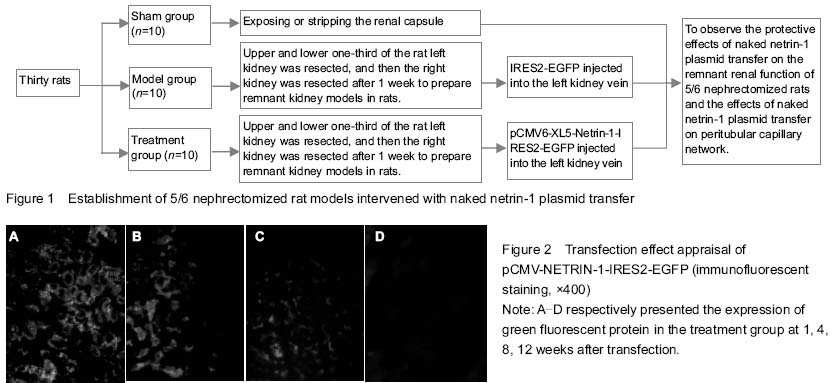
Renal interstitial capillaries refer to the peritubular capillary network derived from efferent arterioles. In various nephropathies, microvascular lesions exit in the renal interstitium, and the distribution disorder of the peritubular capillary network distribution is reduced, and moreover, the reducing degree of peritubular capillary network is positively correlated with the degree of renal interstitial fibrosis[28-29]. In this study, renal tubules and interstitium in the sham group had no significant changes, and the peritubular capillary network showed normal distribution and morphology; in the remnant kidney of 5/6 nephrectomized rats, the renal tubules was expanded or shrunk, the renal interstitium was widened, peritubular capillary lesions were focally distributed and disorganized, the capillaries were shrunk and deformed, and the density of the peritubular capillary network density was decreased over the disease course, thereby resulting in renal dysfunction. Experimental findings from the present study show that the decrease in the peritubular capillary network is one of important pathological features of renal tubule and interstitial injury and fibrosis in the remnant kidney of 5/6 nephrectomized rats. Therefore, how to solve the peritubular capillary network loss and to protect the microvascular endothelial cells in the kidney is the key link to the treatment of renal interstitial fibrosis.
With the progress in molecular biology, gene transfection has been widely used in the medical field. Although the use of viral vectors can achieve a therapeutic effect in the kidney, it may cause a strong immune response, resulting in inflammatory phenomena or adverse reactions in the host[30-34]. The naked gene transfection has no serious immune response, and it is simple to prepare. Recent studies have confirmed a certain amount of naked plasmid DNA injected via the renal vein can achieve the purpose of generating the required target gene and protein[35]. In this study, the naked plasmid DNA was transfected successfully via the renal vein into the remnant kidney of 5/6 nephrectomized rats. Immunofluorescence staining showed that the target protein expressed in renal tubular epithelial cells, and netrin-1 protein expression was significantly increased in the remnant kidney tissue of the treatment group.
Netrin-1 is a laminin-like molecule. In the nervous system guided by the combination of DCC and UNC5H, its classic role is to induce the axon growth and migration of growth cones by binding to its receptor. Blood vessels and nerves are both complex branching structures, and they have anatomical similarities largely, follow the same route and are mutually dependent in the nerve fibers and blood vessels of peripheral tissues, indicating that the development process of these two systems is correlated[36-43]. Netrin-1 has been attracted wide attentions in the vascular system, and in vitro experiments have shown that netrin-1 is a vascular endothelial cell mitogen, which is able to stimulate the migration and proliferation of primarily cultured human umbilical vein endothelial cells and induce angiogenesis. Wilson et al [44] showed that in zebrafish and mammals, netrins can stimulate angiogenesis, among which, netrin-1 can induce the migration, proliferation and tube formation of a variety of endothelial cell lines. To suppress the mRNA expression of netrin-1 is to inhibit vascular sprouting. In mammals, Netrins can activate angiogenesis, accelerate blood vessel formation and reperfusion in ischemic tissues, and then recover the nerve conduction velocity. As above mentioned, netrin-1 for protection of vascular endothelial cells can repair the peritubular capillary network, improve renal interstitial fibrosis, thereby provide opportunities for delaying the progression of chronic kidney diseases.
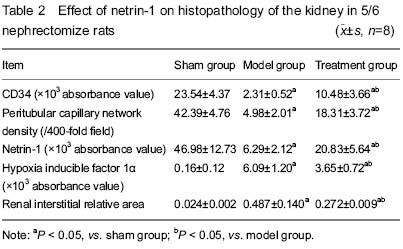
Experimental results showed that after netrin-1 transfection, the renal function of 5/6 nephrectomized rats was significantly improved: the blood urea nitrogen and creatinine levels were significantly lower than those in the model group (P < 0.05), and the 24-hour urine protein level was similar to that in the model group (P > 0.05), indicating netrin-1 can improve renal function, which is independent of the urinary protein.
