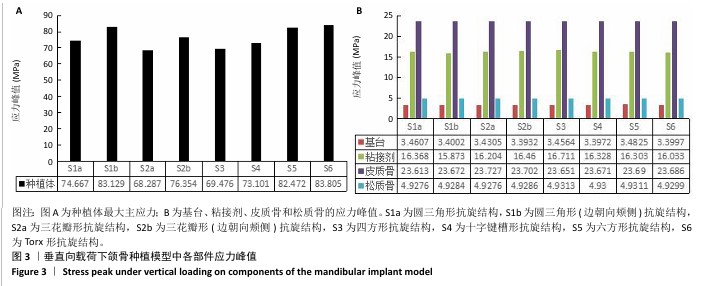
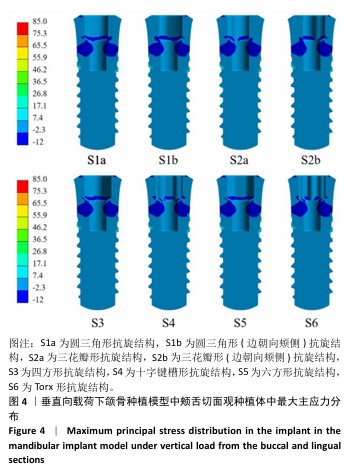
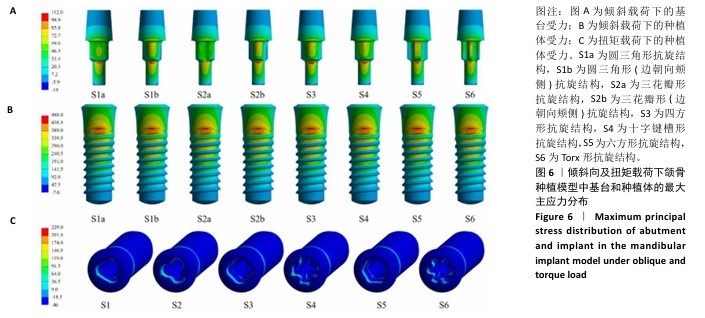
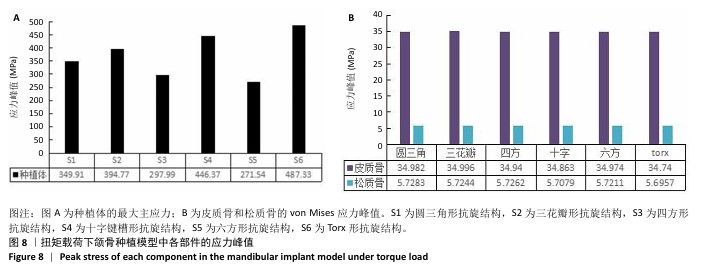
[1] 洪光.氧化锆牙种植体的现状与未来[J].口腔材料器械杂志,2022, 31(2):77-81.
[2] POLI PP, DE MIRANDA FV, POLO TOB, et al. Titanium Allergy Caused by Dental Implants: A Systematic Literature Review and Case Report. Materials (Basel). 2021;14(18):5239.
[3] KIM KT, EO MY, NGUYEN TTH, et al. General review of titanium toxicity. Int J Implant Dent. 2019;5(1):10.
[4] CHOPRA D, JAYASREE A, GUO T, et al. Advancing dental implants: Bioactive and therapeutic modifications of zirconia. Bioact Mater. 2021;13:161-178.
[5] XIONG J, MILLER CM, SHARMA D. Effect of Bergenin on Human Gingival Fibroblast Response on Zirconia Implant Surfaces: An In Vitro Study. J Funct Biomater. 2023;14(9):474.
[6] ALGHAULI M, ALQUTAIBI AY, WILLE S, et al. 3D-printed versus conventionally milled zirconia for dental clinical applications: Trueness, precision, accuracy, biological and esthetic aspects. J Dent. 2024;144:104925.
[7] RIMONDINI L, CERRONI L, CARRASSI A, et al. Bacterial colonization of zirconia ceramic surfaces: an in vitro and in vivo study. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2002;17(6):793-798.
[8] SPITZNAGEL FA, BALMER M, WIEDEMEIER DB, et al. Clinical outcomes of all-ceramic single crowns and fixed dental prostheses supported by ceramic implants: A systematic review and meta-analyses. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2022;33(1):1-20.
[9] 夏昭鑫,高亦辰,邓雨瑶,等.不同材料种植体修复单颗上前牙缺失的三维有限元分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2025,29(22):4687-4693.
[10] MONTAZERIAN M, ZANOTTO ED. Bioactive and inert dental glass-ceramics. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2017;105(2):619-639.
[11] SANZ M, NOGUEROL B, SANZ-SANCHEZ I, et al. European Association for Osseointegration Delphi study on the trends in Implant Dentistry in Europe for the year 2030. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2019;30(5):476-486.
[12] BOLLEN C, HAKOBAYAN G, JÖRGENS M. One-piece versus two-piece ceramic dental implants. Br Dent J. 2024;236(5):383-387.
[13] CIONCA N, HASHIM D, MOMBELLI A. Zirconia dental implants: where are we now, and where are we heading? Periodontol 2000. 2017;73(1):241-258.
[14] GUL A, PAPIA E, NAIMI-AKBAR A, et al. Zirconia dental implants; the relationship between design and clinical outcome: A systematic review. J Dent. 2024;143:104903.
[15] ZHANG F, MONZAVI M, LI M, et al. Fracture analysis of one/two-piece clinically failed zirconia dental implants. Dent Mater. 2022;38(10):1633-1647.
[16] KAMMERMEIER A, ROSENTRITT M, BEHR M, et al. In vitro performance of one- and two-piece zirconia implant systems for anterior application. J Dent. 2016;53:94-101.
