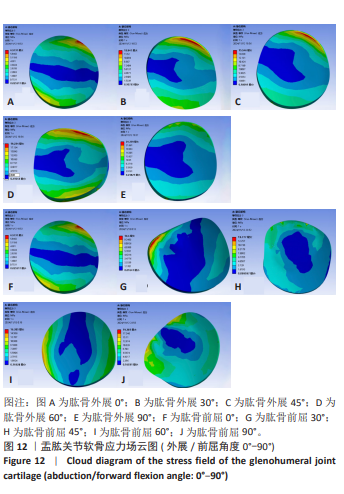
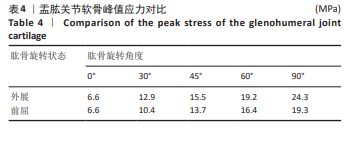
[1] HAERING D, RAISON M, BEGON M. Measurement and description of three-dimensional shoulder range of motion with degrees of freedom interactions. J Biomech Eng. 2014;136(8). doi: 10.1115/1.4027665.
[2] ENGIN AE, CHEN SM. Statistical data base for the biomechanical properties of the human shoulder complex--I: Kinematics of the shoulder complex. J Biomech Eng. 1986;108(3):215-221.
[3] MCCAUSLAND C, SAWYER E, EOVALDI BJ, et al. Anatomy, Shoulder and Upper Limb, Shoulder Muscles. StatPearls. Treasure Island (FL) ineligible companies. Disclosure: Ethan Sawyer declares no relevant financial relationships with ineligible companies. Disclosure: Benjamin Eovaldi declares no relevant financial relationships with ineligible companies. Disclosure: Matthew Varacallo declares no relevant financial relationships with ineligible companies.: StatPearls Publishing Copyright © 2024, StatPearls Publishing LLC.; 2024.
[4] FLORES DV, GOES PK, GÓMEZ CM, et al. Imaging of the Acromioclavicular Joint: Anatomy, Function, Pathologic Features, and Treatment. Radiographics. 2020;40(5):1355-1382.
[5] POZZI F, PLUMMER HA, SHANLEY E, et al. Preseason shoulder range of motion screening and in-season risk of shoulder and elbow injuries in overhead athletes: systematic review and meta-analysis. Br J Sports Med. 2020;54(17):1019-1027.
[6] CHANG RF, LEE CC, LO CM. Quantitative diagnosis of rotator cuff tears based on sonographic pattern recognition. PLoS One. 2019;14(2):e0212741.
[7] SAMBANDAM SN, KHANNA V, GUL A, et al. Rotator cuff tears: An evidence based approach. World J Orthop. 2015;6(11):902-918.
[8] NYFFELER RW, SCHENK N, BISSIG P. Can a simple fall cause a rotator cuff tear? Literature review and biomechanical considerations. Int Orthop. 2021;45(6):1573-1582.
[9] ENSOR KL, KWON YW, DIBENEDITTO MR, et al. The rising incidence of rotator cuff repairs. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2013;22(12):1628-1632.
[10] TOOTH C, GOFFLOT A, SCHWARTZ C, et al. Risk Factors of Overuse Shoulder Injuries in Overhead Athletes: A Systematic Review. Sports Health. 2020; 12(5):478-487.
[11] LIN DJ, WONG TT, KAZAM JK. Shoulder Injuries in the Overhead-Throwing Athlete: Epidemiology, Mechanisms of Injury, and Imaging Findings. Radiology. 2018;286(2):370-387.
[12] BEDI A, BISHOP J, KEENER J, et al. Rotator cuff tears. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2024;10(1):8.
[13] WESTERHOFF P, GRAICHEN F, BENDER A, et al. In vivo measurement of shoulder joint loads during activities of daily living. J Biomech. 2009;42(12): 1840-1849.
[14] ISLÁN MARCOS M, LECHOSA URQUIJO E, BLAYA HARO F, et al. Behavior under Load of A Human Shoulder: Finite Element Simulation and Analysis. J Med Syst. 2019;43(5):132.
[15] YANG Z, XU G, YANG J, et al. Effect of different loads on the shoulder in abduction postures: a finite element analysis. Sci Rep. 2023;13(1):9490.
[16] CHAPMAN RM, TORCHIA MT, BELL JE, et al. Assessing Shoulder Biomechanics of Healthy Elderly Individuals During Activities of Daily Living Using Inertial Measurement Units: High Maximum Elevation Is Achievable but Rarely Used. J Biomech Eng. 2019;141(4):0410011-7.
[17] 禹铭杨. 肩峰形态变异的临床意义及其对肩关节生物力学影响的有限元分析[D]. 长春:吉林大学,2015.
[18] WAKABAYASHI I, ITOI E, SANO H, et al. Mechanical environment of the supraspinatus tendon: a two-dimensional finite element model analysis. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2003;12(6):612-617.
[19] DUPREY S, BRUYERE K, VERRIEST JP. Human shoulder response to side impacts: a finite element study. Comput Methods Biomech Biomed Engin. 2007;10(5):361-370.
[20] SANO H, YAMASHITA T, WAKABAYASHI I, et al. Stress distribution in the supraspinatus tendon after tendon repair: suture anchors versus transosseous suture fixation. Am J Sports Med. 2007;35(4):542-546.
