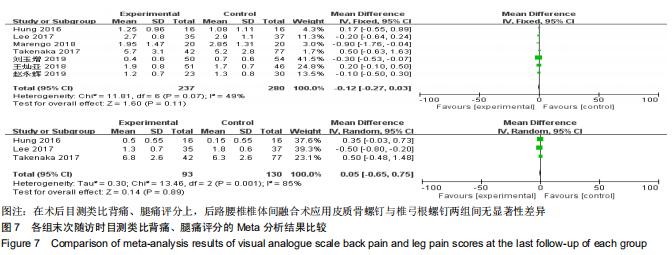
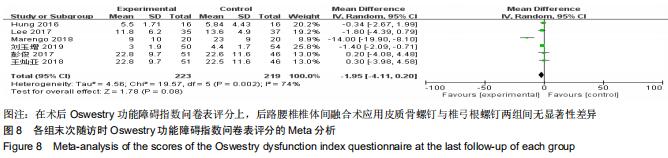
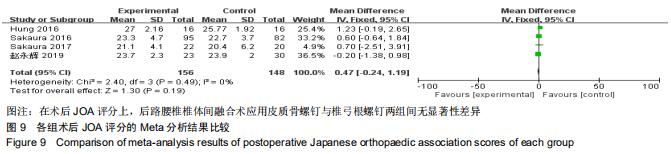
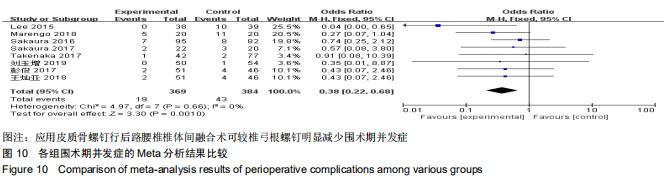
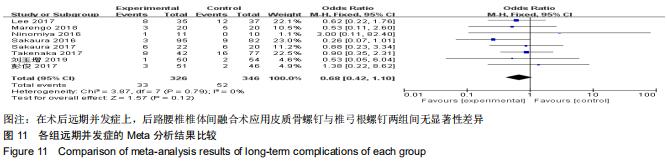
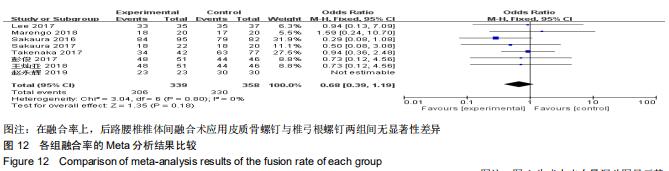
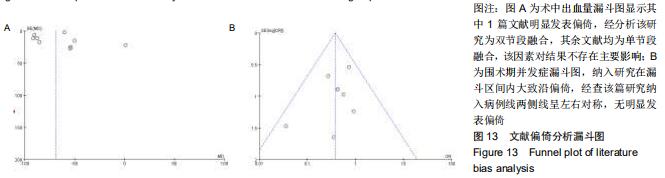
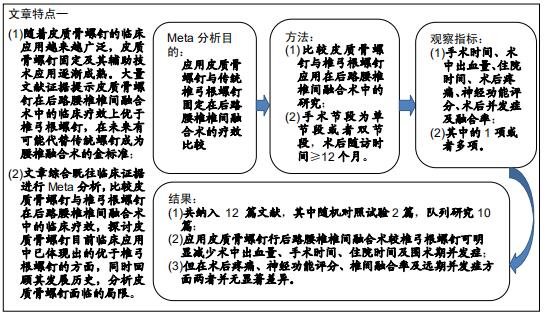
|
[1] GAINES RW. The use of pedicle-screw internal fixation for the operative treatment of spinal disorders. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2000;82(10):1458-1476.
[2] RANTANEN J, HURME M, FALCK B, et al. The lumbar multifidus muscle five years after surgery for a lumbar intervertebral disc herniation. Spine.1993;18(5):568-574.
[3] EL SAMAN A, MEIER S, SANDER A, et al. Reduced loosening rate and loss of correction following posterior stabilization with or without PMMA augmentation of pedicle screws in vertebral fractures in the elderly. Eur J Trauma Emerg Surg. 2013;39(5):455-460.
