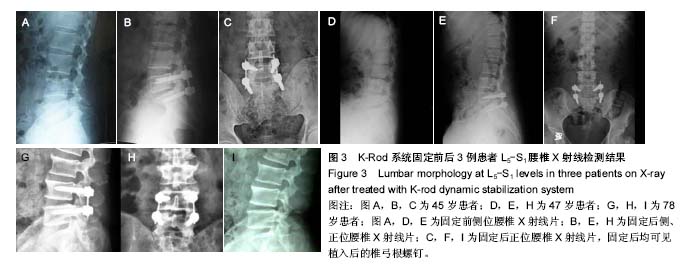
| [1] Eck JC, Humphreys SC, Hodges SD. Adjacent-segment degeneration after lumbar fusion: a review of clinical, biomechanical, and radiologic studies. Am J Orthop. 1999; 28(6):336-340.[2] Lee CK. Accelerated degeneration of the segment adjacent to a lumbar fusion. Spine. 1988;13(3):375-377.[3] Lehmann TR, Spratt KF, Tozzi JE, et al. Long-term followup of lower lumbar fusion patients. Spine. 1987;12(2):97-104.[4] Grob D, Benini A, Junge A, et al. Clinical experience with the Dynesys semirigid fixation system for the lumbar spine: surgical and patient-oriented outcome in 50 cases after an average of 2 years. Spine. 2005;30:324-331.[5] Welch WC, Cheng BC, Awad TE, et al. Clinical outcomes of the Dynesys dynamic neutralization system: 1-year reliminary results. Neurosurg Focus. 2007;22:E8.[6] Mandigo CE, Sampath P, Kaiser MG. Posterior dynamic stabilization of the lumbar spine: pedicle based stabilization with the AccuFlex rod system. Neurosurg Focus. 2007;22:E9.[7] Nockels RP. Dynamic stabilization in the surgical management of painful lumbar spinal disorders. Spine 2005;30:68-72.[8] Tayierjiang J, Waresijiang N, Wang H. Clinical results of the patients with severe kyphosis and paraplegia in different spine segment due to tuberculosis of thoracic and lumbar treated by one stage posterior surgical procedure to debriment of lesion bone fusion with internal fixation by pedicle screw system. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2016; 96(37): 2993-2997. [9] Schimmel JJ, Poeschmann MS, Horsting PP, et al. PEEK cages in lumbar fusion: mid-term clinical outcome and radiologic fusion. Clin Spine Surg. 2016;29(5):E252-E258. [10] Lai Z, Shi SY, Fei J, et al. Mid-term outcome of surgical operation for thoracolumbar tuberculosis. Zhongguo Gu Shang. 2016;29(2):157-161. [11] Ibrahim FM, Abd El-Rady Ael-R. Mono segmental fixation of selected types of thoracic and lumbar fractures; a prospective study. Int Orthop. 2016;40(6):1083-1089. [12] Yuan Q, Han X, Han X, et al. Krag versus Caudad trajectory technique for pedicle screw insertion in osteoporotic vertebrae: biomechanical comparison and analysis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2014;39(26 Spec No.):B27-B35. [13] Techy F, Mageswaran P, Colbrunn RW, et al. Properties of an interspinous fixation device (ISD) in lumbar fusion constructs: a biomechanical study. Spine J. 2013;13(5): 572-579. [14] Dong JW, Feng F, Zhao WD, et al. Biomechanical stability of unilateral pedicle screw fixation on cadaveric model simulated two-level posterior lumbar interbody fusion. Zhonghua Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2011;49(5):436-439. [15] Shirazi-Adl A. Analysis of large compression loads on lumbar spine in flexion and in torsion using a novel wrapping element. J Biomech. 2006;39(2):267-275.[16] 王化瑾,张健,盛伟斌.腰椎单双侧钉棒系统置入内固定与非内固定修复腰椎间盘突出症的比较[J].中国组织工程研究,2016, 20(53):7939-7945.[17] 侯煜,杨雯,杨帆,等.钴合金椎弓根螺钉植入修复脊柱结核重度后凸畸形:自身对照临床试验方案[J].中国组织工程研究, 2016, 20(44):6661-6666.[18] Middendorp M, Vogl TJ, Kollias K, et al. Association between intervertebral disc degeneration and the Oswestry Disability Index. J Back Musculoskelet Rehabil. 2016. doi: 10.3233/BMR-150516.[19] Furunes H, Storheim K, Brox JI, et al. Total disc replacement versus multidisciplinary rehabilitation in patients with chronic low back pain and degenerative discs: Eight-year follow-up of a randomized controlled multicenter trial. Spine J. 2017. doi: 10.1016/j.spinee.2017.05.011. [20] Ebata S, Takahashi J, Hasegawa T, et al. Role of weekly teriparatide administration in osseous union enhancement within six months after posterior or transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion for osteoporosis-associated lumbar degenerative disorders: a multicenter, prospective randomized study. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2017;99(5): 365-372. [21] Keorochana G, Setrkraising K, Woratanarat P, et al. Clinical outcomes after minimally invasive transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion and lateral lumbar interbody fusion for treatment of degenerative lumbar disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Neurosurg Rev. 2016. doi: 10.1007/s10143-016-0806-8.[22] Kim HJ, Kang KT, Park SC, et al. Biomechanical advantages of robot-assisted pedicle screw fixation in posterior lumbar interbody fusion compared with freehand technique in a prospective randomized controlled trial-perspective for patient-specific finite element analysis. Spine J. 2017;17(5):671-680. [23] Lotzke H, Jakobsson M, Brisby H, et al. Use of the PREPARE (PREhabilitation, Physical Activity and exeRcisE) program to improve outcomes after lumbar fusion surgery for severe low back pain: a study protocol of a person-centred randomised controlled trial. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2016;17(1):349.[24] Lindbäck Y, Tropp H, Enthoven P, et al. PREPARE: Pre-surgery physiotherapy for patients with degenerative lumbar spine disorder: a randomized controlled trial protocol. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2016;17:270. [25] Morgan JP, Miller AL, Thompson PA, et al. The Asfora Bullet Cage System Shows Comparable Fusion Rate Success Versus Control Cage in Posterior Lumbar Interbody Fusion in a Randomized Clinical Trial. S D Med. 2016;69(4):157-167.[26] Buser Z, Brodke DS, Youssef JA, et al. Synthetic bone graft versus autograft or allograft for spinal fusion: a systematic review. J Neurosurg Spine. 2016;25(4):509-516.[27] Tschugg A, Michnacs F, Strowitzki M, et al. A prospective multicenter phase I/II clinical trial to evaluate safety and efficacy of NOVOCART Disc plus autologous disc chondrocyte transplantation in the treatment of nucleotomized and degenerative lumbar disc to avoid secondary disease: study protocol for a randomized controlled trial. Trials. 2016; 17(1):108. [28] Garcia R Jr, Yue JJ, Blumenthal S, et al. Lumbar Total Disc Replacement for Discogenic Low Back Pain: Two-year Outcomes of the activL Multicenter Randomized Controlled IDE Clinical Trial. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2015;40(24): 1873-1881.[29] Patel VV, Nunley PD, Whang PG, et al. Superion(®) InterSpinous Spacer for treatment of moderate degenerative lumbar spinal stenosis: durable three-year results of a randomized controlled trial. J Pain Res. 2015;8:657-662. [30] Archer KR, Devin CJ, Vanston SW, et al. Cognitive-Behavioral-Based Physical Therapy for Patients With Chronic Pain Undergoing Lumbar Spine Surgery: a Randomized Controlled Trial. J Pain. 2016;17(1):76-89.[31] Van de Kelft E, Van Goethem J. Trabecular metal spacers as standalone or with pedicle screw augmentation, in posterior lumbar interbody fusion: a prospective, randomized controlled trial.Eur Spine J. 2015;24(11):2597-2606. [32] Litrico S, Recanati G, Gennari A, et al. Single-use instrumentation in posterior lumbar fusion could decrease incidence of surgical site infection: a prospective bi-centric study. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2016;26(1):21-26. [33] Jalalpour K, Neumann P, Johansson C, et al. A Randomized Controlled Trial Comparing Transforaminal Lumbar Interbody Fusion and Uninstrumented Posterolateral Fusion in the Degenerative Lumbar Spine. Global Spine J. 2015;5(4): 322-328. [34] Cao Y, Chen Z, Jiang C, et al. The combined use of unilateral pedicle screw and contralateral facet joint screw fixation in transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion. Eur Spine J. 2015; 24(11):2607-2613. [35] Ruiz-España S, Arana E, Moratal D. Semiautomatic computer-aided classification of degenerative lumbar spine disease in magnetic resonance imaging. Comput Biol Med. 2015;62:196-205.[36] Rolving N, Nielsen CV, Christensen FB, et al. Does a preoperative cognitive-behavioral intervention affect disability, pain behavior, pain, and return to work the first year after lumbar spinal fusion surgery? Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2015; 40(9):593-600. [37] Lavelle W, McLain RF, Rufo-Smith C, et al. Prospective randomized controlled trial of The Stabilis Stand Alone Cage (SAC) versus Bagby and Kuslich (BAK) implants for anterior lumbar interbody fusion. Int J Spine Surg. 2014. doi: 10.14444/1008.[38] Rihn JA, Hilibrand AS, Zhao W, et al. Effectiveness of surgery for lumbar stenosis and degenerative spondylolisthesis in the octogenarian population: analysis of the Spine Patient Outcomes Research Trial (SPORT) data. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2015;97(3):177-185. [39] Sardar Z, Alexander D, Oxner W, et al. Twelve-month results of a multicenter, blinded, pilot study of a novel peptide (B2A) in promoting lumbar spine fusion. J Neurosurg Spine. 2015; 22(4):358-566.[40] van den Akker-van Marle ME, Moojen WA, Arts MP, et al. Interspinous process devices versus standard conventional surgical decompression for lumbar spinal stenosis: cost-utility analysis. Spine J. 2016;16(6):702-710. [41] Xu Y, Zhou M, Liu H, et al. Effect of 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 on posterior transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion in patients with osteoporosis and lumbar disc degenerative disease. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2014;28(8): 969-972. [42] Liu Z, Fei Q, Wang B, et al. A meta-analysis of unilateral versus bilateral pedicle screw fixation in minimally invasive lumbar interbody fusion. PLoS One. 2014;9(11):e111979. [43] Siewe J, Bredow J, Oppermann J, et al. Evaluation of efficacy of a new hybrid fusion device: a randomized, two-centre controlled trial. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2014;15:294. [44] Liu J, Tang J, Liu H. Comparison of one versus two cages in lumbar interbody fusion for degenerative lumbar spinal disease: a meta-analysis. Orthop Surg. 2014;6(3):236-243. [45] Zheng Y, Wang J, Yuan C, et al. Effect of intravenous mannitol or dexamethasone on low back and leg pain after lumbar fusion surgery. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2014;28(5):544-548. [46] Puzzilli F, Gazzeri R, Galarza M, et al. Interspinous spacer decompression (X-STOP) for lumbar spinal stenosis and degenerative disk disease: a multicenter study with a minimum 3-year follow-up. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2014; 124:166-174. [47] Kaiser MG, Groff MW, Watters WC 3rd, et al. Guideline update for the performance of fusion procedures for degenerative disease of the lumbar spine. Part 16: bone graft extenders and substitutes as an adjunct for lumbar fusion. J Neurosurg Spine. 2014;21(1):106-132. [48] Vieira-Pellenz F, Oliva-Pascual-Vaca A, Rodriguez-Blanco C, et al. Short-term effect of spinal manipulation on pain perception, spinal mobility, and full height recovery in male subjects with degenerative disk disease: a randomized controlled trial. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2014;95(9): 1613-1619. [49] Shen X, Zhang H, Gu X, et al. Unilateral versus bilateral pedicle screw instrumentation for single-level minimally invasive transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion. J Clin Neurosci. 2014;21(9):1612-1616. [50] Parker SL, Godil SS, Mendenhall SK, et al. Two-year comprehensive medical management of degenerative lumbar spine disease (lumbar spondylolisthesis, stenosis, or disc herniation): a value analysis of cost, pain, disability, and quality of life: clinical article. J Neurosurg Spine. 2014;21(2): 143-149.[51] Rolving N, Oestergaard LG, Willert MV, et al. Description and design considerations of a randomized clinical trial investigating the effect of a multidisciplinary cognitive-behavioural intervention for patients undergoing lumbar spinal fuson surgery. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2014;15:62.[52] Hart R, Komzák M, Okál F, et al. Allograft alone versus allograft with bone marrow concentrate for the healing of the instrumented posterolateral lumbar fusion. Spine J. 2014; 14(7):1318-1324. |
.jpg)

.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)