| [1]Chen Y,Wang X,Chen D,et al.Posterior hybrid technique for ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament associated with segmental instability in the cervical spine.J Spinal Disord Tech.2014;27(4):240-244.[2]Barz T,Melloh M,Lord SJ,et al.A Conceptual Model of Compensation/ Decompensation in Lumbar Segmental Instability. Med Hypotheses.2014;83(3):312-316.[3]费琦,赵凡,杨雍,等.腰椎后路融合手术对失稳模型节段稳定性及相邻节段力学的影响[J].中华医学杂志, 2015,95(45): 3681-3686.[4]Li H,Sun S,Liu H,et al.Use of a biological reactor and platelet-rich plasma for the construction of tissue-engineered boneto repair articular cartilage defects.Exp Ther Med. 2016; 12(2):711-719.[5]Janson IA,Putnam A J.Extracellular matrix elasticity and topography: material-based cues that affect cell function via conserved mechanisms.J Biomed Mater Res A.2015;103(3): 1246-1258.[6]Bianchi M,Urquia Edreira ER,Wolke JG,et al.Substrate geometry directs the in vitro mineralization of calcium phosphate ceramics.Acta Biomater.2014;10(2):661-669.[7]张琦,浦益琼,王冰,等.羟基磷灰石复合材料制备技术的研究进展[J].中成药,2015,37(12):2722-2725.[8]李浩,曹呈斌,杨惠林,等.丝素蛋白/羟基磷灰石复合物对磷酸钙骨水泥性能的影响[J].现代生物医学进展, 2013,13(33): 6435-6439.[9]Shokrollahi P,Mehmanchi M,Atai M,et al.Effect of interface on mechanical properties and biodegradation of PCL HAp supramolecular nano-composites.J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2014;25(1):23-35.[10]唐俊杰,李文杰,李根,等.骨组织工程诱导性支架材料修复骨缺损[J].中国组织工程研究,2015,19(3):340-346.[11]Tian X,Zhu G,Wang J,et al.Study on the relation between tissues pathologies and traditional chinese medicine syndromes in knee osteoarthritis:Medical image diagnostics by preoperative X-ray and surgical arthroscopy.J Xray Sci Technol.2016;24(4):509-519.[12]Byvaltsev VA,Kalinin AA,Belykh EG,et al.Optimization of segmental lumbar spine instability treatment using minimally invasive spinal fusion technique.Zh Vopr Neirokhir Im N N Burdenko.2015;79(3):45-54.[13]Ploumis A,Christodoulou P,Kapoutsis D,et al.Surgical treatment of lumbar spinal stenosis with microdecompression and interspinous distraction device insertion.A case series.J Orthop Surg Res.2012;(7):35.[14]Samadian M,Hosseinzadeh Bakhtevari M,Jahangiri Babadi A,et al.Congenital Posterior Spinal Agenesis Leads to L2-L3 Instability: a Case Report and Review of the Literature.Arch Iran Med.2015;8(12):861-864.[15]刘晓光.不稳定型脊柱骨折脱位的内固定技术及进展[J].中国骨伤,2014,27(2):89-91.[16]嘉士健,黄翠华,雷行华,等.针刀配合脊椎平衡手法康复训练治疗下颈椎不稳症临床观察[J].中国中医急症, 2015,24(10): 1829-1831.