中国组织工程研究 ›› 2026, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (3): 671-679.doi: 10.12307/2026.012
• 骨与关节综述 bone and joint review • 上一篇 下一篇
血管内皮生长因子A 靶向调控血管化治疗激素性股骨头坏死的机制
王正业,刘万林,赵振群
- 内蒙古医科大学第二附属医院儿童骨科医学中心,内蒙古自治区呼和浩特市 010090
-
收稿日期:2024-11-21接受日期:2025-02-15出版日期:2026-01-28发布日期:2025-07-05 -
通讯作者:刘万林,硕士,教授,内蒙古医科大学第二附属医院儿童骨科医学中心,内蒙古自治区呼和浩特市 010090 共同通讯作者:赵振群,博士,教授,内蒙古医科大学第二附属医院儿童骨科医学中心,内蒙古自治区呼和浩特市 010090 -
作者简介:王正业,男,1997年生,内蒙古自治区准格尔旗人,汉族,在读硕士,主要从事髋关节的相关研究。 -
基金资助:国家自然科学基金项目(81960397,82260424),项目负责人:刘万林;国家自然科学基金项目(82160414,81760391),项目负责人:赵振群;内蒙古自治区成果转化项目(CGZH2018146),项目负责人:刘万林
Mechanism by which vascular endothelial growth factor A targets regulation of angiogenesis in the treatment of steroid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head
Wang Zhengye, Liu Wanlin, Zhao Zhenqun
- Children's Orthopedic Medical Center, The Second Affiliated Hospital of Inner Mongolia Medical University, Hohhot 010090, Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, China
-
Received:2024-11-21Accepted:2025-02-15Online:2026-01-28Published:2025-07-05 -
Contact:Liu Wanlin, MS, Professor, Children's Orthopedic Medical Center, The Second Affiliated Hospital of Inner Mongolia Medical University, Hohhot 010090, Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, China Co-corresponding author: Zhao Zhenqun, MD, Professor, Children's Orthopedic Medical Center, The Second Affiliated Hospital of Inner Mongolia Medical University, Hohhot 010090, Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, China -
