中国组织工程研究 ›› 2020, Vol. 24 ›› Issue (12): 1859-1863.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2549
• 数字化骨科 digital orthopedics • 上一篇 下一篇
计算机导航辅助置钉与截骨治疗上胸段后凸畸形
何 达,李祖昌,赵经纬,田 伟
- 北京积水潭医院脊柱外科,北京大学第四临床医学院,北京市 100035
Computer navigation-assisted surgical treatment with osteotomy for upper thoracic kyphosis
He Da, Li Zuchang, Zhao Jingwei, Tian Wei
- Department of Spine Surgery, Beijing Jishuitan Hospital, Beijing 100035, China
摘要:
文题释义:
上胸椎后凸畸形:是一种罕见疾病,通常指脊柱T1-T4节段存在的后凸畸形,常见的病因有肿瘤、骨折、医源性不稳定、退行性改变、强直性脊柱炎和结核;由于该病生物力学特点独特,减压和内固定相对困难,既往相关研究及报道较少。该类患者往往因后凸畸形严重影响生活而就诊,因此有效的矫形手术对提高患者生活质量尤为重要。
计算机导航辅助置钉:一项临床上用于辅助置钉的技术,能够通过术中三维CT进行准确指引与导航,选取最佳置钉位置完成螺钉设计及置入,帮助临床解决特殊病例、疑难病例的手术规划与安全问题。
背景:上胸椎后凸畸形的生物力学特点较为独特,减压和内固定相对困难,既往相关的研究及病例报道较少,并且缺少计算机导航辅助下进行上胸段后凸畸形矫正的相关研究。
目的:探究计算机导航辅助置钉与截骨治疗上胸段后凸畸形的临床疗效。
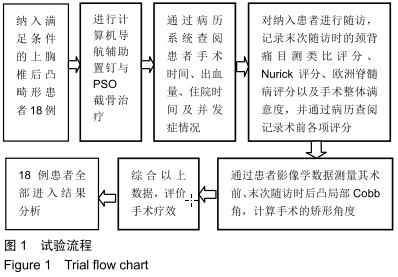
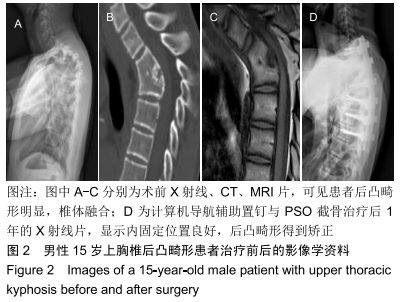
方法:纳入2011年6月至2018年6月北京积水潭医院收治的T1-T4后凸畸形患者18例,其中男11例,女7例,年龄12-59岁,均进行计算机导航辅助置钉与PSO截骨治疗,术后随访检测后凸节段局部Cobb角,评估颈背部目测类比评分、颈椎脊髓功能Nurick评分、欧洲脊髓病EMS评分与患者手术整体满意度。试验通过北京积水潭医院伦理委员会批准,伦理批件号:积伦科审字第201709-23号。
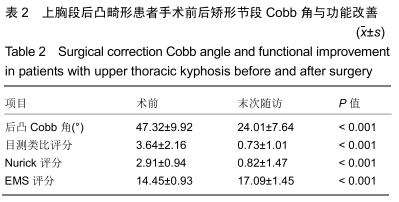
结果与结论:①18例患者均完成术后随访,随访时间6-90个月,平均(33.73±35.33)个月;②18例患者末次随访的局部Cobb角较术前明显改善[(47.32±9.92)°,(24.01±7.64)°,P < 0.001],末次随访的目测类比评分较术前明显降低(3.64±2.16,0.73±1.01,P < 0.001),末次随访的Nurick评分较术前明显降低(2.91±0.94,0.82±1.47,P < 0.001),末次随访的EMS评分较术前明显升高(14.45±0.93,17.09±1.45,P < 0.001);③患者手术满意度为优(16例)或良(2例);④至末次随访时,18例患者均未发生与植入物相关的不良反应,伤口愈合良好,未出现螺钉松动等问题;⑤结果表明,使用计算机导航辅助置钉与截骨定位进行合理的截骨矫形,可以使上胸段后凸畸形获得有效治疗。
ORCID: 0000-0001-6341-7506(何达)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:人工关节;骨植入物;脊柱;骨折;内固定;数字化骨科;组织工程
中图分类号: