| [1] Harris ST, Blumentals WA, Miller PD. Ibandronate and the risk of non-vertebral and clinical fractures in women with postmenopausal osteoporosis: results of a meta-analysis of phase III studies.Curr Med Res Opin. 2008;24(1): 237-245. [2] Hopkins RB, Goeree R, Pullenayegum E, et al. The relative efficacy of nine osteoporosis medications for reducing the rate of fractures in post-menopausal women.BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2011;26(12): 209-210.[3] Wallace DJ.Rapid prevention of vertebral fractures associated with osteoporosis.Orthopedics. 2005;28(3): 291-298.[4] 吕淑兰,邹余粮,曹缵孙,等.围绝经期妇女激素替代治疗的临床研究[J].西安医科大学学报. 2001,22(6): 552-554.[5] Baim S, Wilson CR, Lewiecki EM, et al. Precision assessment and radiation safety for dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry:position paper of the International Society for Clinical Densitometry.J Clin Densitom. 2005;8(8): 371-378.[6] 连帆,王于,杨岫岩,等.绝经后骨质疏松治疗方法的近期疗效观察与比较[J].中山大学学报:医学科学版,2011, 32(3): 379-382.[7] Bachrach LK. Osteoporosis and measurement of bone mass in children and adolescents. Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am.2005;34(10):521-535.[8] Ann C, Peter T, Jonathan A, et al. Mela-analysis of risedrormte for the treatment of postmenopausal women. Endocrine Reviews.2002;23(4):508-523.[9] Bone HG, Hosking D, Devogelaer JP. Ten years experience with alendronate for osteoporosis in postmenopausal women.N Engl J Med.2004; 350(6): 1189-1199.[10] Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, et al. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. BMJ. 2009; 21(7):339-340.[11] Leandro G. Meta-analysis in Medical Research. Massachusetts:Blackwell Publishing Ltd.2005:74-78.[12] 中华医学会,骨科学分会.骨质疏松骨折诊疗指南[J].中华骨科杂志,2008,28(10):875-878.[13] Kanjs JA, Burlet N, Cooper c, et al. European guidance for the diagnosis and management of osteoporosis in postmenopausal women. Oneoporos Int.2008;19(7): 399-428.[14] 周建烈,李乃青.美国NOF预防和治疗骨质疏松的最新临床指南简介[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2009,15(6):471-472.[15] 李静, 李幼平. 不断完善与发展的CochraneMeta分析[J].中国循证医学杂志,2008,8(9):742-743.