About author:Wang Zhengye, Master candidate, Children's Orthopedic Medical Center, The Second Affiliated Hospital of Inner Mongolia Medical University, Hohhot 010090, Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, China -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China, Nos. 81960397 and 82260424 (both to LWL); National Natural Science Foundation of China, Nos 82160414 and 81760391 (both to ZZQ); the Achievement Transformation Project of Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, No. CGZH2018146 (to LWL)
摘要:
文题释义:
激素诱导的股骨头坏死:其特征是股骨头血供中断和软骨下骨坏死,导致关节功能障碍。长期使用糖皮质激素是其主要诱因,病理机制涉及多个因素,包括血管内凝血和骨细胞凋亡等。血管内皮生长因子A:是一种具有高度特异性促血管生成活性的生长因子,它通过与血管内皮细胞上的血管内皮生长因子受体结合,激活下游信号通路,诱导内皮细胞迁移及增殖,以促进血管的生成。
摘要
背景:激素诱导的股骨头坏死是一种严重的骨科疾病,其特征是股骨头血供中断和软骨下骨坏死,最终导致关节功能障碍。长期使用糖皮质激素是激素性股骨头坏死的主要诱因,其病理机制涉及多个因素,包括血管内凝血和骨细胞凋亡等。血管内皮生长因子A作为关键的血管生成因子,在激素诱性股骨头坏死的治疗中具有潜在价值。
目的:总结血管内皮生长因子A在激素性股骨头坏死中的作用机制,包括它在促进血管生成、抗凋亡以及调节脂质代谢等方面的研究进展,并讨论血管内皮生长因子A靶向治疗的临床应用前景。
方法:通过检索PubMed、中国知网、万方数据库及维普数据库建库至2024年11月发表的文献,筛选出与血管内皮生长因子A靶向调控血管化治疗激素性股骨头坏死相关的文献。经过质量评估,共筛选出71篇文献,由独立的研究者提取数据,并通过小组讨论解决分歧。
结果与结论:①血管内皮生长因子A通过与其受体内皮生长因子受体1,2结合,激活下游信号通路,促进血管内皮细胞的增殖、迁移和血管生成,因此它能促进侧支循环的形成,改善骨坏死区域的血液供应;②血管内皮生长因子A的表达降低可能导致骨组织内血管数量减少,加剧股骨头的缺血状态;此外,血管内皮生长因子A具有抗凋亡作用,能够减少骨细胞和骨髓细胞的凋亡,从而保护骨组织;③血管内皮生长因子A在调节脂质代谢和炎症反应中的作用及促进骨髓间充质干细胞的成骨分化,为激素诱导的股骨头坏死的治疗提供了新的视角;④血管内皮生长因子A蛋白递送系统的开发,如脂质纳米粒和基于外泌体的递送系统,为血管内皮生长因子A的临床应用提供了新的可能性;⑤血管内皮生长因子A在激素性股骨头坏死治疗中的研究进展为开发新的治疗策略提供了坚实的基础,并为未来的研究方向和临床应用开辟了新的道路;⑥随着对血管内皮生长因子A作用机制的进一步阐明和递送技术的不断进步,将为激素诱导的股骨头坏死患者提供更有效的治疗方法,改善其预后。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:人工关节;骨植入物;脊柱;骨折;内固定;数字化骨科;组织工程
