| [1] Lu H, Huang D, Ransohoff RM,et al. Acute skeletal muscle injury: CCL2 expression by both monocytes and injured muscle is required for repair.FASEB J. 2011;25(10):3344-3355.
[2] Chien SH, Chen SK, Lin SY,et al. Repair method and healing of skeletal muscle injury. Gaoxiong Yi Xue Ke Xue Za Zhi.1991;7(9):481-488.
[3] Mu X, Peng H, Pan H, et al. Study of muscle cell dedifferentiation after skeletal muscle injury of mice with a Cre-Lox system.PLoS One.2011;6(2):e16699.
[4] Castiglioni A,Corna G,Rigamonti E,et al.Rovere- Querini P.FOXP3+ T Cells Recruited to Sites of Sterile Skeletal Muscle Injury Regulate the Fate of Satellite Cells and Guide Effective Tissue Regeneration.PLoS One.2015;10(6):e0128094.
[5] 王光.细胞生长因子对失神经骨骼肌萎缩的作用机制分析[J].医学综述,2010,16(18):2754-2757.
[6] Nicholas J, Voss JG, Tsuji J,et al.Time course of chemokine expression and leukocyte infiltration after acute skeletal muscle injury in mice.Innate Immun. 2015 Apr;21(3):266-274.
[7] Radi ZA, Koza-Taylor PH, Bell RR,et al. Increased serum enzyme levels associated with kupffer cell reduction with no signs of hepatic or skeletal muscle injury.Am J Pathol. 2011;179(1):240-247
[8] de Almeida P, Tomazoni SS, Frigo L,et al.What is the best treatment to decrease pro-inflammatory cytokine release in acute skeletal muscle injury induced by trauma in rats: low-level laser therapy, diclofenac, or cryotherapy? Lasers Med Sci.2014;29(2):653-658.
[9] Wirsdörfer F, Bangen JM, Pastille E,et al. Breaking the co-operation between bystander T-cells and natural killer cells prevents the development of immunosuppression after traumatic skeletal muscle injury in mice.Clin Sci (Lond). 2015;128(11):825-838.
[10] Gumucio JP, Flood MD, Phan AC,et al.Targeted inhibition of TGF-β results in an initial improvement but long-term deficit in force production after contraction-induced skeletal muscle injury. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2013 Aug 15;115(4):539-45.
[11] Park JK, Ki MR, Lee EM,et al. Losartan improves adipose tissue-derived stem cell niche by inhibiting transforming growth factor-β and fibrosis in skeletal muscle injury. Cell Transplant.2012;21(11):2407-2424.
[12] 黄人健,彭宝珍,周国瑛,等.人心肌肌球蛋白轻链1与重链和肌动蛋白的结合[J].生物化学与生物物理学报,2001, (1):41-45.
[13] Fuchs B, Zumstein M, Regenfelder F,et al. Upregulation of alpha-skeletal muscle actin and myosin heavy polypeptide gene products in degenerating rotator cuff muscles.J Orthop Res.2008; 26(7):1007-11.
[14] Onuoha GN, Alpar EK, Laprade M,et al. Effects of bone fracture and surgery on plasma myosin heavy chain fragments of skeletal muscle. Clin Invest Med. 1999;22(5):180-184.
[15] Lu H, Huang D, Saederup N,et al. Macrophages recruited via CCR2 produce insulin-like growth factor-1 to repair acute skeletal muscle injury.FASEB J. 2011; 25(1):358-369.
[16] Lefaucheur JP, Gjata B, Lafont H,et al.Angiogenic and inflammatory responses following skeletal muscle injury are altered by immune neutralization of endogenous basic fibroblast growth factor, insulin-like growth factor-1 and transforming growth factor-beta 1.J Neuroimmunol. 1996 Oct;70(1):37-44.
[17] 刘建华,柏志全,黎昭洪,等.bFGF对大鼠坐骨神经损伤后骨骼肌功能恢复的促进作用[J].广州医药,1999,30(3): 15-17.