[16] Higgins JPT, Green S.Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions version 5.0.2.The Cochrane Collaboration. 2009:201-203.[17] Turpin DL. CONSORT and QUOROM guidelines for reporting randomized clinical trials and systematic reviews. American journal of orthodontics and dentofacial orthopedics: official publication of the American Association of Orthodontists, its constituent societies, and the American Board of Orthodontics. 2005;128(6):681-685.[18] Jadad AR, Moore RA, Carroll D, et al. Assessing the quality of reports of randomized clinical trials: is blinding necessary?. Controlled clinical trials.1996; 17(1):1-12.[19] Walsh C, Walsh S, Tang T, et al. Total abdominal hysterectomy versus total laparoscopic hysterectomy for benign disease: A meta-analysis. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol.2009;144(1):1-2.[20] Liberati A, Altman D G, Tetzlaff J, et al. The PRISMA statement for reporting systematic reviews and meta-analyses of studies that evaluate healthcare interventions: explanation and elaboration.BMJ.2009; 21(6): 339-340.[21] 王丹,翟俊霞,牟振云,等.Meta分析中的异质性及其处理方法[J].中国循证医学杂志,2009,9(10):1115-1118.[22] Brian S E, Torsten H. A handbook of statistical analyses using R.CRC press.2006:163-169.[23] 麦劲壮,李河,方积乾,等. Meta分析中失安全系数的估计[J].循证医学,2006,6(5):297-300.[24] Dando TM, Noble S. Once-monthly ibandronate.Treat Endocrinol. 2005;4(6):381-387.[25] Emkey R, Delmas PD, Bolognese M, et al. Efficacy and tolerability of once-monthly oral ibandronate (150 mg) and once-weekly oral alendronate (70 mg): additional results from the Monthly Oral Therapy With Ibandronate For Osteoporosis Intervention (MOTION) study.Clin Ther. 2009;31(4):751-761.[26] Pyon EY. Once-monthly ibandronate for postmenopausal osteoporosis: review of a new dosing regimen.Clin Ther. 2006;28(4):475-490.[27] Rizzoli R. Bisphosphonates for post-menopausal osteoporosis: are they all the same?.QJM. 2011; 104(4): 281-300.[28] Sambrook P.Quarterly intravenous injection of ibandronate to treat osteoporosis in postmenopausal women.Clin Interv Aging. 2007;2(1):65-72.