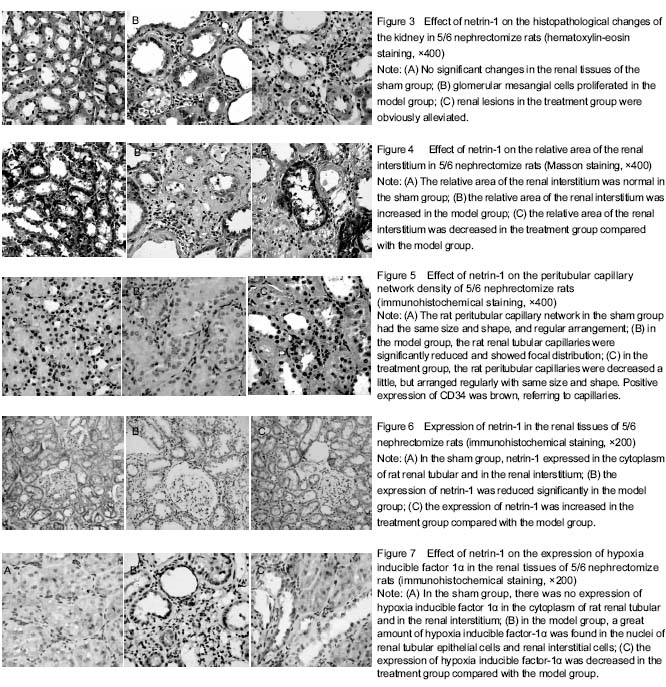
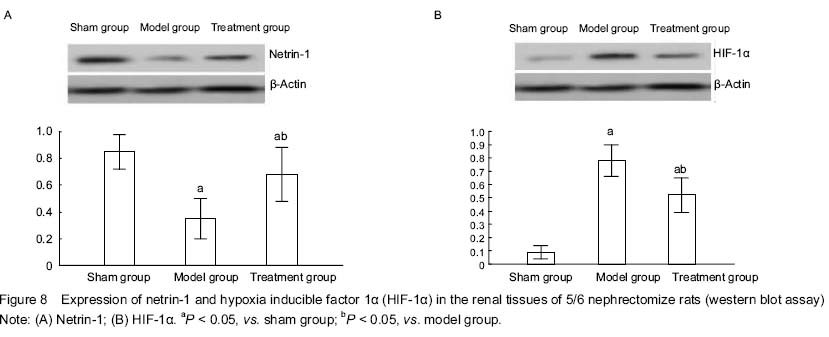
As reported, netrin-1 is mainly distributed in the peritubular capillary network and the cytoplasm of mouse renal tubular epithelial cells[44-50]. In this study, immunohistochemical staining showed that netrin-1 was abundantly expressed in the renal tissue of rats in the sham group, which was mainly located in the cytoplasm of renal tubular epithelial cells and a little in the renal interstitium. In the model group, the netrin-1 only expressed in the cytoplasm of renal tubular epithelial cells, and its expression level was decreased obviously due to the damage to the renal tubule. In the treatment group, the expression level of netrin-1 in the cytoplasm of renal tubular epithelial cells was increased as compared with the model group, and there was also a little expression in the renal interstitium. Results from western blot assay showed that the expression level of netrin-1 was higher in the sham group, lower in the model group, but increased significantly in the treatment group. In the sham group, the peritubular capillary network had regular arrangement, normal density and similar sizes. In the model group, the peritubular capillary network was reduced, dyed pale or completely lack, and the density was decreased significantly. In the treatment group, the peritubular capillary network density showed a small decline, but remained the regular arrangement, same sizes and shapes. Moreover, in the model group, renal interstitial fibrosis was serious, accompanied by significant expansion of renal interstitial area; in the treatment group, renal interstitial fibrosis was not obvious. After naked plasmid netrin-1 transfection, the level of netrin-1 was increased significantly, which promoted the proliferation of vascular endothelial cells and thereby alleviated the damage to the peritubular capillary network and reduced renal interstitial fibrosis.
Once kidney damage reaches a certain level, the process of kidney diseases are mostly progressive, irreversible, and independent of primary lesions. Renal interstitial hypoxia is one of the common pathways of renal interstitial fibrosis[51-56]. The peritubular capillary network is the branching outcome of efferent arterioles, resulting in the lower the pressure within the blood vessels, which is vulnerable to further reduce blood flow due to various factors. Such structural characteristics determine that the renal interstitium is susceptible to hypoxic injury. Renal microvascular damage can cause a series of functional and metabolic disorders of local tissues by reducing the supply of oxygen and nutrients to cells. The decline in the peritubular capillary network results in reduced oxygen supply, leading to increased expression of hypoxia inducible factor-1α, inflammatory cell infiltration and fibrosis squeeze. Hypoxia is persistent in the process of renal interstitial fibrosis. Development of interstitial edema, inflammation and fibrosis can reduce local blood flow and oxygen supply. Chronic kidney diseases are often associated with anemia. All of these have aggravated the hypoxic state, and eventually form a vicious circle that will further induce peritubular capillary network atrophy and loss, and aggravate renal interstitial ischemia and hypoxia, promoting the progress of fibrosis[57-59]. This experiment confirmed that in the treatment group, the damage to the peritubular capillary network was reduced along with the increase of netrin-1 expression, and hypoxia inducible factor 1α protein expression in the remnant kidney tissue was also significantly reduced.
These findings indicate that netrin-1 can maintain kidney microvascular function and the number of capillaries, and improve chronic hypoxia of the renal interstitium, which effectively antagonize renal interstitial fibrosis. Netrin-1 may be used as a new treatment and molecular target, which is important for preventing the persistent development of kidney diseases.