中图分类号:
引用本文
王正业, 刘万林, 赵振群. 血管内皮生长因子A 靶向调控血管化治疗激素性股骨头坏死的机制[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(3): 671-679.
Wang Zhengye, Liu Wanlin, Zhao Zhenqun. Mechanism by which vascular endothelial growth factor A targets regulation of angiogenesis in the treatment of steroid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(3): 671-679.
点[11-12]。到了2000年代,VEGF-A在激素性股骨头坏死治疗中的潜力开始受到关注。2001年,美国骨科医师学会发布了关于激素性股骨头坏死治疗的指南,其中特别提到VEGF-A作为潜在的治疗靶点,这标志着VEGF-A在激素性股骨头坏死治疗中的研究开始受到学术界的重视。2008年刘万林教授团体发现激素可导致血小板源性生长因子生理活性相对下降以及VEGF mRNA转录下调,进而影响血小板源性生长因子与VEGF对血管生成的正常调节,是激素导致股骨头坏死的重要病理学基础。2010年代见证了VEGF-A递送系统的重要发展[6]。大约在2010年,麻省理工学院的Robert Langer博士和Daniel Anderson博士的研究团队开发了脂质纳米粒技术,用于递送VEGF-A mRNA,这一技术的开发为VEGF-A的临床应用,尤其是在基因治疗领域,提供了新的可能性[13]。
到了2020年代,VEGF-A与其他治疗策略的联合应用成为研究的新趋势。这种联合治疗策略的开发为提高激素性股骨头坏死的治疗效果提供了新的途径,展现了VEGF-A在治疗激素性股骨头坏死中的新潜力和应用前景。
2.1 VEGF-A的血管化机制 VEGF-A 是一种高度保守的27 kD二聚体糖蛋白,VEGF家族包括VEGF-A、VEGF-B、VEGF-C、VEGF-D、VEGF-E以及胎盘生长因子等多个成员。通常所说的VEGF实际上是指VEGF-A,因为它是VEGF家族中最主要的成员,且在血管生成中起核心作用。VEGF-A存在多种亚型,包括VEGFA121、VEGFA165、VEGFA189和VEGFA206,这些亚型由可变剪接产生,含有不同数量的氨基酸[14]。VEGF-A由多种细胞类型分泌,包括内皮细胞、平滑肌细胞和巨噬细胞。VEGF-A通过与其受体VEGFR-1和VEGFR-2结合,启动血管生成过程[15]。VEGF-A是一种分泌型糖蛋白,能够以多种异构体形式存在,其中VEGF-A165是最常见的形式。VEGF-A可以与VEGFR-1以高亲和力结合,这种结合促使VEGFR-1发生二聚化,激活其内在的酪氨酸激酶活性。同时,VEGF-A与VEGFR-1的结合主要促进了血管通透性的增加,这对于血管生成的早期阶段至关重要,因为它允许血浆成分和免疫细胞通过血管壁,为新生血管提供必要的营养和细胞成分。VEGFR-1的激活也与内皮细胞的存活和迁移相关,但其对血管生成的直接促进作用相对较弱,部分原因是VEGFR-1的激酶活性相对较低。