中国组织工程研究 ›› 2019, Vol. 23 ›› Issue (16): 2493-2499.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.1205
• 骨科植入物 orthopedic implant • 上一篇 下一篇
股骨近端解剖型锁定加压钢板和防旋型髓内钉内固定修复股骨转子下长段粉碎性骨折:非随机对照临床研究
张杰荣1,熊时喜1,田晓林1,高方茂1,林 超1,杨利学2
- 1三亚市中医院骨一科,海南省三亚市 572000;2陕西中医药大学第一附属医院骨科,陕西省咸阳市 712000
Efficacy and safety of proximal femoral anatomical locking compression plate and proximal femoral nail antirotation for long-segment comminuted subtrochanteric fractures of the femur: a non-randomized controlled trial
Zhang Jierong1, Xiong Shixi1, Tian Xiaolin1, Gao Fangmao1, Lin Chao1, Yang Lixue2
- 1First Department of Orthopedics, Sanya Municipal Hospital of Chinese Medicine, Sanya 572000, Hainan Province, China; 2Department of Orthopedics, the First Affiliated Hospital of Shaanxi University of Chinese Medicine, Xianyang 712000, Shaanxi Province, China
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg)
文题释义:
解剖型锁定加压钢板:在临床中广泛用于治疗股骨转子下长段粉碎性骨折,术中采用解剖型钢板,其近端呈扁平状扩张部可完全覆盖大转子外部,不同开口方向的螺钉可牢固固定股骨头,抗拔出能力较强,可有效防止修复后产生旋转现象。
防旋型髓内钉:是治疗股骨转子下长段粉碎性骨折常用治疗方法,在术中采用螺旋刀片锁定替代螺钉固定,刀片进入骨质时不需要扩孔并能起到较好填压作用,锁定后的刀片可与骨质紧密锚合,可有效防止松动退出现象产生。
摘要
背景:目前股骨近端解剖型锁定加压钢板和防旋型髓内钉内固定是治疗股骨转子下长段粉碎性骨折常用的修复方法,但关于两种植入物的疗效及安全性的差异比较相关研究较少。
目的:试验旨在比较股骨近端解剖型锁定加压钢板和防旋型髓内钉内固定修复股骨转子下长段粉碎性骨折的有效性及安全性差异,以筛选最佳的植入物治疗方案。
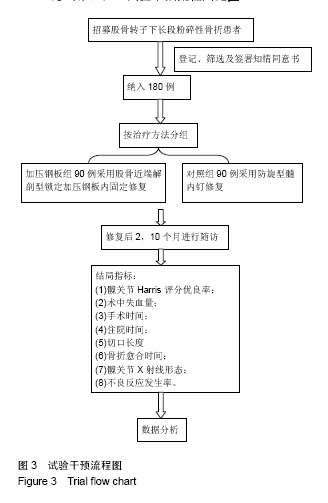
方法:方案设计为前瞻性、单中心、非随机对照临床研究。将纳入三亚市中医院的股骨转子下长段粉碎性骨折患者180例,按修复方法不同分为加压钢板组和髓内钉组,每组90例,分别采用解剖型锁定加压钢板和防旋型髓内钉内固定修复。随访时间为2,10个月。试验对象招募和资料收集时间为2019-06-30/2020-06-30,结果分析时间为2020-07-01/30,试验完成时间为2022-08-01。试验经三亚市中医院医学伦理委员会批准[审批时间:2013-03-15,审批号:(2013)第(02)号]。研究符合世界医学会制定的《赫尔辛基宣言》的要求;参与者家属或本人均对试验方案和过程知情同意,并签署知情同意书。试验已在中国临床试验注册中心注册(注册号:ChiCTR1900021251),注册时间:2019-02-03,方案版本号1.0。
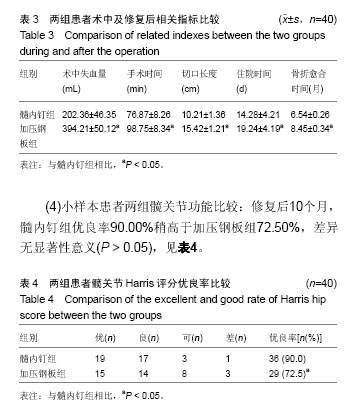
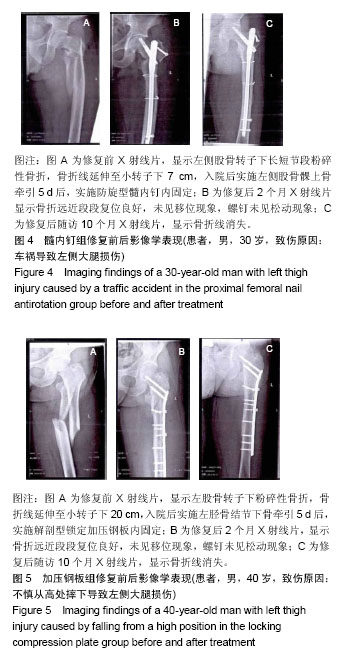
结果与结论:①研究的主要结局指标:以修复后10个月髋关节Harris评分优良率评估修复后髋关节功能恢复情况;②研究的次要结局指标:修复前、修复后2个月髋关节Harris评分优良率,术中失血量、手术时间、切口长度、住院时间、骨折愈合时间,修复前、修复后2,10个月髋关节X射线形态,修复后2,10个月不良发应发生率。③课题组于前期(2013年2月至2016年2月)纳入了此类患者80例,包括加压钢板组和髓内钉组各40例,随访10个月发现,髓内钉组术中失血量、手术时间、切口长度、住院时间及骨折愈合时间均少于加压钢板组(P < 0.05);髓内钉组优良率高于加压钢板组(P < 0.05);髓内钉组不良反应发生率(10.0%)稍低于加压钢板组(12.5%),但差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05),前期80例患者的小样本试验结果证明,防旋型髓内钉置入内固定股骨转子下长段粉碎性骨折的有效性及安全性较好。试验希望证实,相比与解剖型锁定加压钢板,防旋型髓内钉置入内固定股骨转子下长段粉碎性骨折会取得修复后更好的髋关节功能恢复效果,且安全性能好。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:人工关节;骨植入物;脊柱;骨折;内固定;数字化骨科;组织工程
ORCID: 0000-0001-8353-3918(张杰荣)
中图分类号:
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)