中国组织工程研究 ›› 2018, Vol. 22 ›› Issue (31): 4993-4997.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.0334
• 骨与关节图像与影像 bone and joint imaging • 上一篇 下一篇
X射线、CT、MRI评估C7椎体显示不清颈椎退变性疾病C2-7 Cobb角的可靠性
吴 涛,刘 军,王 刚
- 南京医科大学第二附属医院骨科,江苏省南京市 210011
Reliability of evaluating C2-7 Cobb angle for cervical degenerative disease with unclear C7 vertebrae on X-ray, CT and MRI
Wu Tao, Liu Jun, Wang Gang
- Department of Orthopedics, the Second Affiliated Hospital of Nanjing Medical University, Nanjing 210011, Jiangsu Province, China
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg)
文题释义:
颈椎矢状位形态:颈椎矢状位生理性前凸是颈椎最为直观的形态学特征,该形态是保持颈椎正常稳定性与灵活性的重要前提。既往研究显示,颈椎矢状位形态异常与颈椎退变性疾病的发生发展存在密切关系,而且通过评估患者颈椎矢状位形态能够初步了解颈椎退变性疾病严重程度,协助制定相关治疗方案,甚至能够一定程度上判断患者预后。因此,颈椎矢状位形态评估在颈椎退变性疾病诊疗过程中发挥重要作用。
C2-7 Cobb角:临床上C2-7 Cobb角是目前国际上常用于评估颈椎矢状位的指标,具有操作简单、稳定性高的特点。但临床实践过程中,部分颈椎退变性疾病患者由于肩背部遮挡等解剖问题导致颈椎侧位片中C7椎体显示不清从而影响该指标测量的可靠性。而CT矢状位重建与MRI由于均为断层扫描,可解决这一问题,但由于CT与MRI均为平卧位拍摄,颈椎矢状位形态可能受到相应影响。
摘要
背景:临床工作中发现部分颈椎退变性疾病患者由于自身解剖原因C7椎体于颈椎侧位片中显示不清,严重影响C2-7 Cobb角的测量准确性。
目的:针对部分C7椎体显示不清的颈椎退变性疾病患者,探讨采用CT及MRI取代X射线评估颈椎矢状位形态的可行性。
方法:符合入选标准的颈椎手术患者共82例,根据C7椎体轮廓于颈椎侧位片上显示情况分组,A组28例X射线中C7椎体轮廓显示不清,B组54例C7椎体轮廓显示清楚。采用C2-7 Cobb角指标分别评估每位患者X射线、CT及MRI颈椎矢状位形态。采用配对t检查、组内相关系数、Pearson相关性分析探讨不同影像学技术评估颈椎矢状位形态的差异、可靠性及相关性。
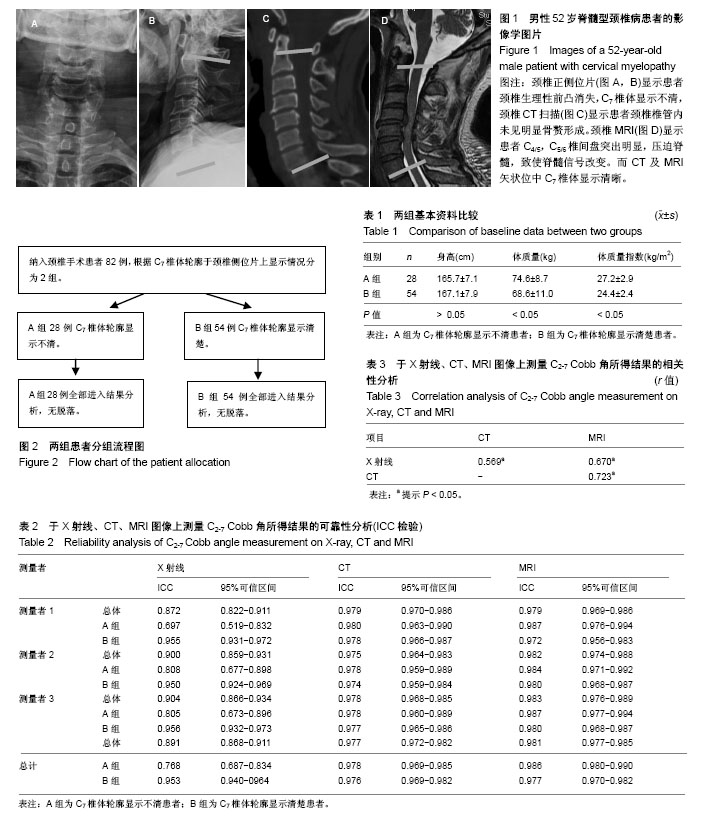
结果与结论:①CT、MRI中测量所得C2-7 Cobb角均明显低于X射线中测量所得C2-7 Cobb角(P < 0.05)。将上述患者按C7椎体轮廓显示状况进行分组后,发现X射线测量A组患者C2-7 Cobb角可靠性较CT、MRI明显降低(ICC=0.768,0.977,0.986),而于X射线测量B组患者可靠性与CT、MRI相近(ICC=0.953,0.976,0.977);②相关性分析结果显示CT及MRI下所测C2-7 Cobb角均与X射线下所得测量值存在显著相关性(r=0.569,P < 0.05;r=0.670,P < 0.05);③通过建立散点图计算X射线、CT、MRI下所得C2-7 Cobb角测量值间计算公式如下:C2-7 Cobb角(CT)= 0.60×C2-7 Cobb角(X射线)-6.78°;C2-7 Cobb角(MRI)= 0.70×C2-7 Cobb角(X射线)-0.30°;④结果显示,尤其是C7椎体显示不清患者,可采用CT或MRI技术评估颈椎矢状位形态,以解决X射线评估颈椎矢状位形态可靠性不佳的相关问题。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:人工关节;骨植入物;脊柱;骨折;内固定;数字化骨科;组织工程
ORCID: 0000-0002-4643-0458(吴涛)
中图分类号:
.jpg)