[29] Sieber P, Lardelli P, Kraenzlin CA, et al. Intravenous bisphosphonates for postmenopausal osteoporosis: safety profiles of zoledronic acid and ibandronate in clinical practice.Clin Drug Investig. 2013;33(2): 117-122.[30] Stakkestad JA, Lakatos P, Lorenc R, et al. Monthly oral ibandronate is effective and well tolerated after 3 years: the MOBILE long-term extension.Clin Rheumatol. 2008; 27(8):955-960. [31] Strampel W, Emkey R, Civitelli R. Safety considerations with bisphosphonates for the treatment of osteoporosis.Drug Saf. 2007;30(9):755-763.[32] 包丽华,林华,李永军,等.伊班膦酸钠和阿仑膦酸钠对绝经后骨质疏松的干预研究[J].中国骨质疏松杂志.2011, 17(3): 232-235.[33] 李改丽,呼永河,张汝,等.伊班膦酸钠输注液和阿伦膦酸纳片防治老年性骨质疏松症的疗效对比研究[J].中国全科医学,2012,15(30):3469-3472.[34] Bonnick SL, Silverman S, Tanner SB, et al. Patient satisfaction in postmenopausal women treated with a weekly bisphosphonate transitioned to once-monthly ibandronate.J Womens Health (Larchmt). 2009; s18(7): 935-943.[35] Schafer AL, Burghardt AJ, Sellmeyer DE, et al. Postmenopausal women treated with combination parathyroid hormone (1-84) and ibandronate demonstrate different microstructural changes at the radius vs. tibia: the PTH and Ibandronate Combination Study (PICS).Osteoporos Int. 2013;4(16):53-54.[36] Johnson N, Barlow D, Lethaby A, et al. Methods of hysterectomy: systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. BMJ.2005;330(7506): 1478-1480. |
.jpg) 文题释义:
继发性骨质疏松:是由其他病因引起的。如慢性疾病:慢性肾功能衰竭、胃切除、肠改道、钙吸收不良综合征、多发性骨髓瘤等;内分泌疾病:高泌乳素血症、甲状腺功能亢进、肾上腺皮质激素分泌过多、糖尿病、甲状旁腺功能亢进等。医源性因素:长期应用抗癫痫药、含铝抗酸剂、服用过量甲状腺素或长期应用糖皮质激素、促性腺激素释放激素(GnRH)激动剂等。
绝经后骨质疏松:是多因素性疾病,遗传、生活方式、营养等均与发病有关。具有以下高危因素者易患绝经后骨质疏松症:白人及亚洲妇女、骨质疏松症家族史、或具有影响骨量的特殊基因的妇女、钙摄入不足、缺乏体力活动、大量吸烟及饮酒、早绝经或绝经前行双侧卵巢切除术者。是否发生骨质疏松症,取决于其骨峰值及其骨丢失的速度,骨峰值高及(或)骨丢失慢者,不易发生,骨峰值低及(或)骨丢失快者容易发生。
伊班膦酸:分子式为C9H22NO7P2NaH2O,静脉注射,无色澄明的液体。适应于治疗肿瘤引起的病理性(异常)血钙升高(高钙血症),儿童、孕妇及哺乳期妇女禁用,严重肾功能不全者禁用。
文题释义:
继发性骨质疏松:是由其他病因引起的。如慢性疾病:慢性肾功能衰竭、胃切除、肠改道、钙吸收不良综合征、多发性骨髓瘤等;内分泌疾病:高泌乳素血症、甲状腺功能亢进、肾上腺皮质激素分泌过多、糖尿病、甲状旁腺功能亢进等。医源性因素:长期应用抗癫痫药、含铝抗酸剂、服用过量甲状腺素或长期应用糖皮质激素、促性腺激素释放激素(GnRH)激动剂等。
绝经后骨质疏松:是多因素性疾病,遗传、生活方式、营养等均与发病有关。具有以下高危因素者易患绝经后骨质疏松症:白人及亚洲妇女、骨质疏松症家族史、或具有影响骨量的特殊基因的妇女、钙摄入不足、缺乏体力活动、大量吸烟及饮酒、早绝经或绝经前行双侧卵巢切除术者。是否发生骨质疏松症,取决于其骨峰值及其骨丢失的速度,骨峰值高及(或)骨丢失慢者,不易发生,骨峰值低及(或)骨丢失快者容易发生。