此外,VEGF-A与VEGFR-2的结合是血管生成中最为关键的步骤之一,因为VEGFR-2具有更高的酪氨酸激酶活性。VEGF-A与VEGFR-2的结合同样导致受体二聚化和自身磷酸化,从而激活VEGFR-2的激酶活性。这种激活进一步促进了内皮细胞的增殖、迁移和存活,这些是新血管形成的基础[16-19]。这一发现对于理解激素性股骨头坏死的病理生理学至关重要,也为开发新的治疗策略提供了理论基础。因此推测,通过调节VEGF-A的表达或其受体的活性,可能实现对激素性股骨头坏死病程的干预,尤其是在改善股骨头血供方面。
VEGF诱导的信号传导导致细胞周期相关基因表达增加,促进内皮细胞从G0/G1期进入S期,从而增加细胞数量。同时,VEGF-A通过改变细胞骨架的动态重组,增强内皮细胞的迁移能力,这对于新血管的延伸和分支形成至关重要[20]。而且,VEGF-A能够迅速增加血管的通透性,涉及Src家族激酶和Rho家族三磷酸鸟苷酶的激活,导致血管内皮细胞间的连接蛋白如血管内皮钙黏蛋白和紧密连接蛋白的重排。新形成的血管需要进一步的稳定和成熟,这一过程涉及到周细胞和基底膜的形成。VEGF-A通过促进血小板源性生长因子B的表达,招募周细胞到新血管基底膜,增强血管的稳定性,见图3。同时,VEGF-A还与Notch、酪氨酸激酶受体Tie-2等信号通路相互作用,调节血管的成熟和功能。
近期研究发现,VEGF-A与VEGFR-2结合后,激活Ras-丝裂原活化蛋白激酶信号通路,从而调控细胞增殖与基因表达。VEGF-A通过VEGFR-2的Y1175残基的磷酸化,诱导磷脂酶Cγ依赖的钙离子动员和激活蛋白激酶C,进而激活丝裂原活化蛋白激酶通路,导致细胞持续增殖[21]。
此外,VEGF-A诱导的信号传导激活黏着斑激酶/桩蛋白信号通路,参与细胞骨架重排[22],这一过程对于内皮细胞的形态变化和迁移至关重要,因为细胞骨架的重组是细胞迁移和血管形成的基础。有研究表明,VEGF-A同样可以通过VEGFR-2激活磷脂酰肌醇3激酶/蛋白激酶B信号通路,调控细胞存活。丝氨酸/苏氨酸蛋白激酶B的激活可以促进细胞周期进程,抑制凋亡,并增强细胞对营养和生长因子的响应。VEGF-A还可以激活磷脂酶Cγ通路,控制血管通透性。磷脂酶Cγ的激活导致肌醇三磷酸和二酯甘油的产生,进而增加细胞内钙离子浓度,激活蛋白激酶C,促进血管通透性增加。不同VEGF-A亚型可能激活不同的下游信号通路,例如,VEGF-A165处理促进了磷脂酶Cγ1磷酸化的增加,这与随后的胞浆钙离子的增加成比例。这种VEGF-A同种型特异性钙离子通量的主要结果是差异脱磷酸作用和随后转录因子活化T细胞核因子2的核易位[23]。VEGF-A刺激的内皮细胞迁移功能所需的功能是活化T细胞核因子2,其核易位导致基因表达的变化,这对于内皮细胞的迁移和血管形成至关重要。
通过表1,可以更清晰地看到VEGF-A与VEGFR-1及VEGFR-2结合时在血管生成中的作用差异。VEGFR-2在促进血管生成和维持血管稳定性方面发挥着更为关键的作用,而VEGFR-1则在调节血管通透性和炎症反应中扮演重要角色。这种差异性为针对特定血管生成相关疾病的治疗提供了潜在的靶点选择。
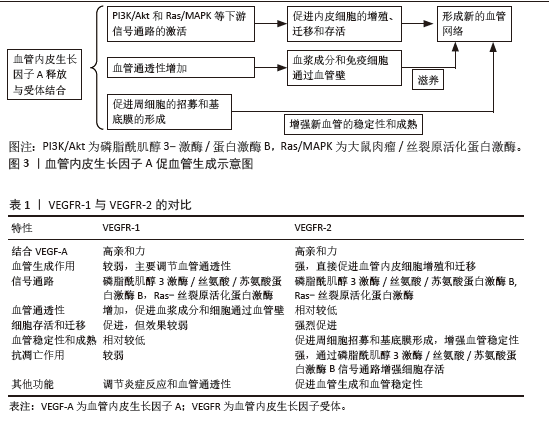
