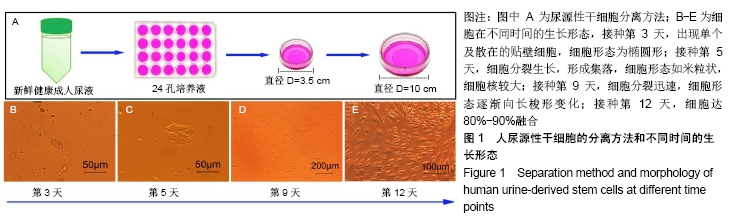
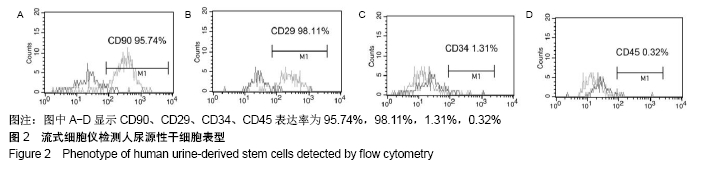
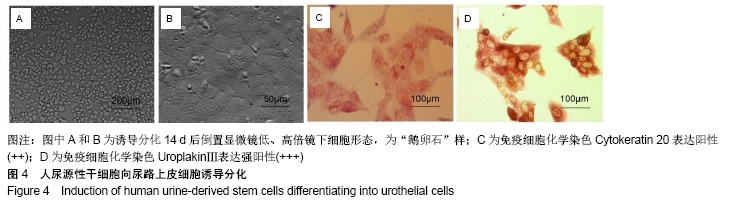
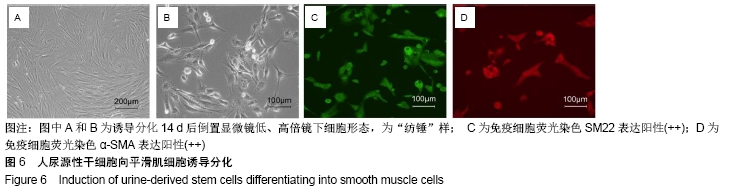
[1] ROGERS EH, HUNT JA, PEKOVIC-VAUGHAN V. Adult stem cell maintenance and tissue regeneration around the clock: do impaired stem cell clocks drive age-associated tissue degeneration? Biogerontology. 2018;19(6):497-517.
[2] BHARADWAJ S, LIU G, SHI Y, et al. Multipotential differentiation of human urine-derived stem cells: potential for therapeutic applications in urology. Stem Cells. 2013;31(9):1840-1856.
[3] ZHANG D, WEI G, LI P, et al. Urine-derived stem cells: A novel and versatile progenitor source for cell-based therapy and regenerative medicine. Genes Dis. 2014;1(1):8-17.
[4] GAO P, JIANG D, LIU W, et al. Urine-derived Stem Cells, A New Source of Seed Cells for Tissue Engineering. Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. 2016;11(7):547-553.
[5] PAVATHUPARAMBIL ABDUL MANAPH N, AL-HAWWAS M, BOBROVSKAYA L, et al. Urine-derived cells for human cell therapy. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2018;9(1):189.
[6] BODIN A, BHARADWAJ S, WU S, et al. Tissue-engineered conduit using urine-derived stem cells seeded bacterial cellulose polymer in urinary reconstruction and diversion. Biomaterials. 2010;31(34): 8889-8901.
[7] WU S, LIU Y, BHARADWAJ S, et al. Human urine-derived stem cells seeded in a modified 3D porous small intestinal submucosa scaffold for urethral tissue engineering. Biomaterials. 2011;32(5):1317-1326.
[8] LANG R, LIU G, SHI Y, et al. Self-renewal and differentiation capacity of urine-derived stem cells after urine preservation for 24 hours. PLoS One. 2013;8(1):e53980.
[9] ATALA A, BAUER SB, SOKER S, et al. Tissue-engineered autologous bladders for patients needing cystoplasty. Lancet. 2006;367(9518): 1241-1246.
[10] RAYA-RIVERA A, ESQUILIANO DR, YOO JJ, et al. Tissue-engineered autologous urethras for patients who need reconstruction: an observational study. Lancet. 2011;377(9772):1175-1182.
[11] DAVIS NF, CUNNANE EM, QUINLAN MR, et al. Biomaterials and Regenerative Medicine in Urology. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2018;1107: 189-198.
[12] XIE M, XU Y, SONG L, et al. Tissue-engineered buccal mucosa using silk fibroin matrices for urethral reconstruction in a canine model. J Surg Res. 2014;188(1):1-7.
[13] LIAO W, YANG S, SONG C, et al. Tissue-engineered tubular graft for urinary diversion after radical cystectomy in rabbits. J Surg Res. 2013;182(2):185-191.
[14] MENG L, LIAO W, YANG S, et al. Tissue-engineered tubular substitutions for urinary diversion in a rabbit model. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2016;241(2):147-156.
[15] LIU G, WU R, YANG B, et al. Human Urine-Derived Stem Cell Differentiation to Endothelial Cells with Barrier Function and Nitric Oxide Production. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2018;7(9):686-698.
[16] CHOI JY, CHUN SY, HA YS, et al. Potency of Human Urine-Derived Stem Cells for Renal Lineage Differentiation. Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2017;14(6):775-785.
[17] GUAN J, ZHANG J, GUO S, et al. Human urine-derived stem cells can be induced into osteogenic lineage by silicate bioceramics via activation of the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Biomaterials. 2015;55:1-11.