[17]封亚平,章翔,封雨.加强脊髓脊柱术后不稳与重建研究[J].中华神经外科疾病研究杂志,2013,12(2):97-100.[18]Pound BG.Passive films on metallic biomaterials under simulated physiological conditions.J Biomed Mater Res A.2014;102(5):1595-1604.[19]Bing W,Dong J,Li Q,et al.Mechanism of inhibition on L929 rat fibroblasts proliferation induced by potential adhesion barrier material poly(p-dioxanone-co-l-phenylalanine) electrospun membranes].J Biomed Mater Res A. 2014; 102(11):4062-4070.[20]Pa?cu EI,Stokes J,McGuinness GB.McGuinness.Electrospun composites of PHBV,silk fibroin and nano-hydroxyapatite for bone tissue engineering.Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2013;33(8):4905-4916.[21]侯立刚,杨建义.骨修复中应用的生物降解可吸收材料[J].中国组织工程研究,2016,20(3):441-445.[22]贾世双,张堃,李双.股骨颈并股骨干骨折的修复:骨移植与组织及细胞移植效果评价[J].中国组织工程研究, 2015,19(21): 3424-3428.[23]邢麟子,桂鉴超,徐燕,等.微骨折技术结合自体骨软骨碎屑样移植修复兔膝关节软骨缺损的实验研究[J].中华创伤骨科杂志, 2012, 14(5):424-428.[24]王凤玲.SPIO标记细胞磁靶向移植修复关节软骨缺损可行性的初步研究[D].第三军医大学,2013.[25]李练兵,张其清,侯志伟,等.复合人工骨材料对骨形成影响的实验研究[J].北京生物医学工程,2014,33(3):240-246.[26]马立坤,叶鹏,邓江,等.丝素蛋白/壳聚糖/纳米羟基磷灰石骨组织工程支架材料的体外细胞毒性评价[J].西部医学, 2014,26(8): 975-977,980.[27]帅亚俊,张璨,邓连霞,等.矿化柞蚕丝胶膜表面粗糙度的调控及其对骨髓间充质干细胞生长行为的影响[J].复合材料学报,2 015, 32(5):1527-1535.[28]Zhu M,Kai W,Mei J,et al.Fabrication of highly interconnected porous silk fibroin scaffolds for potential use as vascular grafts.Acta Biomater.2014;10(5):2014-2023.[29]Hofmann S,Stok K S,Kohler T,et al.Effect of sterilization on structural and material properties of 3-D silk fibroin scaffolds. Acta Biomaterialia.2014;10(1):308-317.[30]Lai GJ,Shalumon KT,Chen SH,et al.Composite chitosan/silk fibroin nanofibers for modulation of osteogenic differentiation and proliferation of human mesenchymal stem cells. Carbohydr Polym.2014;111(111):288-297.[31]Niu B,Li B,Gu Y,et al.In vitro evaluation of electrospun silk fibroin/nano-hydroxyapatite/BMP-2 scaffolds for bone regeneration.J Biomater Sci Polym Ed.2017;28(3):257-270. [32]Le TD,Liaudanskaya V,Bonani W,et al.Enhancing bioactive properties of silk fibroin with diatom particles for bone tissue engineering applications.J Tissue Eng Regen Med.2016.doi: 10.1002/term.2373. [Epub ahead of print][33]Yao MZ,Huang-Fu MY,Liu HN,et al.Fabrication and characterization of drug-loaded nano-hydroxyapatite/polyamide 66 scaffolds modified with carbon nanotubes and silk fibroin.Int J Nanomedicine.2016;11:6181-6194.[34]Ran J,Hu J,Sun G,et al.A novel chitosan-tussah silk fibroin/nano-hydroxyapatite composite bone scaffold platform with tunable mechanical strength in a wide range.Int J Biol Macromol.2016;93(Pt A):87-97. [35]Ding Z,Fan Z,Huang X,et al.Silk-Hydroxyapatite Nanoscale Scaffolds with Programmable Growth Factor Delivery for Bone Repair.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces.2016;8(37): 24463-24470.[36]Hu JX,Ran JB,Chen S,et al.Carboxylated Agarose (CA)-Silk Fibroin (SF) Dual Confluent Matrices Containing Oriented Hydroxyapatite (HA) Crystals: Biomimetic Organic/Inorganic Composites for Tibia Repair.Biomacromolecules. 2016; 17(7):2437-2447. [37]Wu J,Liu J,Shi Y,et al.Rheological, mechanical and degradable properties of injectable chitosan/silk fibroin/hydroxyapatite/glycerophosphate hydrogels.J Mech Behav Biomed Mater.2016;64:161-172.[38]Bhattacharjee P,Naskar D,Maiti TK,et al.Non-mulberry silk fibroin grafted poly (?-caprolactone)/nano hydroxyapatite nanofibrous scaffold for dual growth factor delivery to promote bone regeneration.J Colloid Interface Sci.2016;472:16-33. [39]Sinlapabodin S,Amornsudthiwat P,Damrongsakkul S,et al.An axial distribution of seeding, proliferation, and osteogenic differentiation of MC3T3-E1 cells and rat bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells across a 3D Thai silk fibroin/gelatin/hydroxyapatite scaffold in a perfusion bioreactor.Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl.2016;58:960-970. [40]王海莹,张旭,丁文元,等.椎间盘退变动物模型的研究进展[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2015,25(3):279-282.[41]钟锐,刘少喻.腰椎间盘退变动物模型构建的研究进展[J].中华实验外科杂志,2015,32(7):1760-1762.[42]王鹏.骨质疏松大鼠脊柱融合后邻近节段椎间盘退变的实验性研究[D].河北联合大学,2015.[43]杨泽雨,杨欣建,陈扬,等.新型3D打印多孔钛人工椎体在猪脊柱模型置换前后的生物力学测试研究[J].生物骨科材料与临床研究,2016,13(1):7-9.[44]牛伟民,于德水,李名武,等.椎体间纤维性融合重建兔脊柱稳定性的初步探索[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2012,22(12):1108-1112.[45]杨洋,黎庆初,朱召银,等.双节段前路颈椎自锁式融合器融合术后矢状位影像学参数的变化[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2016,26(2): 116-123.[46]谭海涛,孟志斌,黄涛,等.三点稳定式脊柱融合技术效果的动物实验研究[J].临床医学工程,2014,21(3):278-280.[47]张春霖,王若愚,李莹,等.腰椎失稳症患者腰椎间隙X线解剖分型及其临床意义[J].中华解剖与临床杂志,2015,20(6):488-493.[48]吕厚辰,唐佩福.骨组织形态及微观结构的影像学评价及进展[J].中华骨质疏松和骨矿盐疾病杂志,2016,9(1):68-74.[49]江祖炘,谭波,代辉,等.骨髓间充质干细胞和软骨细胞共培养在组织工程化软骨中的研究进展[J].实用医院临床杂志,2014,11(1): 188-190.[50]孙庆治.纳米羟基磷灰石/丝素蛋白人工骨修复骨缺损[J].中国组织工程研究,2015,19(8):1190-1194. |
.jpg)
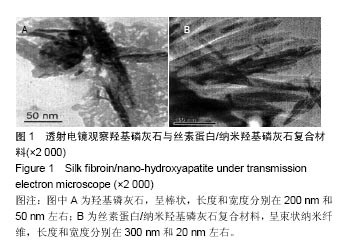
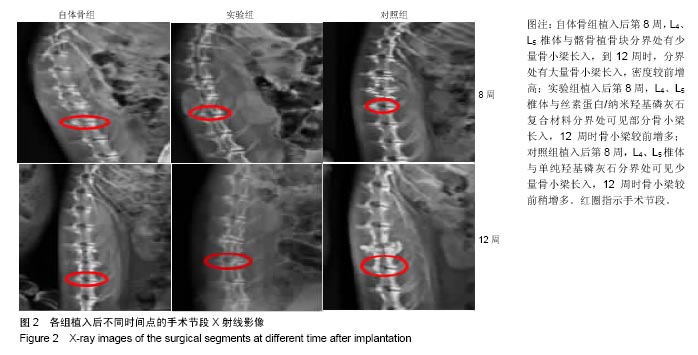
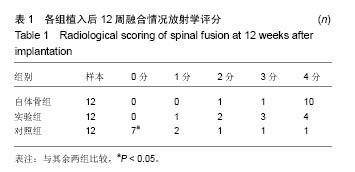

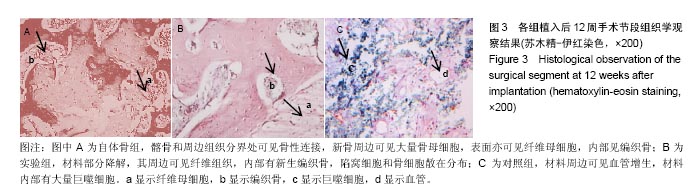
.jpg)