[21] 徐彪, 路坦, 姜亚琼, 等. 有限元分析不同程度冈上肌断裂对肩关节应力的影响[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2025,29(9):1768-1774.
[22] REMIA LF, RAVALIN RV, LEMLY KS, et al. Biomechanical evaluation of multidirectional glenohumeral instability and repair. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2003;(416):225-236.
[23] 何仿. 人体肩关节三维有限元模型的建立、验证及在肱骨骨折机制研究方面的应用[D].上海:第二军医大学,2006.
[24] 何仿, 苟三怀, 卜海富. 不同肩关节功能位置上肱骨三维有限元应力分析[J]. 临床骨科杂志,2006,9(6):559-561.
[25] MCLEAN A, TAYLOR F. Classifications in Brief: Bigliani Classification of Acromial Morphology. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2019;477(8):1958-1961.
[26] ARNER JW, NOLTE PC, RUZBARSKY JJ, et al. Correlation of Acromial Morphology With Risk and Direction of Shoulder Instability: An MRI Study. Am J Sports Med. 2023;51(12):3211-3216.
[27] MEYER DC, RAHM S, FARSHAD M, et al. Deltoid muscle shape analysis with magnetic resonance imaging in patients with chronic rotator cuff tears. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2013;14:247.
[28] KAMONSEKI DH, HAIK MN, RIBEIRO LP, et al. Scapular movement training is not superior to standardized exercises in the treatment of individuals with chronic shoulder pain and scapular dyskinesis: randomized controlled trial. Disabil Rehabil. 2023;45(18):2925-2935.
[29] RIBEIRO LP, COOLS A, CAMARGO PR. Rotator cuff unloading versus loading exercise program in the conservative treatment of patients with rotator cuff tear: protocol of a randomised controlled trial. BMJ Open. 2020;10(12):e040820.
[30] BECHTOL CO. Biomechanics of the shoulder. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1980; (146):37-41.
[31] REUTHER KE, THOMAS SJ, SARVER JJ, et al. Effect of return to overuse activity following an isolated supraspinatus tendon tear on adjacent intact tendons and glenoid cartilage in a rat model. J Orthop Res. 2013;31(5):710-715.
[32] YAMAMOTO A, TAKAGISHI K, OSAWA T, et al. Prevalence and risk factors of a rotator cuff tear in the general population. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2010;19(1):116-120.
[33] LEWIS JS. Rotator cuff tendinopathy. Br J Sports Med. 2009;43(4):236-241.
[34] KIM JH, JUNG SH. Delaminated Rotator Cuff Tear: Concurrent Concept and Treatment. Clin Shoulder Elb. 2019;22(3):159-170.
[35] LONGO UG, BERTON A, PAPAPIETRO N, et al. Epidemiology, genetics and biological factors of rotator cuff tears. Med Sport Sci. 2012;57:1-9.
[36] YANG Z, LIN Q, NIU Y, et al. Visualizing Trends and Bibliometric Study in Tissue Engineering for Rotator Cuff Injuries. Tissue Eng Part B Rev. 2025; 31(2):190-207.
[37] SCIARRETTA FV, MOYA D, LIST K. Current trends in rehabilitation of rotator cuff injuries. Sicot J. 2023;9:14.
[38] BIGLIANI LU, KELKAR R, FLATOW EL, et al. Glenohumeral stability. Biomechanical properties of passive and active stabilizers. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1996(330):13-30.
[39] SIGRIST B, FERGUSON S, BOEHM E, et al. The Biomechanical Effect of Bone Grafting and Bone Graft Remodeling in Patients With Anterior Shoulder Instability. Am J Sports Med. 2020;48(8):1857-1864.
[40] KIBLER WB, SCIASCIA AD, GRANTHAM WJ. The shoulder joint complex in the throwing motion. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2024;33(2):443-449.
[41] FOX AJS, FOX OJK, SCHÄR MO, et al. The glenohumeral ligaments: Superior, middle, and inferior: Anatomy, biomechanics, injury, and diagnosis. Clin Anat. 2021;34(2):283-296.
[42] TUPE RN, TIWARI V. Anteroinferior Glenoid Labrum Lesion (Bankart Lesion). StatPearls. Treasure Island (FL) ineligible companies. Disclosure: Vivek Tiwari declares no relevant financial relationships with ineligible companies.: StatPearls Publishing Copyright © 2024, StatPearls Publishing LLC.; 2024.
[43] DENG R, ZHAO R, ZHANG Z, et al. Chondrocyte membrane-coated nanoparticles promote drug retention and halt cartilage damage in rat and canine osteoarthritis. Sci Transl Med. 2024;16(735):eadh9751.
[44] CHEN P, LIU X, GU C, et al. A plant-derived natural photosynthetic system for improving cell anabolism. Nature. 2022;612(7940):546-554.
[45] CHOI MC, JO J, PARK J, et al. NF-κB Signaling Pathways in Osteoarthritic Cartilage Destruction. Cells. 2019;8(7):734.
[46] LEPETSOS P, PAPAVASSILIOU KA, PAPAVASSILIOU AG. Redox and NF-κB signaling in osteoarthritis. Free Radic Biol Med. 2019;132:90-100.
[47] FRANCESCHI F, GIOVANNETTI DE SANCTIS E, GUPTA A, et al. Reverse shoulder arthroplasty: State-of-the-art. J isakos. 2023;8(5):306-317. |