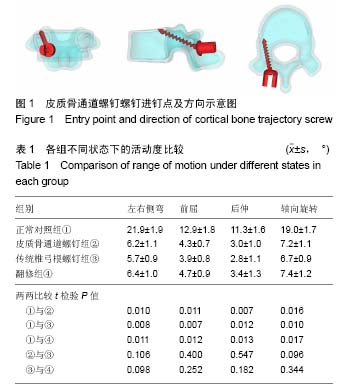
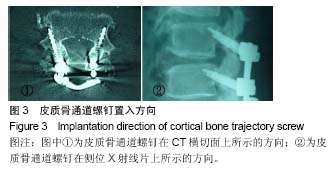
| [1] Ohlin A,Karlsson M,Düppe H, et al.Complications after transpedicular stabilization of the spine. A survivorship analysis of 163 cases.Spine (Phila Pa 1976).1994;19(24): 2774-2779.[2] Wittenberg RH,Shea M,Swartz DE,et al.Importance of bone mineral density in instrument spine fusions. Spine(Phila Pa 1976).1991;16(4):647-652.[3] Santoni BG,Hynes RA,McGilvray KC,et al.Cortical bone trajectory for lumbar pedicle screws.Spine(Phila Pa 1976). 2009;9:366-373.[4] Erkan S,Wu C,Mehbod AA,et al.Biomechanical evaluation of a new AxiaLIF technique for two- level lumbar fusion.Eur Spine J.2009;18(6):807-814.[5] Matsukawa K, Yato Y, Nemoto O, et al.Morphometric Measurement of Cortical Bone Trajectory for Lumbar Pedicle Screw Insertion Using Computed Tomography.J Spinal Disord Tech.2013;26:248-253.[6] Phan K,Hogan J,Maharaj M,et al.Cortical Bone Trajectory for Lumbar Pedicle Screw Placement: A Review of Published Reports.Orthop Surg.2015;7(3):213-221.[7] Roy-Camille R,Saillant G,Mazel C.Plating of thoracic, thoracolumbar, and lumbar injuries with pedicle screw plates.Orthop Clin North Am.1986;17(1):147-159.[8] Gurr KR,McAfee PC,Shih CM.Biomechanical analysis of posterior instrumentation systems after decompressive laminectomy. An unstable calf-spine model.J Bone Joint Surg Am.1988;70(5):680-691.[9] Riley LH 3rd,Eck JC,Yoshida H,et al.A Biomechanical Comparison of Calf Versus Cadaver Lumbar Spine Models.Spine(Phila Pa 1976).2004;29(11):217-220.[10] Steffee AD,Biscup RS,Sitkowski DJ.Segmental Spine Plates with Pedicle Screw Fixation. A New Internal Fixation Device for Disorders of the Lumbar and Thoracolumbar Spine.Clin Orthop Relat Res.1986;203:45-53.[11] Mai HT,Mitchell SM,Hashmi SZ,et al.Differences in bone mineral density of fixation points between lumbar cortical and traditional pedicle screws.Spine J. 2016;16(7):835-841.[12] Matsukawa K,Taguchi E,Yato Y,et al. Evaluation of the Fixation Strength of Pedicle Screws Using Cortical Bone Trajectory: What Is the Ideal Trajectory for Optimal Fixation? Spine(Phila Pa 1976).2015;40(15):E873-878. [13] Matsukawa K,Yato Y,Imabayashi H,et al.Biomechanical evaluation of the fixation strength of lumbar pedicle screws using cortical bone trajectory: a finite element study.J Neurosurg Spine.2015;23(4):471-478. [14] Oshino H,Sakakibara T,Inaba T,et al.A biomechanical comparison between cortical bone trajectory fixation and pedicle screw fixation.J Orthop Surg Res.2015;10:125.[15] Matsukawa K,Yato Y,Kato T,et al.In vivo analysis of insertional torque during pedicle screwing using cortical bone trajectory technique. Spine(Phila Pa 1976).2014; 39(4):240-245.[16] Wittenberg RH,Shea M,Swartz DE,et al.Importance of bone mineral density in instrument spine fusions.Spine(Phila Pa 1976).1991;16(4):647-652.[17] Inceo?lu S,Montgomery WH Jr,St Clair S,et al.Pedicle screw insertion angle and pullout strength:comparison of 2 proposed. strategies.J Neurosurg Spine.2011;14:670-676.[18] Mehta H,Santos E,Ledonio C,et al.Biomechanical analysis of pedicle screw thread differential design in an osteoporotic cadaver model.Clin Biomech.2012;27:234-240.