中国组织工程研究 ›› 2015, Vol. 19 ›› Issue (37): 5923-5927.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2015.37.004
• 骨组织构建 bone tissue construction • 上一篇 下一篇
人成骨细胞分化及骨保护素分泌:R-脊椎蛋白1通过Wnt/β-catenin通路的作用
吴思敏,刘庆梅,马彦云,王久存,赵东宝
- 解放军第二军医大学附属长海医院风湿免疫科,上海市 200433
Differentiation and osteoprotegerin secretion of human osteoblasts: R-spondin 1 effect via Wnt/beta-catenin signal pathway
Wu Si-min, Liu Qing-mei, Ma Yan-yun, Wang Jiu-cun, Zhao Dong-bao
- Department of Rheumatology and Immunology, Changhai Hospital, the Second Military Medical University, Shanghai 200433, China
摘要:
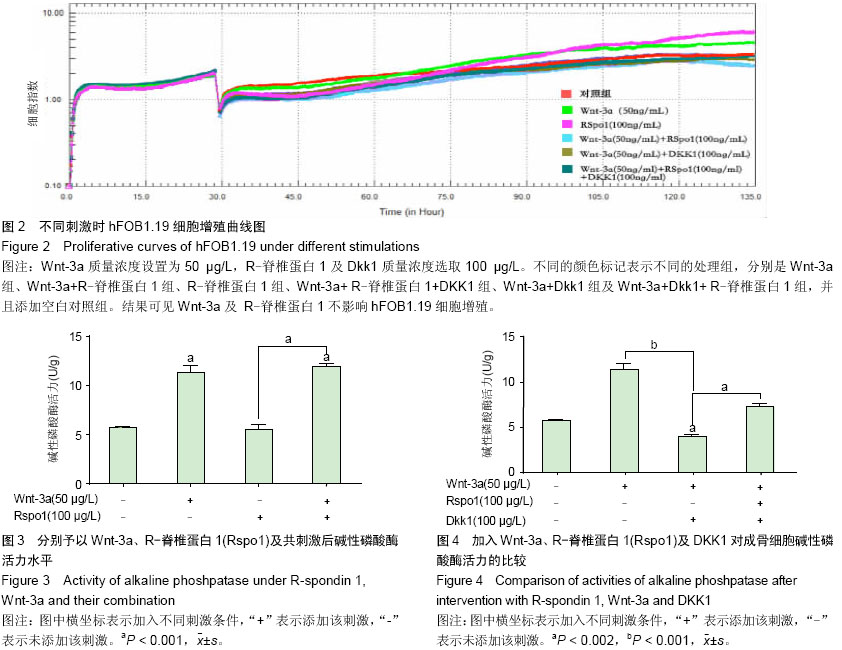
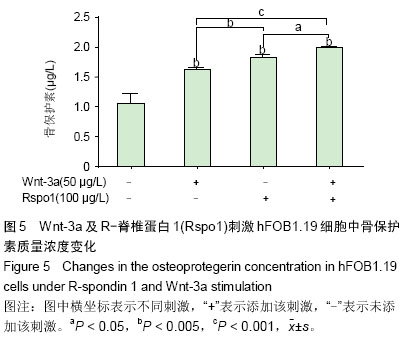
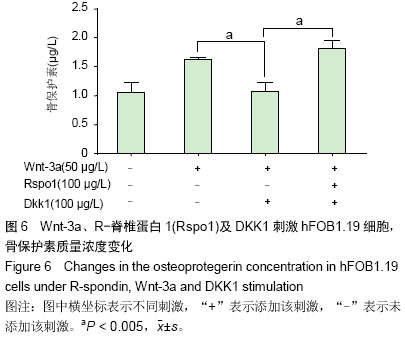
背景:研究表明Wnt/β-catenin信号通路活性受抑是类风湿关节炎骨侵蚀的始动因素,增强该通路有望治疗类风湿关节炎关节破坏。R-脊椎蛋白1(RSpo1)可能是Wnt激活剂,尚无人成骨细胞相关研究。 目的:验证R-脊椎蛋白1抑制DKK1促进该细胞的分化成熟。 方法:给予S40转染人成骨细胞株hFOB 1.19 Wnt-3a、R-脊椎蛋白1及Wnt信号通路抑制剂DKK1不同刺激,通过检测细胞增殖、碱性磷酸酶活性及骨保护素水平,观察R-脊椎蛋白1在成骨细胞中的作用。 结果与结论:R-脊椎蛋白1对hFOB 1.19细胞增殖无影响,Wnt-3a上调碱性磷酸酶活性,与R-脊椎蛋白1共刺激可增强该作用;R-脊椎蛋白1可减少DKK1对hFOB1.19细胞碱性磷酸酶活力的抑制作用。R-脊椎蛋白1可提高骨保护素质量浓度,但R-脊椎蛋白1对骨保护素的增强作用大于DKK1对其的抑制作用。提示R-脊椎蛋白1通过抑制DKK1,参与Wnt/β-catenin信号通路,促进成骨细胞分化成熟,分泌骨保护素。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
中图分类号: