| [1] New PW, Reeves RK, Smith E, et al. International retrospective comparison of inpatient rehabilitation for patients with spinal cord myelopathy: Epidemiology and clinical outcomes. Arch Phys Med Rehabil.2015;3:3-10.
[2] 李建军,周红俊,洪毅,等. 2002年北京市脊髓损伤发病率调查[J]. 中国康复理论与实践,2004,10(7):412-413.
[3] 潘杰,李昕,曾诚,等. 2005-2007年上海市浦东新区脊柱脊髓损伤调查分析[J].同济大学学报:医学版,2009,30(5):131-135.
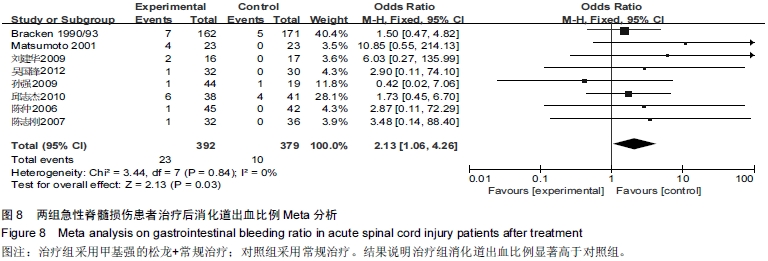
[4] Bracken MB, Collins WF, Freeman DF, et al. Efficacy of methylprednisolone in acute spinal cord injury. JAMA. 1984; 251(1):45-52.
[5] Bracken MB, Shepard MJ, Hellenbrand KG, et al. Methylprednisolone and neurological function one year after spinal cord injury. J Neurosurg.1985;63:704-713.
[6] Bracken MB, Shepard MJ, Collins WF, et al. A randomized controlled trial of methylprednisolone or naloxone in the treatment of acute spinal cord injury. N Engl J Med. 1990; 322(20):1405-1411.
[7] Bracken MB, Shepard MJ, Collins WF, et al.Methylprednisolone or naloxone treatment after acute spinal cord injury: 1 year follow-up data. J Neurosurg. 1992;76(1):23-31.
[8] Bracken MB, Shepard MJ, Holford TR, et al. Methylprednisolone or tirilazad mesylate administration after acute spinal cord injury:1-year follow up. J Neurosurg. 1998;89(5):699-706.
[9] Bracken MB, Shepard MJ, Holford TR, et al. Administration of methylprednisolone for 24 or 48 hours or tirilazad mesylate for 48 hours in the treatment of acute spinal cord injury. JAMA. 1997;277(20):1597-1604.
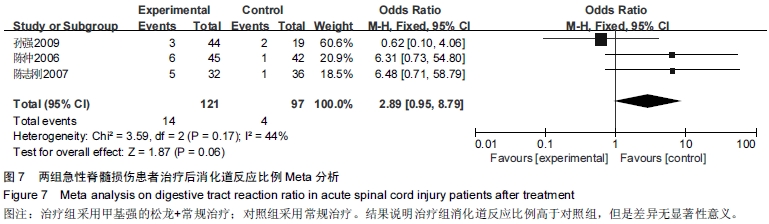
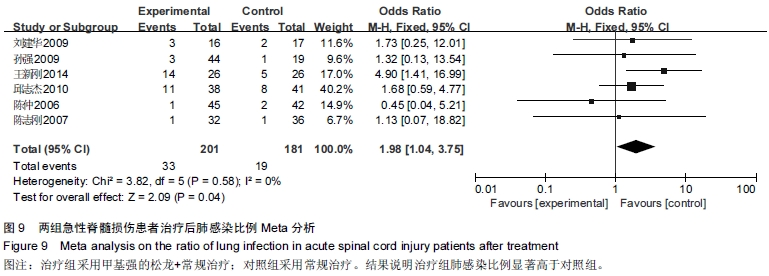
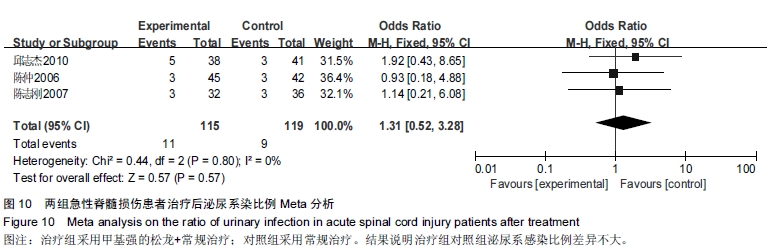
[10] 陈仲,杨华刚,杨洪昌,等.大剂量甲基强的松龙冲击治疗急性脊髓损伤疗效分析[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2006,16(12):33-37.
[11] 邱志杰,杨惠林,魏立.甲基强的松龙冲击治疗脊髓损伤疗效及并发症分析[J].山东医药,2010,50(14):52-53.
[12] 王新刚,段豪,夏斌,等.应用甲基强的松龙冲击疗法治疗脊髓损伤的疗效观察[J].当代医药论丛,2014,12(9):273-275.
[13] 刘建华,戴双武.大剂量甲基强的松龙治疗急性脊髓损伤的临床研究[J].临床外科杂志,2009,14(4):272-275.
[14] 孙强,徐杰.大剂量甲基强的松龙冲击治疗急性脊髓损伤的疗效观察[J].中国伤残医学, 2009,17(6):5-7.
[15] 陈志刚,张烽.早期大剂量甲基强的松龙治疗急性脊髓损伤32例[J]. 南通大学学报,2007,27(3):209-211.
[16] 吴国锋,郭宁原.甲基强的松龙联合早期手术治疗急性无骨折脱位颈髓损伤的疗效[J]. 中国实用医刊,2012,39(15):86-88.
[17] 王俊,陈增海,陈鹏. 继发性脊髓损伤的药物预防[J]. 海南医学院学报,2004,10(15):316-318.
[18] Matsumoto T, Tetsuya T, Mamoru K, et al. Early Complications of High-Dose Methylprednisolone Sodium Succinate Treatment in the Follow-Up of Acute Cervical Spinal Cord Injury. Spine.2001;26(4):426-430.
[19] Petitjean ME, Pointillart V, Dixmeriasl F, et al. Traitement mkdicamenteux de la lecion mbdullaire traumatique au stade aigu. Ann Fr Anesrh Re’nnim.1998; 17:114-122.
[20] 谭志强,廖永德,陈秋生,等. 甲基强的松龙冲击治疗脊髓损伤的临床疗效观察[J]. 江西医药,2013;48(10):880-883.
[21] 张冉,孙宏志,陈耀辉. 甲基强的松龙在伴有严重脊髓受压的脊柱手术中的应用价值[J]. 广西医科大学学报, 2010,27(6): 922-924.
[22] 常锐,李金洲,李强. 大剂量甲基强的松龙早期治疗脊髓损伤的疗效观察[J]. 菏泽医学专科学校学报, 2009,21(3):36-37.
[23] 赵理铭,陈国平,陈勇. 大剂量甲基强的松龙治疗17例急性脊髓损伤临床观察[J]. 中国临床康复, 2002,7(8):1151-1152.
[24] 胡勇,徐荣明,何贤峰. 甲基强的松龙冲击法治疗急性脊髓损伤的近期观察[J]. 实用骨科杂志,2008,14(6):337-339.
[25] 李晓彬,刘涛,蔡腾. 神经节苷脂联合甲基强的松龙早期治疗急性脊髓损伤疗效分析[J]. 中国实用神经疾病杂志, 2013,16(23): 92-93.
[26] 明江华,周建林,刘世清. 早期减压并应用大剂量甲基强的松龙治疗急性脊髓损伤[J].中闻中医骨伤秘杂, 2007,15(3):4-6.
[27] Todd NV, Skinner D, Wilson-MacDonald J. Secondary neurological deterioration in traumatic spinal injury: data from medicolegal cases. Bone Joint.2015; 97(4):527-531.
[28] Suardaz M, Galan-Arriero I, Avila-Martin G, et al. Spinal cord compression injury in lysophosphatidic acid 1 receptor-null mice promotes maladaptive pronociceptive descending control. Eur J Pain.2015;29(3):695.
[29] Powell A, Davidson L. Pediatric spinal cord injury: a review by organ system. Phys Med Rehabil Clin N Am. 2015;26(1):109-32
[30] Noreau L, Noonan VK, Cobb J, et al. Spinal Cord Injury Community Survey: Understanding the Needs of Canadians with SCI. Top Spinal Cord Inj Rehabil. 2014;20(4):265-76.
[31] Silva NA, Gimble JM, Sousa N, et al. Combining adult stem cells and olfactory ensheathing cells: the secretome effect. Stem Cells Dev.2013;22(8):1232-1240.
[32] Binder H. Traumatic spinal cord injury. Handb Clin Neurol. 2013;110(2):411-426.
[33] Muradov JM, Hagg T. Intravenous infusion of magnesium chloride improves epicenter blood flow during the acute stage of contusive spinal cord injury in rats. J Neurotrauma. 2013; 30(10):840-852.
[34] Forgione N, Fehlings MG. Rho-ROCK inhibition in the treatment of spinal cord injury. World Neurosurg. 2014;82(3): 535-539.
[35] Qu Y, Zhao J, Wang Y, Gao Z. Silencing ephrinB3 improves functional recovery following spinal cord injury. Mol Med Rep. 2014;9(5):1761-1766.
[36] Zupanc GK, Sîrbulescu RF. Cell replacement therapy: lessons from teleost fish. Exp Neurol.2015;263(1):272-276.
[37] Kirshblum SC, Biering-S, rensen F, et al. International standards for neurological classification of spinal cord injury: cases with classification challenges. Top Spinal Cord Inj Rehabil.2014;20(2):81-89.
[38] Skaper SD, Facci L, Giusti P. Neuroinflammation, microglia and mast cells in the pathophysiology of neurocognitive disorders: a review. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets.2014;1 3(10):1654-1666.
|