| [1]Geiger M,Li RH,Friess W.Collagen sponges for bone regeneration with rhBMP-2.Adv Drug Del Rev.2003; 55(12): 1613-1629.[2]Chattopadhyay S,Raines RT.Review collagen-based biomaterials for wound healing.Biopolymers. 2014;101(8): 821-833.[3]Ramshaw John AM.Biomedical applications of collagens.J Biomed Mater Res. 2016;104(4):665-675.[4]Silva JC,Barros AA,Aroso IM,et al.Extraction of Collagen/Gelatin from the Marine Demosponge Chondrosia reniformis (Nardo, 1847) Using Water Acidified with Carbon Dioxide - Process Optimization.Ind Eng Chem Res.2016; 55(25):6922-6930.[5]Ghodbane Salim A,Dunn Michael G.Physical and mechanical properties of cross-linked type I collagen scaffolds derived from bovine, porcine, and ovine tendons.J Biomed Mater Res A.2016;104(11):2685-2692.[6]康岚,姚霞,朱健勋,等.林蛙皮中胶原蛋白的含量测定研究[J].吉林中医药,2014,34(10):1011-1013.[7]郑淼,周亚丹,赵敏.东北林蛙皮中胶原蛋白含量的测定及提取工艺[J].东北林业大学学报,2008,36(7):81-83.[8]Zheleva DI.Review and comparative analysis of keratin biocomposites with composites based on collagen.Bulg Chem Commun.2015;47:10-15. [9]Ma L,Gao C,Mao Z,et al.Collagen/chitosan porous scaffolds with improved biostability for skin tissue engineering. Biomaterials. 2003,24(26):4833-4841.[10]Weadock KS,Miller EJ,Bellincampi LD,et al.Physical crosslinking of collagen fibers: comparison of ultraviolet irradiation and dehydrothermal treatment.J Biomed Mater Res.1995;29(11):1373-1379.[11]Lew DH,Liu PH,Orgill DP.Optimization of UV cross-linking density for durable and nontoxic collagen GAG dermal substitute.J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater.2007;82(1):51-56.[12]Martinez AW,Caves JM,Ravi S,et al.Effects of crosslinking on the mechanical properties, drug release and cytocompatibility of protein polymers.Acta Biomater. 2014;10:26-33.[13]Kishen A,Shrestha S,Shrestha A,et al.Characterizing the collagen stabilizing effect of crosslinked chitosan nanoparticles against collagenase degradation.Dent Mater. 2016;32(8):968-977.[14]黄煜.鱼鳞胶原的提取及胶原止血海绵的制备[D].福建农林大学硕士论文,2012.[15]张立彦,芮汉明,张玲.制备条件对壳聚糖-胶原蛋白海绵敷料性能的影响[J].化工进展,2011,30(2):390-395.[16]汪海婴,梁艳萍,李云雁,等.鱼源胶原蛋白海绵材料的构建及其生物学性能[J].华中科技大学学报(医学版),2012,41(6):709-715.[17]但年华,刘新华,但卫华,等.猪源I 型胶原/壳聚糖复合海绵的制备[J].皮革科学与工程,2014,24(3):17-22.[18]Nistor MT,Chiriac AP,Vasile C,et al.Synthesis of hydrogels based on poly(NIPAM) inserted into collagen sponge.Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces.2011;87(2):382-390..[19]Kim MS,Hong KD,Shin HW,et al. Preparation of porcine small intestinal submucosa sponge and their application as a wound dressing in full-thickness skin defect of rat. Int J Biol Macromol.2005;36(1-2):54-60.[20]何兰.牛骨胶原蛋白的提取及复合海绵的制备研究[D].华中农业大学硕士论文,2012.[21]汪海波,梁艳萍,李云雁,等. 交联方法对草鱼皮胶原蛋白海绵性能的影响[J].水产学报,2013,37(1):132-138.[22]Lin YK , Liu DC.Studies of novel hyaluronic acid-collagen sponge materials composed of two different species of type I collagen.J Biomater Appl.2007;21(3):265-281.[23]江颖,邓明霞,汪海婴,等.热变性对鱼胶原海绵材料性能的影响[J].功能材料,2015,46(9): 9045-9051. [24]Miles CA,Bailey AJThermal denaturation of collagen revisited.Proc Indian Acad Sci(Chem Sci).1999;111:71-80.[25]许媛媛.胶原海绵的改性及其作为活性因子载体的研究[D].中国人民解放军军事医学科学院硕士论文,2008[26]Horn MM,Martins VCA,de Guzzi Plepis AM.Interaction of anionic collagen with chitosan: effect on thermal and morphological characteristics.Carbohydr Polym.2009; 77(2): 239-243.