[17] PREIS V, KAMMERMEIER A, HANDEL G, et al. In vitro performance of two-piece zirconia implant systems for anterior application. Dent Mater. 2016;32(6):765-774.
[18] BRUNELLO G, RAUCH N, BECKER K, et al. Two-piece zirconia implants in the posterior mandible and maxilla: A cohort study with a follow-up period of 9 years. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2022;33(12):1233-1244.
[19] 马吾兰江·阿不都仁木,孜拉来·居来提,白布加甫·叶力思,等.上颌中切牙种植联冠应用角度基台在不同种植体间距的应力分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2025,29(16):3351-3359.
[20] SEN N, US YO. Fatigue survival and failure resistance of titanium versus zirconia implant abutments with various connection designs. J Prosthet Dent. 2019;122(3):315.e1-315.e7.
[21] IIJIMA N, HOMMA S, NAKANO R, et al. Fatigue properties of hollow zirconia implants. Dent Mater J. 2021;40(4):885-893.
[22] CHOI SM, CHOI H, LEE DH, et al. Comparative finite element analysis of mandibular posterior single zirconia and titanium implants: a 3-dimensional finite element analysis. J Adv Prosthodont. 2021;13(6):396-407.
[23] 王天瑜,牛一龙,周健邦,等.氧化锆口腔种植体的动态植入过程分析与设计[J].力学学报,2022,54(1):220-231.
[24] HANAOKA M, GEHRKE SA, MARDEGAN F, et al. Influence of implant/abutment connection on stress distribution to implant-surrounding bone: a finite element analysis. J Prosthodont. 2014;23(7):565-571.
[25] FALCINELLI C, VALENTE F, VASTA M, et al. Finite element analysis in implant dentistry: State of the art and future directions. Dent Mater. 2023;39(6): 539-556.
[26] CAGLAR A, BAL BT, AYDIN C, et al. Evaluation of stresses occurring on three different zirconia dental implants: three-dimensional finite element analysis. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2010;25(1):95-103.
[27] ROSENTRITT M, HAGEMANN A, HAHNEL S, et al. In vitro performance of zirconia and titanium implant/abutment systems for anterior application. J Dent. 2014;42(8):1019-1026.
[28] ROSENTRITT M, REMBS A, BEHR M, et al. In vitro performance of implant-supported monolithic zirconia crowns: Influence of patient-specific tooth-coloured abutments with titanium adhesive bases. J Dent. 2015;43(7):839-845.
[29] ANDREIOTELLI M, KOHAL RJ. Fracture strength of zirconia implants after artificial aging. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res. 2009;11(2):158-166.
[30] MATSUOKA T, NAKANO T, YAMAGUCHI S, et al. Effects of Implant-Abutment Connection Type and Inter-Implant Distance on Inter-Implant Bone Stress and Microgap: Three-Dimensional Finite Element Analysis. Materials (Basel). 2021;14(9):2421.
[31] FAEGH S, MÜFTÜ S. Load transfer along the bone-dental implant interface. J Biomech. 2010;43(9):1761-1770.
[32] CHO SY, HUH YH, PARK CJ, et al. Three-Dimensional Finite Element Analysis on Stress Distribution of Internal Implant-Abutment Engagement Features. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2018;33(2):319-327.
[33] ON SW, YI SM, PARK IY, et al. Fracture and Fatigue of Dental Implants Fixtures and Abutments with a Novel Internal Connection Design: An In Vitro Pilot Study Comparing Three Different Dental Implant Systems. J Funct Biomater. 2022;13(4):239.
[34] SUN F, XU L, HAN J, et al. Effect of the connection structure of zirconia dental implants on biomechanical properties. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2025;161:106800.
[35] ČADA R, FRYDRÝŠEK K, SEJDA F, et al. Analysis of Locking Self-Taping Bone Screws for Angularly Stable Plates. J Med Biol Eng. 2017;37(4):612-625.
[36] KUL E, KORKMAZ İH. Effect of different design of abutment and implant on stress distribution in 2 implants and peripheral bone: A finite element analysis study. J Prosthet Dent. 2021;126(5):664.e1-664.e9.
[37] PAPAVASILIOU G, KAMPOSIORA P, BAYNE SC, et al. 3D-FEA of osseointegration percentages and patterns on implant-bone interfacial stresses. J Dent. 1997;25(6):485-491.
[38] KONDAREDDY S, N S, AVINASH CK A, et al. The Effect of Different Abutment Designs and Materials on Stress Distribution in Implants and Peripheral Bones: A Three-Dimensional Finite Element Analysis. Cureus. 2024;16(7):e64871.
[39] ABOELFADL A, KEILIG L, EBEID K, et al. Biomechanical behavior of implant retained prostheses in the posterior maxilla using different materials: a finite element study. BMC Oral Health. 2024;24(1):455.
[40] MUTLU-SAĞESEN HLE, SAĞESEN EA, ÖZCAN M. Bibliometric analysis of zirconia publications between 1980 and 2021: Global productivity and publication trends. J Prosthodont Res. 2024;68(1):147-155.
[41] AKÇA K, IPLIKÇIOĞLU H. Finite element stress analysis of the effect of short implant usage in place of cantilever extensions in mandibular posterior edentulism. J Oral Rehabil. 2002;29(4):350-356.
[42] OPLER R, WADHWANI C, CHUNG KH. The effect of screwdriver angle variation on the off-axis implant abutment system and hexalobular screw. J Prosthet Dent. 2020;123(3):524-528.
[43] REZENDE CE, BORGES AF, GONZAGA CC, et al. Effect of cement space on stress distribution in Y-TZP based crowns. Dent Mater. 2017;33(2):144-151. |