2.2 VEGF-A与激素性股骨头坏死 VEGF-A与激素性股骨头坏死的关系是多维度的,并且其在疾病发展中的作用机制复杂。VEGF-A作为一种关键的血管生成因子,在激素性股骨头坏死中的作用不仅限于促进血管生成,还包括抗凋亡、调节脂质代谢以及维持骨组织健康,见图4。值得注意的是,VEGF-A抗凋亡作用能够减少骨细胞和骨髓细胞的凋亡,保护骨组织。大剂量激素的使用对脂质代谢产生显著影响,导致骨髓间充质干细胞倾向于向脂肪细胞分化,而非成骨细胞,这种分化过程中形成的微栓子影响了正常的血液循环,逐渐导致骨组织坏死。在激素性股骨头坏死患者中,股骨头坏死区域的脂肪含量明显高于非坏死区域,这一发现揭示了激素引起的髓内脂肪堆积与脂质代谢异常之间的密切联系。此外,大剂量激素还会导致凝血纤溶系统失调和血液流动缓慢,进而在股骨头的微血管中形成血栓,这是激素性股骨头坏死发展的一个重要机制[24]。血液高度黏稠和广泛微血栓激活的存在,表明血液高凝状态是股骨头坏死的一个高危因
素[25]。长期大量应用激素还会导致骨量和骨矿物质密度降低,影响骨结构的支撑稳定性,增加骨折和骨坏死的风险。激素通过改变骨组织的正常代谢水平,使得股骨头更易发生骨质疏松[26]。过量的激素还会引起大量骨细胞凋亡,减弱股骨头的稳定性,使其更易发生骨折和塌陷。激素性股骨头坏死中存在的DNA氧化损伤和细胞凋亡增加的证据表明,激素不仅抑制了成骨分化,促进了成脂分化,还可能通过氧化应激损伤促进骨细胞凋亡[27]。在间充质干细胞的分化过程中,CCAAT增强子结合蛋白α通过靶向过氧化物酶体增殖物激活受体γ信号通路促进成脂分化,而其过表达则损害成骨分化。过氧化物酶体增殖物激活受体γ的组蛋白H3K27乙酰化在激素性股骨头坏死的表观遗传机制中起着重要作用,CCAAT增强子结合蛋白α通过抑制组蛋白脱乙酰酶1上调过氧化物酶体增殖物激活受体γ启动子区域的组蛋白H3K27乙酰化水平,影响间充质干细胞的分化方向[28]。这些机制为开发针对性治疗策略提供了潜在的靶点。
在激素性股骨头坏死的病理过程中,VEGF-A的表达降低可能导致骨组织内血管数量减少,从而加剧股骨头的缺血状态[6]。
VEGF-A的不同异构体在功能上也存在差异。例如,VEGF-A165a是生物活性最强、分泌量多、最具有代表性亚型,参与血管的生成、刺激内皮细胞增殖,形成血管结构;而VEGF-A165b由于C端序列的变化,不能有效使VEGFR2磷酸化,极弱激活VEGFR2激酶结构域,导致下游靶点蛋白激酶和细胞外调节蛋白激酶短暂微弱的磷酸化,具有抗血管生成、抗渗透性和抗迁移的特性[29]。值得注意的是,VEGF-A的表达异常可能与多种因素有关。例如,糖皮质激素处理可以降低VEGF-A的表达,进而影响血管生成和骨组织修复[6,30]。
2.2.1 VEGF-A与骨组织 VEGF-A影响成骨细胞功能的不同机制,包括骨修复过程中的旁分泌、自分泌和内分泌信号。其在骨修复不同阶段的作用,包括炎症、软骨内骨化、骨痂形成和骨重塑过程中的膜内骨化阶段[8]。
有研究发现,在低氧状态下,缺氧诱导因子1α的羟基化受到抑制,导致非羟基化的缺氧诱导因子1α在细胞质中积聚,随后转运到细胞核中与缺氧诱导因子1β发生二聚反应,引起氧适应性调节,调节骨代谢,促进骨形成[31]。缺氧诱导因子1α信号传导限制细胞耗氧量,避免活性氧自由基积累,保持氧化还原平衡,诱导调节自身耗能方式,减少能量损耗,增加细胞存活率。
成骨细胞衍生的VEGF-A在骨缺损愈合中发挥关键作用,促进巨噬细胞募集和血管生成反应,并在膜内骨化发生修复的区域耦合血管生成和成骨,可能在此过程中充当旁分泌因子。H亚型血管在骨再生过程中起关键性作用,其内皮细胞分泌的核因子κB受体激活因子配体通过核因子κB受体激活因子配体-核因子κB受体激活因子信号机制支持多信号通路,如缺氧诱导因子1α和Notch通路,参与血管生成和骨再生的调控,为骨代谢提供适宜的微环境,并通过旁分泌途径调节血管周围骨骼细胞的活性,使血管新生与骨形成相互耦联[32]。