[27]马茂.壳聚糖-类人胶原蛋白海绵的生物相容性及止血效果研究[D].西北大学博士论文,2008.[28]Sun KH,Liu Z,Liu C,et al.Evaluation of in vitro and in vivo biocompatibility of a myo-inositol hexakisphosphate gelated polyaniline hydrogel in a rat model.Sci Rep.2016;13;6:23931.[29]段志广.类人胶原蛋白止血海绵的性能研究[D].西北大学硕士论文,2008.[30]叶真铭.胶原蛋白止血海绵的研制[D].哈尔滨工业大学硕士论文,2013.[31]王慰慰.中国林蛙皮肤活性肽研究进展[J].新农业.2013;11:4-5.[32]Mahmoud Azza A,Salama Alaa H.Norfloxacin-loaded collagen/chitosan scaffolds for skin reconstruction: Preparation, evaluation and in-vivo wound healing assessment. Eur J Pharm Sci.2016;83:155-165.[33]付佳奇.鲤鱼鱼皮胶原蛋白交联物的制备研究[D].大连海洋大学硕士论文,2015.[34]郭豪.鱼胶原基复合海绵的制备及其用作缓释药膜的研究[D].福州大学硕士论文,2014.[35]Park H,Guo X,Temenoff JS,et al.Effect of swelling ratio of injectable hydrogel composites on chondrogenic differentiation of encapsulated rabbit marrow mesenchymal stem cells in vitro.Biomacromolecules.2009;10:541-546.[36]Angele P,Abke J,Kujat R,et al.Influence of different collagen species on physico-chemical properties of crosslinked collagen matrices.Biomaterials. 2004;25:2831-2841.[37]Santhosh KB,Sahaja A,Vijaya RD.Air-dried 3D-collagen-chitosan biocomposite scaffold for tissue engineering application.Polym Compos.2012;33(11): 2029-2035.[38]Jeevithan E,Shakila RJ,Varatharajakumar A,et al. Physico-functional and mechanical properties of chitosan and calcium salts incorporated fish gelatin scaffolds. Int J Biol Macromol.2013;60:262-267.[39]Pal P,Srivas PK,Dadhich P,et al.Accelerating full thickness wound healing using collagen sponge of mrigal fish (Cirrhinus cirrhosus) scale origin.Int J Biol Macromol.2016;93(SI):1507- 1518.[40]Chandika P,Ko SC,Oh GW,et al.Fish collagen/alginate/ chitooligosaccharides integrated scaffold for skin tissue regeneration application.Int J Biol Macromol.2015;81: 504-513. [41]Muthukumar T,Prabu P,Ghosh K,et al.Fish scale collagen sponge incorporated with Macrotyloma uniflorum plant extract as a possible wound/burn dressing material.Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces.2014;113:207-212.[42]Zhou T,Wang N,Xue Y,et al.Electrospun tilapia collagen nanofibers accelerating wound healing via inducing keratinocytes proliferation and differentiation.Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces.2016;143:415-422. [43]Shekhter AB,Guller AE,Istranov LP,et al.Morphology of collagen matrices for tissue engineering (biocompatibility, biodegradation, tissue response).Arkh Patol. 2015;77(6): 29-38. [44]Venugopal B,Fernandez FB,Harikrishnan VS,et al.Post implantation fate of adipogenic induced mesenchymal stem cells on Type I collagen scaffold in a rat model.J Mater Sci Mater Med.2017;28(2):28. [45]Zhou T,Wang N,Xue Y,et al.Development of biomimetic tilapia collagen nanofibers for skin regeneration through inducing keratinocytes differentiation and collagen synthesis of dermal fibroblasts.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces.2015;7(5):3253-3262.[46]汪海波,梁艳萍,李云雁,等.交联方法对草鱼皮胶原蛋白海绵性能的影响[J].水产学报,2013,37(1):132-140. |
.jpg)
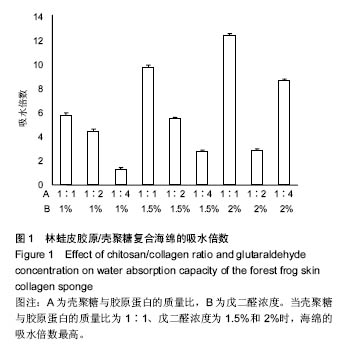
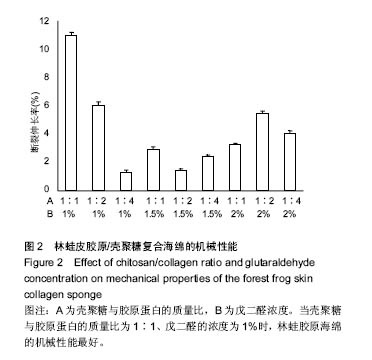
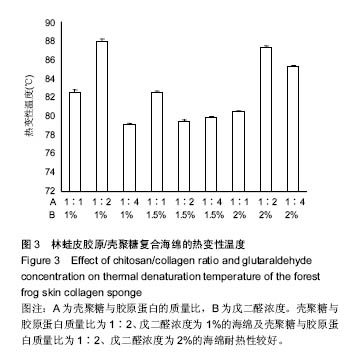
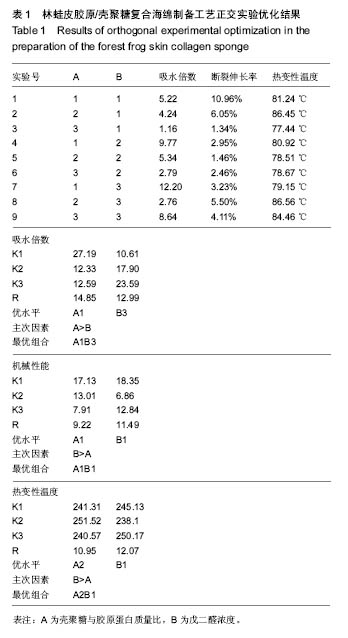
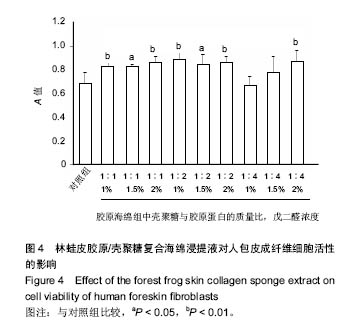
.jpg)
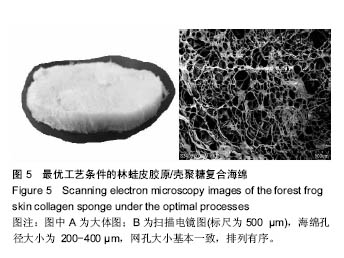
.jpg)