伊班膦酸:分子式为C9H22NO7P2NaH2O,静脉注射,无色澄明的液体。适应于治疗肿瘤引起的病理性(异常)血钙升高(高钙血症),儿童、孕妇及哺乳期妇女禁用,严重肾功能不全者禁用。.jpg) 文题释义:
继发性骨质疏松:是由其他病因引起的。如慢性疾病:慢性肾功能衰竭、胃切除、肠改道、钙吸收不良综合征、多发性骨髓瘤等;内分泌疾病:高泌乳素血症、甲状腺功能亢进、肾上腺皮质激素分泌过多、糖尿病、甲状旁腺功能亢进等。医源性因素:长期应用抗癫痫药、含铝抗酸剂、服用过量甲状腺素或长期应用糖皮质激素、促性腺激素释放激素(GnRH)激动剂等。
绝经后骨质疏松:是多因素性疾病,遗传、生活方式、营养等均与发病有关。具有以下高危因素者易患绝经后骨质疏松症:白人及亚洲妇女、骨质疏松症家族史、或具有影响骨量的特殊基因的妇女、钙摄入不足、缺乏体力活动、大量吸烟及饮酒、早绝经或绝经前行双侧卵巢切除术者。是否发生骨质疏松症,取决于其骨峰值及其骨丢失的速度,骨峰值高及(或)骨丢失慢者,不易发生,骨峰值低及(或)骨丢失快者容易发生。
伊班膦酸:分子式为C9H22NO7P2NaH2O,静脉注射,无色澄明的液体。适应于治疗肿瘤引起的病理性(异常)血钙升高(高钙血症),儿童、孕妇及哺乳期妇女禁用,严重肾功能不全者禁用。
文题释义:
继发性骨质疏松:是由其他病因引起的。如慢性疾病:慢性肾功能衰竭、胃切除、肠改道、钙吸收不良综合征、多发性骨髓瘤等;内分泌疾病:高泌乳素血症、甲状腺功能亢进、肾上腺皮质激素分泌过多、糖尿病、甲状旁腺功能亢进等。医源性因素:长期应用抗癫痫药、含铝抗酸剂、服用过量甲状腺素或长期应用糖皮质激素、促性腺激素释放激素(GnRH)激动剂等。
绝经后骨质疏松:是多因素性疾病,遗传、生活方式、营养等均与发病有关。具有以下高危因素者易患绝经后骨质疏松症:白人及亚洲妇女、骨质疏松症家族史、或具有影响骨量的特殊基因的妇女、钙摄入不足、缺乏体力活动、大量吸烟及饮酒、早绝经或绝经前行双侧卵巢切除术者。是否发生骨质疏松症,取决于其骨峰值及其骨丢失的速度,骨峰值高及(或)骨丢失慢者,不易发生,骨峰值低及(或)骨丢失快者容易发生。
伊班膦酸:分子式为C9H22NO7P2NaH2O,静脉注射,无色澄明的液体。适应于治疗肿瘤引起的病理性(异常)血钙升高(高钙血症),儿童、孕妇及哺乳期妇女禁用,严重肾功能不全者禁用。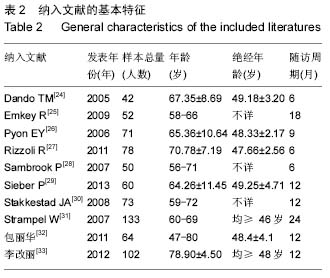
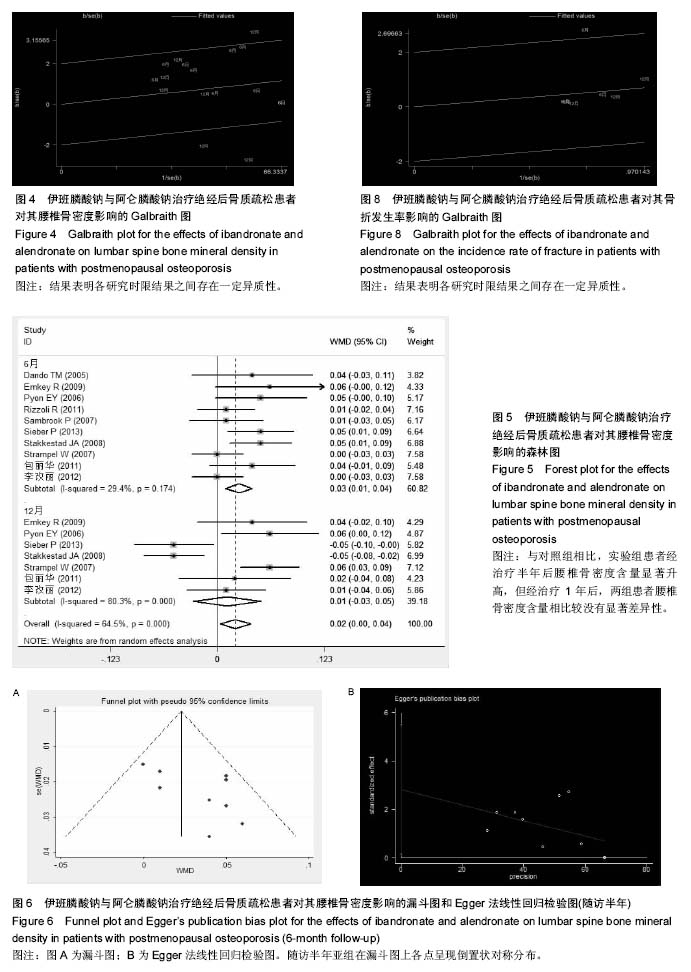

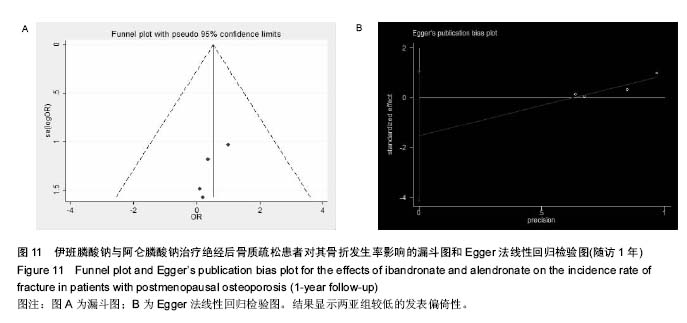
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg) 文题释义:
继发性骨质疏松:是由其他病因引起的。如慢性疾病:慢性肾功能衰竭、胃切除、肠改道、钙吸收不良综合征、多发性骨髓瘤等;内分泌疾病:高泌乳素血症、甲状腺功能亢进、肾上腺皮质激素分泌过多、糖尿病、甲状旁腺功能亢进等。医源性因素:长期应用抗癫痫药、含铝抗酸剂、服用过量甲状腺素或长期应用糖皮质激素、促性腺激素释放激素(GnRH)激动剂等。
绝经后骨质疏松:是多因素性疾病,遗传、生活方式、营养等均与发病有关。具有以下高危因素者易患绝经后骨质疏松症:白人及亚洲妇女、骨质疏松症家族史、或具有影响骨量的特殊基因的妇女、钙摄入不足、缺乏体力活动、大量吸烟及饮酒、早绝经或绝经前行双侧卵巢切除术者。是否发生骨质疏松症,取决于其骨峰值及其骨丢失的速度,骨峰值高及(或)骨丢失慢者,不易发生,骨峰值低及(或)骨丢失快者容易发生。
伊班膦酸:分子式为C9H22NO7P2NaH2O,静脉注射,无色澄明的液体。适应于治疗肿瘤引起的病理性(异常)血钙升高(高钙血症),儿童、孕妇及哺乳期妇女禁用,严重肾功能不全者禁用。
文题释义:
继发性骨质疏松:是由其他病因引起的。如慢性疾病:慢性肾功能衰竭、胃切除、肠改道、钙吸收不良综合征、多发性骨髓瘤等;内分泌疾病:高泌乳素血症、甲状腺功能亢进、肾上腺皮质激素分泌过多、糖尿病、甲状旁腺功能亢进等。医源性因素:长期应用抗癫痫药、含铝抗酸剂、服用过量甲状腺素或长期应用糖皮质激素、促性腺激素释放激素(GnRH)激动剂等。
绝经后骨质疏松:是多因素性疾病,遗传、生活方式、营养等均与发病有关。具有以下高危因素者易患绝经后骨质疏松症:白人及亚洲妇女、骨质疏松症家族史、或具有影响骨量的特殊基因的妇女、钙摄入不足、缺乏体力活动、大量吸烟及饮酒、早绝经或绝经前行双侧卵巢切除术者。是否发生骨质疏松症,取决于其骨峰值及其骨丢失的速度,骨峰值高及(或)骨丢失慢者,不易发生,骨峰值低及(或)骨丢失快者容易发生。
伊班膦酸:分子式为C9H22NO7P2NaH2O,静脉注射,无色澄明的液体。适应于治疗肿瘤引起的病理性(异常)血钙升高(高钙血症),儿童、孕妇及哺乳期妇女禁用,严重肾功能不全者禁用。