有研究发现,在骨形成过程中,成骨细胞和内皮细胞之间的相互作用至关重要,内皮细胞分泌的胰岛素样生长因子、前列腺素、集落刺激因子等促进骨细胞的增殖、分化以及骨组织生长,而成骨细胞分泌的VEGF-A和成纤维细胞生长因子则促进血管形成[33]。并且VEGF-A与多种生长因子如骨形态发生蛋白、胰岛素样生长因子等具有协同作用,共同促进骨组织的修复和再生[34],骨形态发生蛋白2、VEGF和碱性成纤维细胞生长因子的联合应用可以促进骨髓间充质干细胞的成骨分化[35]。而且还有研究表明,VEGF-A可能通过影响骨保护素的表达和功能,调节骨代谢,骨保护素作为核因子κB受体激活因子配体的诱导受体,通过与核因子κB受体激活因子配体的结合减少破骨细胞的产生,在骨形成和骨吸收的过程中起到重要作用[36]。
成纤维细胞生长因子信号通路在软骨内成骨和膜内成骨中起着关键作用,VEGF-A可能通过与成纤维细胞生长因子信号通路的相互作用,共同调节成骨细胞的分化和骨形成[37],这些机制共同作用,使其在调节成骨细胞分化和骨形成中发挥着重要作用。此外有研究表明,VEGF-A在骨髓间充质干细胞的成脂分化中起到抑制作用,在骨坏死的病理过程中,骨髓间充质干细胞的成脂分化增加会导致骨形成减少[38]。VEGF-A能够通过降低过氧化物酶体增殖剂激活受体γ2和脂肪酸结合蛋白4的基因表达、下调过氧化物酶体增殖物激活受体γ的磷酸化水平,从而抑制骨髓间充质干细胞向脂肪细胞分化[39]。VEGF-A通过激活磷脂酰肌醇3激酶/丝氨酸/苏氨酸蛋白激酶B信号通路,同样可以增强骨髓间充质干细胞的成骨分化能力[40]。这一信号通路的激活不仅促进了骨髓间充质干细胞的成骨分化,还增加了VEGF的分泌,进一步促进了血管生成和骨修复。VEGF-A与骨形态发生蛋白6共表达的骨髓间充质干细胞在修复新西兰兔股骨骨缺损中具有协同作用,比单纯应用骨形态发生蛋白6或VEGF的作用更大[40]。这表明VEGF-A与骨形态发生蛋白的联合应用可以更有效地促进骨髓间充质干细胞的成骨分化和骨组织修复。其通过影响Hedgehog信号通路中的GLI家族转录因子,进而影响骨髓间充质干细胞的分化和功能。这种影响可能涉及到VEGF-A对GLI因子表达的调节,进而影响骨髓间充质干细胞的成骨和成脂分化[41]。
2.2.2 骨坏死中的保护作用 首先,VEGF-A通过激活磷脂酰肌醇3激酶/丝氨酸/苏氨酸蛋白激酶B信号通路,增强成骨细胞和内皮细胞的抗凋亡能力,这一过程通过抑制促凋亡蛋白如BCL2-Associated
X蛋白和半胱氨酸天冬氨酸蛋白酶3的表达,减少细胞凋亡,从而保护骨组织[42]。其次,VEGF-A的表达增加促进新的血管形成,这一作用通过促进内皮细胞增殖和迁移实现,为受损的骨组织提供必要的营养和氧气,减少骨细胞的死亡[43]。
并且,VEGF-A还能促进侧支循环的形成,改善骨坏死区域的血液供应,这一机制通过增加血管的分支和连接来实现。在炎症反应的调节中,VEGF-A通过减少炎症因子如肿瘤坏死因子α和白细胞介素1β的释放,减轻炎症对骨组织的破坏作用,有助于保护骨组织,防止骨坏死的进一步发展。因为其有助于保护和维持血-骨屏障的完整性,减少炎症细胞的浸润,减轻骨坏死区域的炎症反应,从而保护骨组织,这一机制可能涉及VEGF-A对内皮细胞间紧密连接蛋白表达的调节[44]。
