1.1 设计 回顾性科学研究。
1.2 时间及地点 实验于2017年6至12月在云南省第一人民医院基础研究所完成。
1.3 材料
1.3.1 实验动物 健康4周龄SPF级C57BL/6小鼠20只,体质量(23.8±2.2) g,均为雄性,由成都达硕实验动物中心提供,动物许可证号为SCXK(川)2015-030。所有动物的喂养、观察均按照GLP(非临床研究管理规范)规定执行。
1.3.2 实验试剂和仪器 C57BL/6小鼠BMSCs培养基(低糖培养基,含体积分数为10%胎牛血清)(美国Cyagen Biosciences公司);Dead Cell Apoptosis Kit with Annexin V Alexa Fluor®488 & PI-for Flow Cytometry(美国Invitrogen公司);CD29、CD44、CD11b、SCA-1抗体(美国BioLegend公司);CD11bMicroBeads(美国Miltenyi公司);小鼠BMSCs成脂肪、成骨、成软骨分化试剂盒(美国Cyagen Biosciences公司);ExoQuick-TC试剂盒及RA800TC-1 seraMir Exosome RNA Amplification kit from Media and Urine试剂盒(美国SBI公司);小鼠心肌细胞(赛齐(上海)生物工程有限公司);Q-PCR仪(美国ABI公司);Accuri C6流式细胞仪(美国BD公司)。
1.4 实验方法
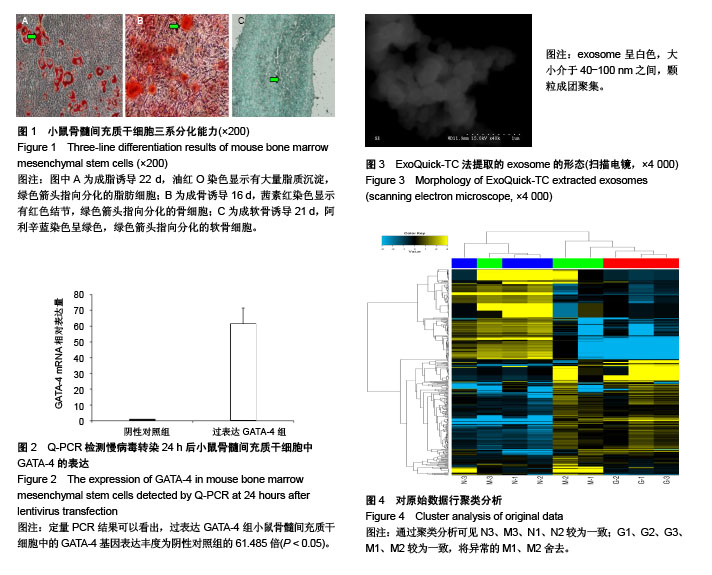
1.4.1 小鼠BMSCs的分离、培养及鉴定 全骨髓法培养小鼠BMSCs,胰酶消化传代至第3代时采用CD11b的磁珠负选,去除造血干祖细胞。继续传代,取生长至第8代BMSCs,待细胞融合达80%-90%时,制备单细胞悬液,采用流式细胞仪检测CD29、CD11b、CD44、SCA-1的表达,其中PE-CD29单抗5 μL进行1︰20稀释至100 μL、PE-CD11b单抗5 μL进行1︰40稀释至100 μL、PE/Cy5-CD44 5 μL进行1︰20稀释至100 μL、FITC anti-mouse SCA-1 5 μL进行1︰20稀释至100 μL。然后按Cyagen Biosciences公司脂肪、骨、软骨分化说明书操作完成小鼠BMSCs三系分化检测。
1.4.2 慢病毒载体及基因开启技术构建过表达GATA-4 BMSCs ①将已构建成功的GATA-4基因插入慢病毒包装质粒GV308中,构建GV308-GATA-4重组慢病毒包装质粒;②将构建成功的GV308-GATA-4重组慢病毒包装质粒转染入第10代小鼠BMSCs并加入基因开启剂强力霉素;③转染成功后利用Q-PCR方法检测转染24 h GATA-4基因的表达。
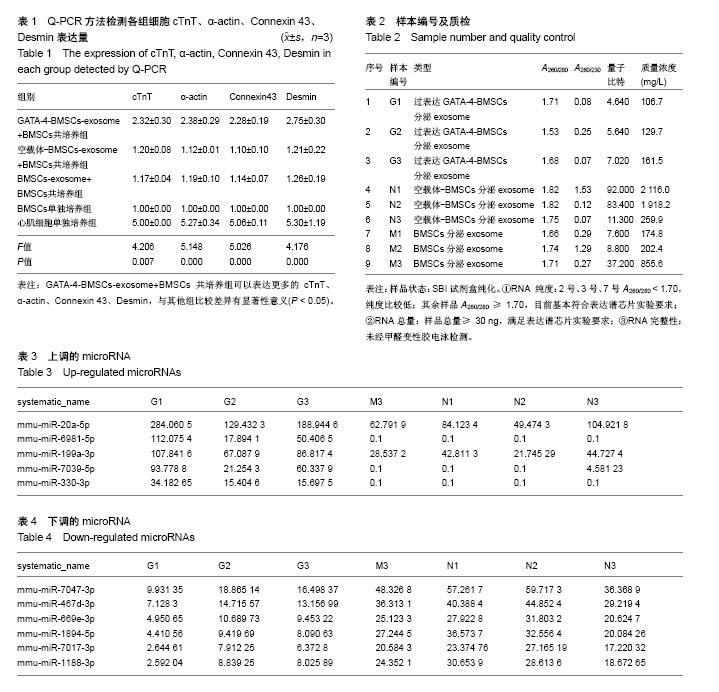
1.4.3 exosome提取 转染后,待细胞长满25 cm2培养瓶时加入强力霉素48 h,按照SBI公司ExoQuick-TC说明书提取exosome并利用扫描电镜观察exosome的形态。
1.4.4 Exosome与BMSCs共培养 提取过表达GATA- 4-BMSCs,空载体-BMSCs,BMSCs分泌的exosome,用BCA法检测各自的蛋白浓度。实验设5组:①GATA-4- BMSCs-exosome+BMSCs共培养组;②空载体-BMSCs- exosome+BMSCs共培养组;③BMSCs-exosome+BMSCs共培养组;④BMSCs单独培养组;⑤心肌细胞单独培养组。将BMSCs和小鼠心肌细胞分别消化后制备成单细胞悬液,并用血球计数板计数,调整细胞浓度为1×109 L-1。将14 mm细胞爬片放入24孔板中,根据不同的分组将BMSCs和心肌细胞分别接种到24孔板中,每孔5×104个细胞。前4组用小鼠骨髓间充质干细胞专用培养基补足至500 μL,心肌细胞单独培养组用心肌细胞专用培养基补足至500 μL。同时,在前3组的各孔中分别加入不同的exosome,各组exosome 的终质量浓度为20 g/L。每个样品做3个重复孔。
1.4.5 Q-PCR检测共培养后心肌细胞特异性分子表达 GATA-4-BMSCs-Exosome与BMSCs共培养,空载体-BMSCs-Exosome与BMSCs共培养,BMSCs-Exosome与BMSCs共培养、BMSCs单独培养及小鼠心肌细胞单独培养24 h,采用Q-PCR方法检测细胞中cTnT、α-actin、Connexin 43、Desmin的表达。实验重复3次。
1.4.6 Exosome与心肌细胞共培养 提取过表达GATA-4-BMSCs,空载体-BMSCs,BMSCs分泌的exosome,用BCA法检测各自的蛋白浓度。实验设5组:①GATA-4-BMSCs-exosome+心肌细胞共培养组;②空载体-BMSCs-exosome+心肌细胞共培养组;③BMSCs-exosome+心肌细胞共培养组;④心肌细胞单独培养组;⑤阴性对照组。前4组细胞于低氧环境下无血清培养诱导细胞凋亡。阴性对照组心肌细胞在正常条件下单独培养。
1.4.7 流式细胞技术检测细胞凋亡率 GATA-4-BMSCs-exosome与心肌细胞共培养,空载体-BMSCs-exosome与心肌细胞共培养,BMSCs-exosome与心肌细胞共培养以及单独心肌细胞在低氧(体积分数为1%)无血清培养条件下培养24 h诱导细胞凋亡。按Dead Cell Apoptosis Kit with Annexin V Alexa Fluor®488 & PI - for Flow Cytometry说明书上流式细胞仪检测心肌细胞凋亡率,实验重复3次。
1.4.8 提取exosome中的RNA 按照RA800TC-1 seraMir Exosome RNA Amplification kit from Media and Urine 试剂盒说明书提取过表达GATA-4-BMSCs分泌的eosome、空载体-BMSCs分泌的eosome、BMSCs分泌的eosome中的总RNA。
1.4.9 构建MicroRNA芯片 ①RNA质检;②纯化:使用mirVanaTM miRNA Isolation Kit(AM1561)对 total RNA 进行纯化;③总RNA去磷酸化及标记反应;④在Agilent公司杂交炉中过夜杂交。备注:在整个芯片实验过程中,加入Agilent公司的标记外标(Labeling spike-in)RNA和杂交外标(Hyb spike-in) RNA作为整个实验过程的质控;⑤芯片清洗及扫描;⑥数据提取及分析:使用Agilent Feature Extraction(v10.7)软件对杂交图片进行分析并提取数据;然后使用Agilent GeneSpring软件对数据进行归一化,并采用GeneSpring软件进行组间的差异分析,例如T-test方法进行两组差异表达基因分析;ANOVA方法进行多组差异表达基因分析。
1.5 主要观察指标 采用小鼠Agilent microRNA 芯片检测过表达GATA-4 BMSCs分泌exosome内有关细胞分化及抗凋亡的microRNA。
.jpg)
.jpg)