[19] Ueno M,Sakai R,Tanaka K,et al.Should we use cortical bone screws for cortical bone trajectory?J Neurosurg Spine.2015; 22(4):416-421. [20] Perez-Orribo L,Kalb S,Phillip M,et al.Biomechanics of Lumbar Cortical Screw–Rod Fixation Versus Pedicle Screw-Rod Fixation With and Without Interbody Support.Spine(Phila Pa 1976).2013;38:635-641.[21] Baluch DA,Patel AA,Lullo B,et al.Effect of physiological loads on cortical and traditional pedicle screw fixation.Spine(Phila Pa 1976).2014;39(22):E1297-1302.[22] Kasukawa Y,Miyakoshi N,Hongo M,et al.Short-Term Results of Transforaminal Lumbar Interbody Fusion Using Pedicle Screw with Cortical Bone Trajectory Compared with Conventional Trajectory.Asian Spine J.2015;9(3):440-448.[23] Skinner R,Maybee J,Transfeldt E,et al.Experimental pullout testing and comparison of variables in transpedicular screw fixation. A biomechanical study.Spine(Phila Pa 1976).1990; 15(3):195-201.[24] Hirano T,Hasegawa K,Takahashi HE,et al.Structural characteristics of the pedicle and its role in screw stability.Spine(Phila Pa 1976). 1997;22(21):2504-2509.[25] Hirano T,Hasegawa K,Washio T,et al. Fracture risk during pedicle screw insertion in osteoporotic spine.Spinal Disord. 1998;11(6):493-497.[26] Fan S,Liu S,Deng Y.An in vitro biomechanical evaluation of effect of augmentation pedicle screw fixation with polymethylmethacrylate on osteoporotic spine stability. Zhong guo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi.2004;18(3):168-170.[27] Polly DW JR,Orchowski JR,Ellenbogen RG.Revision pedicle screws. Bigger, longer shims--what is best? Spine(Phila Pa 1976).1998;23(12):1374-1379.[28] Mizuno M,Kuraishi K,Umeda Y,et al.Midline lumbar fusion with cortical bone trajectory screw.Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo). 2014;54(9):716-721. [29] Song T,Hsu WK,Ye T.Lumbar pedicle cortical bone trajectory screw.Chin Med J (Engl).2014;127(21):3808-3813.[30] Rodriguez A,Neal MT,Liu A,et al.Novel placement of cortical bone trajectory screws in previously instrumented pedicles for adjacent-segment lumbar disease using CT image-guided navigation.Neurosurg Focus.2014;36(3):E9. [31] Takata Y,Matsuura T,Higashino K,et al.Hybrid technique of cortical bone trajectory and pedicle screwing for minimally invasive spine reconstruction surgery: a technical note.J Med Invest.2014;61(3-4):388-392.[32] Ninomiya K,Iwatsuki K,Ohnishi Y,et al.Radiological Evaluation of the Initial Fixation between Cortical Bone Trajectory and Conventional Pedicle Screw Technique for Lumbar Degenerative Spondylolisthesis.Asian Spine J.2016;10(2): 251-257.[33] Kotani Y,Abumi K,Ito M,et al.Mid-term clinical results of minimally invasive decompression and posterolateral fusion with percutaneous pedicle screws versus conventional approach for degenerative spondylolisthesis with spinal stenosis.Eur Spine J.2012;21(6):1171-1177. [34] Phan K,Hogan J,Maharaj M,et al.Cortical Bone Trajectory for Lumbar Pedicle Screw Placement: A Review of Published Reports.Orthop Surg.2015;7(3):213-221. |
.jpg)

.jpg)