此外,VEGF-A还能促进骨膜的增生和活化,骨膜中的干细胞被激活后可以分化为成骨细胞,参与骨修复过程,这种骨膜反应在骨坏死的治疗中起到关键作用。VEGF-A通过影响破骨细胞的活性和数量,间接影响骨吸收过程,这一机制可能涉及核因子κB受体激活因子配体/骨保护素系统,其中VEGF-A可能通过增加骨保护素的表达,减少核因子κB受体激活因子配体的作用,从而减少骨吸收,保护骨组织[45]。通过这些机制,VEGF-A在骨坏死中的保护作用得以发挥,为治疗激素性股骨头坏死提供了新的策略和方法。
2.3 VEGF-A的抗凋亡作用
2.3.1 磷脂酰肌醇3激酶/丝氨酸/苏氨酸蛋白激酶B信号通路的调节 VEGF-A通过与其受体VEGFRs结合,特别是VEGFR-2,
激活下游的磷脂酰肌醇3激酶/丝氨酸/苏氨酸蛋白激酶B信号通路,这是其抗凋亡作用的主要机制之一[5,46]。其激活可以抑制促凋亡蛋白,进而抑制半胱氨酸天冬氨酸蛋白酶9及其下游效应因子,避免细胞发生凋亡。同时,它还能增加凋亡抑制蛋白的表达,从而抑制半胱氨酸天冬氨酸蛋白酶3,7,9介导的细胞凋亡。
磷脂酰肌醇3激酶/丝氨酸/苏氨酸蛋白激酶B信号通路的负反馈主要是由同源性磷酸酶-张力蛋白和含Src同源结构域的肌醇多磷酸酯5-磷酸酶2调节的。同源性磷酸酶-张力蛋白可以从磷脂酰肌醇3,4,5-三磷酸的3′去磷酸使其转变为磷脂酰肌醇(4,5)二磷酸,含Src同源结构域的肌醇多磷酸酯5-磷酸酶2可以从磷脂酰肌醇3,4,5-三磷酸的5′去磷酸使其转变为磷脂酰肌醇(4,5)二磷酸,从而抑制丝氨酸/苏氨酸蛋白激酶B及其下游的分子进一步活化[47]。其活化可激活周期蛋白依赖性激酶2和4,这些与不同的细胞周期蛋白底物结合形成复合物,诱导进入S期的细胞合成DNA、促进G1期向S期转换。此外,丝氨酸/苏氨酸蛋白激酶B通过磷酸化细胞周期检测点激酶1的Ser280位点使磷酸化细胞周期检测点激酶1失活,因为磷酸化细胞周期检测点激酶1是阻止细胞从S期进入G2/M期的重要节点。近期研究者发现,微管关联蛋白4是磷脂酰肌醇3激酶α的互作伴侣,磷脂酰肌醇3激酶α分布在沿微管的小囊泡上,磷脂酰肌醇3激酶α与微管关联蛋白4的直接作用可促进磷脂酰肌醇3激酶α沿着微管分布。微管关联蛋白4的缺失会干扰磷脂酰肌醇3激酶α募集到微管和内体上,影响磷脂酰肌醇3激酶α与激活受体复合物的结合,并减少磷脂酰肌醇3激酶α在内体中活化、磷脂酰肌醇3,4,5-三磷酸的合成导致磷脂酰肌醇3激酶-丝氨酸/苏氨酸蛋白激酶B信号传导的失调[48]。
2.3.2 凋亡相关基因的表达调控 B细胞淋巴瘤2蛋白家族基因在调控细胞凋亡中起着核心作用[30]。VEGF-A通过影响B细胞淋巴瘤2蛋白家族基因的表达,可以抑制细胞凋亡。例如,VEGF-A能够通过磷脂酰肌醇3激酶/丝氨酸/苏氨酸蛋白激酶B信号通路,增加B细胞淋巴瘤2蛋白和B细胞淋巴瘤X蛋白的表达,同时减少B细胞淋巴瘤2-Associated X蛋白质和B淋巴细胞瘤2基因相关启动子的表达,从而抑制线粒体介导的凋亡途径[49]。肿瘤蛋白p53是一个重要的肿瘤抑制基因,其激活可以导致细胞周期阻滞和细胞凋亡。VEGF-A能够通过影响p53的稳定性和活性,进而调节下游凋亡相关基因的表达[50-51]。在某些情况下,VEGF-A通过抑制p53的转录活性或促进其降解,减少p53介导的凋亡效应。
内质网应激途径是细胞凋亡的另一条重要信号通路[3]。VEGF-A可能通过调节内质网应激传感器肌醇需求酶1α和蛋白激酶R样内质网激酶的活性,影响内质网应激相关基因的表达,从而参与细胞凋亡的调控。近期有研究发现,VEGF-A还可能通过调节死亡受体如Fas细胞表面死亡受体和肿瘤坏死因子受体的表达或其下游信号分子的活性,影响死亡受体途径介导的细胞凋亡。这种调控可能涉及到半胱氨酸天冬氨酸蛋白酶8和半胱氨酸天冬氨酸蛋白酶10的激活状态,进而影响细胞的凋亡进程[51-53]。