[18] 柏志全,刘建华,王子栋,等.bFGF对大鼠坐骨神经损伤后腓肠肌功能恢复的影响[J].暨南大学学报(自然科学与医学版),1999(4):1-3.
[19] Stratos I, Madry H, Rotter R,et al. Fibroblast growth factor-2-overexpressing myoblasts encapsulated in alginate spheres increase proliferation, reduce apoptosis, induce adipogenesis, and enhance regeneration following skeletal muscle injury in rats. Tissue Eng Part A. 2011;17(21-22):2867-2877.
[20] Suzuki S, Yamanouchi K, Soeta C,et al.Skeletal muscle injury induces hepatocyte growth factor expression in spleen. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2002;292(3):709-714.
[21] Ikutomo M, Sakakima H, Matsuda F, et al. Midkine- deficient mice delayed degeneration and regeneration after skeletal muscle injury.Acta Histochem. 2014; 116(2):319-326.
[22] Jerkovic R, Argentini C, Serrano-Sanchez A,et al. Early myosin switching induced by nerve activity in regenerating slow skeletal muscle.Cell Struct Funct. 1997;22(1):147-153.
[23] 陈渊,钟天来,李寿田,等.家兔半膜肌各亚部肌球蛋白重链表达差异的实验研究[J].遵义医学院学报,2011,(5): 448-452.
[24] 蔡永清,李名扬,靳仕信.家兔半腱肌和半膜肌的亚部化及肌纤维型构成的研究[J].大连医科大学学报,1988, 10(2): 45-49.
[25] Andrew C,FRY Michael H,FERKIN Brian K,等.雌、雄草原田鼠外周骨骼肌肌球蛋白重链的表达[J].动物学报, 2008, (1):104-110.
[26] Smith HK, Plyley MJ, Rodgers CD,et al.Expression of developmental myosin and morphological characteristics in adult rat skeletal muscle following exercise-induced injury.Eur J Appl Physiol Occup Physiol.1999;80(2):84-91.
[27] Zhang J,Dhoot GK.Localized and limited changes in the expression of myosin heavy chains in injured skeletal muscle fibers being repaired. Muscle Nerve. 1998;21(4):469-81.
[28] Koh IH, Kang HJ, Jeon SW,et al. Passive skeletal muscle excursion after tendon rupture correlates with increased collagen content in muscle.Yonsei Med J. 2014;55(5):1395-1399.
[29] Yun YR, Lee S, Jeon E,et al. Fibroblast growth factor 2-functionalized collagen matrices for skeletal muscle tissue engineering.Biotechnol Lett. 2012;34(4): 771-778.
[30] Baptista J, Martins MD, Pavesi VC,et al. Influence of laser photobiomodulation on collagen IV during skeletal muscle tissue remodeling after injury in rats. Photomed Laser Surg. 2011;29(1):11-17.
[31] Koskinen SO, Wang W, Ahtikoski AM,et al. Acute exercise induced changes in rat skeletal muscle mRNAs and proteins regulating type IV collagen content.Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2001;280(5): R1292-300.
[32] Chen YH, Peng YL, Wang Y,et al.TGF-β1-induced synthesis of collagen fibers in skeletal muscle-derived stem cells.J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci. 2013;33(2):238-243.
[33] de Souza TO, Mesquita DA, Ferrari RA, et al. Phototherapy with low-level laser affects the remodeling of types I and III collagen in skeletal muscle repair. Lasers Med Sci.2011;26(6):803-814.