[4] SANTONI BG, HYNES RA, MCGILVRAY KC, et al. Cortical bone trajectory for lumbar pedicle screws. Spine J. 2009; 9(5):366-373.
[5] MATSUKAWA K, YATO Y, KATO T, et al. In vivo analysis of insertional torque during pedicle screwing using cortical bone trajectory technique. Spine. 2014;39(4):E240-E245.
[6] 王亮,李立军,朱福良,等.皮质骨通道螺钉与椎弓根螺钉固定用于后路腰椎椎体间融合的Meta分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2019, 23(8):1291-1298.
[7] WANG J, HE X, SUN T. Comparative clinical efficacy and safety of cortical bone trajectory screw fixation and traditional pedicle screw fixation in posterior lumbar fusion: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur Spine J. 2019;28(7):1678-161689.
[8] ZHANG T, GUO N, CHEN T, et al. Comparison of outcomes between cortical screws and traditional pedicle screws for lumbar interbody fusion: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Orthop Surg Res. 2019;14(1):269.
[9] KEOROCHANA G, PAIRUCHVEJ S, TRATHITEPHUN W, et al. Comparative outcomes ofcortical screw trajectory fixation and pedicle screw fixation in lumbar spinal fusion:systematic review and meta-analysis. World Neurosurg. 2017;102: 340-349.
[10] STANG A. Critical evaluation of the Newcastle-Ottawa scale for the assessment of the quality of nonrandomized studies in meta-analyses. Eur J Epidemiol. 2010;25(9):603-605.
[11] HUNG CW, WU MF, HONG RT, et al. Comparison of multifidus muscle atrophy after posterior lumbar interbody fusion with conventional and cortical bone trajectory. Clin Neurol Neurosur. 2016;145:41-45.
[12] LEE GW, SON JH, AHN MW, et al. The comparison of pedicle screw and cortical screw in posterior lumbar interbody fusion: a prospective randomized noninferiority trial. Spine J. 2015; 15(7):1519-1526.
[13] LEE GW, AHN MW. Comparative study of cortical bone trajectory-pedicle screw (cortical screw) versus conventional pedicle screw in single-level posterior lumbar interbody fusion: a 2-year post hoc analysis from prospectively randomized data. World Neurosurg. 2018;109:e194-e202.
[14] SAKAURA H, MIWA T, YAMASHITA T, et al. Cortical bone trajectory screw fixation versus tradi-tional pedicle screw fixation for 2-level posterior lumbar interbody fusion: comparison of surgical outcomes for 2-level degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis. J Neurosurg Spine. 2018;28(1):57-62.
[15] SAKAURA H, MIWA T, YAMASHITA T, et al. Posterior lumbar interbody fusion with cortical bone trajectory screw fixation versus posterior lumbar interbody fusion using traditional pedicle screw fixation for degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis: a comparative study. J Neurosurg Spine. 2016;25(5):591-595.
[16] NINOMIYA K, IWATSUKI K, OHNISHI Y, et al. Radiological evaluation of the initial fixation be-tween cortical bone trajectory and conventional pedicle screw technique for lumbar degenerative spondylolisthesis. Asian spine J. 2016;10(2):251-257.
[17] MARENGO N, AJELLO M, PECORARO MF, et al. Cortical bone trajectory screws in posterior lumbar interbody fusion: minimally invasive surgery for maximal muscle sparing-a prospective comparative study with the traditional open technique. Biomed Res Int. 2018;2018:7424568.
[18] TAKENAKA S, MUKAI Y, TATEISHI K, et al. Clinical outcomes after posterior lumbar interbody fusion: comparison of cortical bone trajectory and conventional pedicle screw insertion. Clin Spine Surg. 2017;30(10):E1411-E1418.
[19] 刘玉增,海涌,张希诺,等.皮质骨轨迹螺钉固定与椎弓根螺钉固定在腰椎后路融合术中的疗效[J].中华医学杂志,2019,99(19): 1473-1478.
[20] 彭俊,詹玉林,刘英杰,等.皮质骨通道螺钉与椎弓根螺钉行腰椎后路椎间融合的疗效比较[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2017,31(11): 1341-1345.
[21] 王灿亚,袁宏伟,田志红.皮质骨通道螺钉与椎弓根螺钉行腰椎间融合术的疗效比较[J].临床骨科杂志,2018,21(4):444-447.
