| [1]Ghazanfari S, Khademhosseini A, Smit TH. Mechanisms of lamellar collagen formation in connective tissues. Biomaterials. 2016;97:74-84.[2]Ricard-Blum S, Ruggiero F.The collagen superfamily: from the extracellular matrix to the cell membrane. Pathol Biol (Paris). 2005;53(7):430-442.[3]曾名勇,张联英,刘尊英,等. 几种鱼皮胶原蛋白的理化特性及其影响因素[J]. 中国海洋大学学报:自然科学版, 2005,35(4): 608-612.[4]但卫华,王坤余,曾睿,等. 胶原的医学应用及其发展前景[J]. 生物医学工程与临床,2004,8(1):45-48,52.[5]赵颖,陆金婷,邓超,等. 纤维化胶原蛋白海绵的制备及其自组装工艺[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2015,19(30):4820-4826.[6]汪海波,梁艳萍,李云雁,等. 交联方法对草鱼皮胶原蛋白海绵性能的影响[J]. 水产学报,2013,37(1):132-140.[7]de Wild M, Pomp W, Koenderink GH. Thermal memory in self-assembled collagen fibril networks. Biophys J. 2013; 105(1):200-210.[8]Li Y,Asadi A,Monroe MR,et al. pH effects on collagen fibrillogenesis in vitro : Electrostatic interactions and phosphate binding. Materials Science & Engineering C. 2009;29(5):1643-1649.[9]Burduk PK, Wierzchowska M, Grze?kowiak B, et al. Clinical outcome and patient satisfaction using biodegradable (NasoPore) and non-biodegradable packing, a double-blind, prospective, randomized study. Braz J Otorhinolaryngol. 2016. [Epub ahead of print][10]赵国锋,王东海.纳吸棉在鼻内镜术后鼻腔填塞的应用[J]. 中国误诊学杂志, 2010,10(3):524-525.[11]Zeng SK, Zhang CH, Lin H, et al. Isolation and characterisation of acid-solubilised collagen from the skin of Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Food Chemistry. 2009; 116(4):879-883.[12]Yan M, Li B, Zhao X, et al. Effect of concentration, pH and ionic strength on the kinetic self-assembly of acid-soluble collagen from walleye pollock (Theragra chalcogramma) skin. Food Hydrocolloids.2012;29:199-204.[13]中国农业大学,农业部奶及奶制品质量监督检验测试中心,农业部食品质量监督检验测试中心,农业部乳品质量监督检验测试中心. 中华人民共和国农业行业标准NY/T1678-2008乳与乳制品中蛋白质的测定双缩脲比色法[J]. 农产品质量与安全, 2008(6):32-33.[14]方林,黄红海.ATR-FTIR光谱技术在高聚物研究中的应用[J]. 化学工程师,2008,22(3):33-35,50.[15]Zheng X, Hu J, Chen Y, et al. AFM study of the effects of collagenase and its inhibitors on dentine collagen fibrils. J Dent. 2012;40(2):163-171.[16]Prockop DJ,Hulmes DJS. Assembly of Collagen Fibrils de Novo from Soluble Precursors: Polymerization and Copolymerization of Procollagen, pN-Collagen, and Mutated Collagens. In: Birk DE, Mecham RP, editors. Extracellular Matrix Assembly and Structure. San Diego: Academic Press, 1994:47-90.[17]Li X, Li Y, Hua Y, et al. Effect of concentration, ionic strength and freeze-drying on the heat-induced aggregation of soy proteins. Food Chemistry. 2007; 104(4):1410-1417.[18]Marelli B, Ghezzi CE, Zhang YL, et al. Fibril formation pH controls intrafibrillar collagen biomineralization in vitro and in vivo. Biomaterials. 2015;37:252-259.[19]温祖谍. 胶原的两性及其等电点[J]. 皮革科技, 1980(4): 32-37.[20]赵燕,鲁亮,杨玲,等.草鱼皮胶原的体外自组装动力学研究[J]. 食品科学, 2014, 35(11): 21-26. |
.jpg)
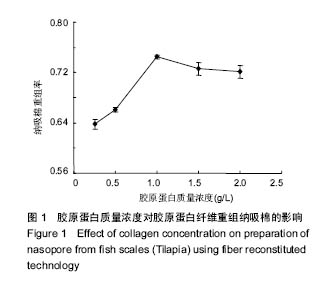
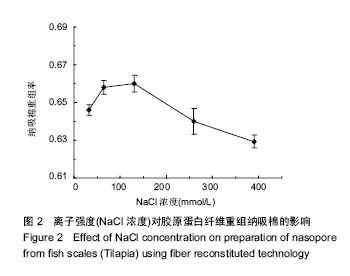
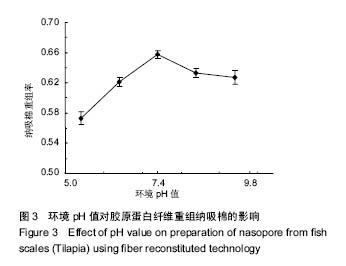
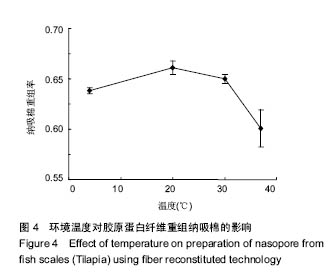
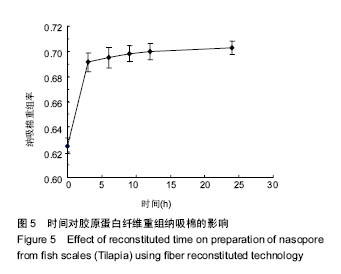
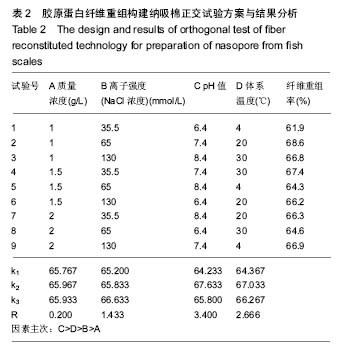
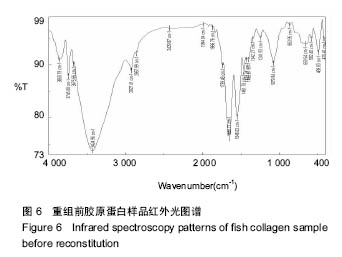
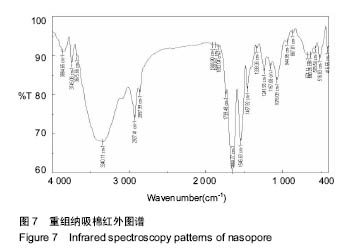

.jpg)
.jpg)