[34] 石艺平.人源Ⅲ型胶原蛋白在毕赤酵母中表达及性质研究[D].福建:福建师范大学, 2014:1-82. |
.jpg) 文题释义:
肌球蛋白:肌原纤维粗丝的组成单位。存在于横纹肌和平滑肌中。在肌肉运动中起重要作用。其分子形状如豆芽状,由2条重链和多条轻链构成。2条重链的大部分相互螺旋形地缠绕为杆状,构成豆芽状的杆;重链的剩余部分与轻链一起,构成豆芽的瓣。被激活后,具有活性的、能分解ATP的ATP酶。其分子量约为51万。在粗丝中,都是分子的头朝向粗丝的两端,呈纵向线性缔合排列。
肝细胞生长因子:存在于骨骼肌,通过激活静止卫星细胞刺激卫星细胞增殖并促进骨骼肌再生。
文题释义:
肌球蛋白:肌原纤维粗丝的组成单位。存在于横纹肌和平滑肌中。在肌肉运动中起重要作用。其分子形状如豆芽状,由2条重链和多条轻链构成。2条重链的大部分相互螺旋形地缠绕为杆状,构成豆芽状的杆;重链的剩余部分与轻链一起,构成豆芽的瓣。被激活后,具有活性的、能分解ATP的ATP酶。其分子量约为51万。在粗丝中,都是分子的头朝向粗丝的两端,呈纵向线性缔合排列。
肝细胞生长因子:存在于骨骼肌,通过激活静止卫星细胞刺激卫星细胞增殖并促进骨骼肌再生。.jpg) 文题释义:
肌球蛋白:肌原纤维粗丝的组成单位。存在于横纹肌和平滑肌中。在肌肉运动中起重要作用。其分子形状如豆芽状,由2条重链和多条轻链构成。2条重链的大部分相互螺旋形地缠绕为杆状,构成豆芽状的杆;重链的剩余部分与轻链一起,构成豆芽的瓣。被激活后,具有活性的、能分解ATP的ATP酶。其分子量约为51万。在粗丝中,都是分子的头朝向粗丝的两端,呈纵向线性缔合排列。
肝细胞生长因子:存在于骨骼肌,通过激活静止卫星细胞刺激卫星细胞增殖并促进骨骼肌再生。
文题释义:
肌球蛋白:肌原纤维粗丝的组成单位。存在于横纹肌和平滑肌中。在肌肉运动中起重要作用。其分子形状如豆芽状,由2条重链和多条轻链构成。2条重链的大部分相互螺旋形地缠绕为杆状,构成豆芽状的杆;重链的剩余部分与轻链一起,构成豆芽的瓣。被激活后,具有活性的、能分解ATP的ATP酶。其分子量约为51万。在粗丝中,都是分子的头朝向粗丝的两端,呈纵向线性缔合排列。
肝细胞生长因子:存在于骨骼肌,通过激活静止卫星细胞刺激卫星细胞增殖并促进骨骼肌再生。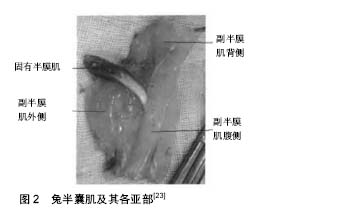
.jpg)
.jpg) 文题释义:
肌球蛋白:肌原纤维粗丝的组成单位。存在于横纹肌和平滑肌中。在肌肉运动中起重要作用。其分子形状如豆芽状,由2条重链和多条轻链构成。2条重链的大部分相互螺旋形地缠绕为杆状,构成豆芽状的杆;重链的剩余部分与轻链一起,构成豆芽的瓣。被激活后,具有活性的、能分解ATP的ATP酶。其分子量约为51万。在粗丝中,都是分子的头朝向粗丝的两端,呈纵向线性缔合排列。
肝细胞生长因子:存在于骨骼肌,通过激活静止卫星细胞刺激卫星细胞增殖并促进骨骼肌再生。
文题释义:
肌球蛋白:肌原纤维粗丝的组成单位。存在于横纹肌和平滑肌中。在肌肉运动中起重要作用。其分子形状如豆芽状,由2条重链和多条轻链构成。2条重链的大部分相互螺旋形地缠绕为杆状,构成豆芽状的杆;重链的剩余部分与轻链一起,构成豆芽的瓣。被激活后,具有活性的、能分解ATP的ATP酶。其分子量约为51万。在粗丝中,都是分子的头朝向粗丝的两端,呈纵向线性缔合排列。
肝细胞生长因子:存在于骨骼肌,通过激活静止卫星细胞刺激卫星细胞增殖并促进骨骼肌再生。