[18] KIM JY, CHUN SY, PARK JS, et al. Laminin and Platelet-Derived Growth Factor-BB Promote Neuronal Differentiation of Human Urine-Derived Stem Cells. Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2017;15(2): 195-209.
[19] KANG HS, CHOI SH, KIM BS, et al. Advanced Properties of Urine Derived Stem Cells Compared to Adipose Tissue Derived Stem Cells in Terms of Cell Proliferation, Immune Modulation and Multi Differentiation. J Korean Med Sci. 2015;30(12):1764-1776.
[20] MISHRA PJ, BANERJEE D. Activation and Differentiation of Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Methods Mol Biol. 2017;1554:201-209.
[21] LV FJ, TUAN RS, Cheung KM, et al. Concise review: the surface markers and identity of human mesenchymal stem cells. Stem Cells. 2014;32(6):1408-1419.
[22] HE Q, YE Z, ZHOU Y, et al. Comparative study of mesenchymal stem cells from rat bone marrow and adipose tissue. Turk J Biol. 2018;42: 477-489.
[23] ESPINOZA JL, ELBADRY MI, CHONABAYASHI K, et al. Hematopoiesis by iPSC-derived hematopoietic stem cells of aplastic anemia that escape cytotoxic T-cell attack. Blood Adv. 2018;2(4): 390-400.
[24] MIGUELES RP, SHAW L, RODRIGUES NP, et al. Transcriptional regulation of Hhex in hematopoiesis and hematopoietic stem cell ontogeny. Dev Biol. 2017;424(2):236-245.
[25] RAMOS-VARA JA, MILLER MA, BOUCHER M, et al. Immunohistochemical detection of uroplakin III, cytokeratin 7, and cytokeratin 20 in canine urothelial tumors. Vet Pathol. 2003;40(1): 55-62.
[26] SLEDGE DG, PATRICK DJ, FITZGERALD SD, et al. Differences in expression of uroplakin III, cytokeratin 7, and cyclooxygenase-2 in canine proliferative urothelial lesions of the urinary bladder. Vet Pathol. 2015;52(1):74-82.
[27] CHU P, WU E, WEISS LM. Cytokeratin 7 and cytokeratin 20 expression in epithelial neoplasms: a survey of 435 cases. Mod Pathol. 2000;13(9):962-972.
[28] WU XR, KONG XP, PELLICER A, et al. Uroplakins in urothelial biology, function, and disease. Kidney Int. 2009;75(11):1153-1165.
[29] MATUSZEWSKI MA, TUPIKOWSKI K, DOŁOWY Ł, et al. Uroplakins and their potential applications in urology. Cent European J Urol. 2016;69(3):252-257.
[30] LEE G. Uroplakins in the lower urinary tract. Int Neurourol J. 2011; 15(1):4-12.
[31] GUHA A, DESHPANDE A, JAIN A, et al. Uroplakin 3a+ Cells Are a Distinctive Population of Epithelial Progenitors that Contribute to Airway Maintenance and Post-injury Repair. Cell Rep. 2017;19(2): 246-254.
[32] OSBORN SL, KURZROCK EA. In Vitro Differentiation and Propagation of Urothelium from Pluripotent Stem Cell Lines. Methods Mol Biol. 2018;1655:137-144.
[33] ZUPANČIČ D, MRAK POLJŠAK K, KREFT ME. Co-culturing porcine normal urothelial cells, urinary bladder fibroblasts and smooth muscle cells for tissue engineering research. Cell Biol Int. 2018;42(4):411-424.
[34] BOUMELHEM BB, FRASER ST, ASSINDER SJ. Differentiation of Urothelium from Mouse Embryonic Stem Cells in Chemically Defined Conditions. Methods Mol Biol. 2019;2029:103-115.
[35] SUZUKI K, KOYANAGI-AOI M, UEHARA K, et al. Directed differentiation of human induced pluripotent stem cells into mature stratified bladder urothelium. Sci Rep. 2019;9(1):10506.
[36] ZHANG Y, MCNEILL E, TIAN H, et al. Urine derived cells are a potential source for urological tissue reconstruction. J Urol. 2008; 180(5):2226-2233.
[37] BHARADWAJ S, LIU G, SHI Y, et al. Characterization of urine-derived stem cells obtained from upper urinary tract for use in cell-based urological tissue engineering.Tissue Eng Part A. 2011;17(15-16): 2123-2132.
[38] GUO X, CHEN SY. Transforming growth factor-β and smooth muscle differentiation. World J Biol Chem. 2012;3(3):41-52.
[39] SINHA S, HOOFNAGLE MH, KINGSTON PA, et al. Transforming growth factor-beta1 signaling contributes to development of smooth muscle cells from embryonic stem cells. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2004;287(6):C1560-1568.
[40] XIE WB, LI Z, MIANO JM, et al. Smad3-mediated myocardin silencing: a novel mechanism governing the initiation of smooth muscle differentiation. J Biol Chem. 2011;286(17):15050-15057.
[41] ALIMPERTI S, YOU H, GEORGE T, et al. Cadherin-11 regulates both mesenchymal stem cell differentiation into smooth muscle cells and the development of contractile function in vivo. J Cell Sci. 2014;127(Pt 12):2627-2638.
[42] HAN Y, LI N, TIAN X, et al. Endogenous transforming growth factor (TGF) beta1 promotes differentiation of smooth muscle cells from embryonic stem cells: stable plasmid-based siRNA silencing of TGF beta1 gene expression. J Physiol Sci. 2010;60(1):35-41.
|