[22] 赵永辉,陆声,马宇龙,等.皮质骨通道螺钉技术在腰椎退变性疾病中的临床应用[J].中华老年骨科与康复电子杂志,2019,5(3): 123-129.
[23] RAJAEE SS, BAE HW, KANIM LE, et al. Spinal fusion in the United States: analysis of trends from 1998 to 2008. Spine. 2012;37(1):67-76.
[24] MOBBS RJ. The "medio-latero-superior trajectory technique": an alternative cortical trajectory for pedicle fixation. Orthop Surg. 2013;5(1):56-59.
[25] MATSUKAWA K, YATO Y, NEMOTO O, et al. Morphometric measurement of cortical bone trajec-tory for lumbar pedicle screw insertion using computed tomography. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2013;26(6):E248-E253.
[26] KASUKAWA Y, MIYAKOSHI N, HONGO M, et al. Short-term results of transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion using pedicle screw with cortical bone trajectory compared with conventional trajectory. Asian Spine J. 2015;9(3):440-448.
[27] GLENNIE RA, DEA N, KWON BK, et al. Early clinical results with cortically based pedicle screw trajectory for fusion of the degenerative lumbar spine. J Clin Neurosci. 2015;22(6): 972-975.
[28] PATEL SS, CHENG WK, DANISA OA. Early complications after instrumentation of the lumbar spine using cortical bone trajectory technique. J Clin Neurosci. 2016;24:63-67.
[29] GAO H, ZHANG R, JIA C, et al. Novel placement of cortical bone trajectory screws in the lumbar spine: a radiographic and cadaveric study. Clin Spine Surg. 2018;31(6):E329-E336.
[30] SENOGLU M, KARADAG A, KINALI B, et al. Cortical bone trajectory screw for lumbar fixation: a quantitative anatomic and morphometric evaluation. world neurosurg. 2017;103: 694-701.
[31] LE X, TIAN W, SHI Z, et al. Robot-assisted versus fluoroscopyassisted cortical bone trajectory screw instrumentation in lumbar spinal surgery: a matched-cohort comparison. World Neurosurg. 2018;120:e745-e751.
[32] KAITO T, MATSUKAWA K, ABE Y, et al. Cortical pedicle screw placement in lumbar spinal surgery with a patient-matched targeting guide: a cadaveric study. J Orthop Sci. 2018;23(6):865-869.
[33] PENNER F, MARENGO N, AJELLO M, et al. Preoperative 3D CT planning for cortical bone tra-jectory screws: a retrospective radiological cohort study. World Neurosurg. 2019;126:e1468-e1474.
[34] 杨民毅,刘西纺,刘世长,等.皮质骨螺钉通道技术在骨质疏松腰椎退行性疾病中的应用[J].实用骨科杂志,2019,25(3):245-249.
[35] 杨再超,陈建,田进财,等.皮质骨螺钉固定技术在腰椎管狭窄症术后邻椎病手术中的应用[J].临床医药文献电子杂志,2019,6(88): 57-58.
[36] UENO M, IMURA T, INOUE G, et al. Posterior corrective fusion using a doubletrajectory technique (cortical bone trajectory combined with traditional trajectory) for degenerative lumbar scoliosis with osteoporosis: technical note. J Neurosurg Spine.2013;19(5):600-607.
[37] COFANO F, MARENGO N, AJELLO M, et al. The era of cortical bone trajectory screws in spine surgery: a qualitative review with rating of evidence. World Neurosurg.2020;134: 14-24.
[38] FENG Z, LI X, TANG Q, et al. Transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion with cortical bone trajectory screws versus traditional pedicle screws fixation: a study protocol of randomised controlled trial. BMJ Open. 2017;7(10):e017227.
[39] TSCHUGG A, KAVAKEBI P, HARTMANN S, et al. Clinical and radiological effect of medialized cortical bone trajectory for lumbar pedicle screw fixation in patients with degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis: study protocol for a randomized controlled trial (mPACT). Trials. 2018;19(1):129.
[40] ZHANG TX, GUO NN, CHEN TT, et al. Comparison of outcomes between cortical screws and traditional pedicle screws for lumbar interbody fusion: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Orthop Surg Res. 2019;14:269.
|