此外,VEGF-A作为一种分泌型因子,可能通过调节细胞外信号分子如细胞因子、趋化因子的表达或活性,影响细胞外途径介导的细胞凋亡信号传导。还有研究表明,高糖条件下VEGF-A表达下调,导致内皮细胞凋亡增加。VEGF-A的添加可以阻止高糖诱导的内皮细胞凋亡,并且能够逆转高糖诱导的活性氧生成、钙超载、B细胞淋巴瘤2-Associated X蛋白质/B细胞淋巴瘤2蛋白比值增加以及半胱氨酸天冬氨酸蛋白酶3激活[54]。近期龚瑜林等[55]研究发现,磷脂酰肌醇3激酶/丝氨酸/苏氨酸蛋白激酶B/哺乳动物雷帕霉素靶蛋白信号通路是调控自噬的主要通路之一,该通路对细胞凋亡、代谢和血管生成等信号转导和生物学过程中起着重要的调节作用。
综上所述,VEGF-A通过与其受体的结合,激活包括磷脂酰肌醇3激酶/丝氨酸/苏氨酸蛋白激酶B和Ras-丝裂原活化蛋白激酶在内的下游信号通路,这些信号通路对于抑制细胞凋亡至关重要。VEGF-A的抗凋亡作用主要体现在以下几个方面:首先,它能够通过磷脂酰肌醇3激酶/丝氨酸/苏氨酸蛋白激酶B信号通路增强成骨细胞和内皮细胞的抗凋亡能力,抑制促凋亡蛋白如BCL2-Associated X蛋白质和半胱氨酸天冬氨酸蛋白酶3的表达,减少细胞凋亡,从而保护骨组织;其次,VEGF-A通过增加新血管形成,为受损的骨组织提供必要的营养和氧气,减少骨细胞的死亡;此外,VEGF-A还能通过减少炎症因子的释放,减轻炎症对骨组织的破坏作用,保护骨组织,防止骨坏死的进一步发展。这些作用共同构成了VEGF-A在抗凋亡中的多效性,这一发现特别重要,因为它不仅涉及到血管生成,还可能影响到骨组织的修复和再生。因此不难发现,VEGF-A的抗凋亡作用可能与其在血管生成中的作用相协同,共同促进骨坏死区域的恢复,使VEGF-A成为治疗激素性股骨头坏死等骨疾病中一个极具潜力的治疗靶点。
2.4 VEGF-A调节脂质代谢的作用 激素性股骨头坏死是一种严重的骨科疾病,其病理过程中涉及多种代谢紊乱,包括脂质代谢异常。VEGF-A作为一种多功能的细胞因子,除了在血管生成中的作用外,其在脂质代谢调节中的作用也逐渐受到重视。研究VEGF-A如何调控脂质代谢,对于理解激素性股骨头坏死的发病机制和开发新的治疗策略具有重要意义。VEGF-A、VEGF-C等家族因子的生物学功能主要表现在淋巴管,并已被证明可通过影响乳糜管来调节肠道对脂质的吸收,并且发现VEGF-A在调节脂蛋白脂肪酶、内皮脂肪酶和重组聚糖1方面有重要作用[56]。
脂质自噬是细胞通过自噬途径降解脂质的过程,对脂质代谢具有重要影响。研究表明,VEGF-A可能通过影响脂质自噬相关基因如Atg14的表达,调节脂质代
谢[57]。Atg14是自噬过程中的关键因子,其表达受FoxO转录因子和生物钟节律的调控,对肝脏自噬和脂质代谢起着至关重要的作用。乙酰辅酶A羧酸酶1是控制脂肪酸合成速率的关键酶。研究发现,VEGF-A可能通过影响乙酰辅酶A羧酸酶1基因的表达,进而通过单磷酸腺苷激活的蛋白激酶-过氧化物酶体增殖物激活受体α-肉碱棕榈酰转移酶1A轴对脂质代谢和线粒体功能进行双重调节,减少脂质积累。铜蓝蛋白是一种含有铜的氧化酶,参与铁代谢和脂质氧化过程。最新研究进展显示,铜蓝蛋白在脂质代谢稳态调控中起着重要作用,可能通过调节铁水平影响脂质代谢[58]。铜蓝蛋白缺乏的小鼠模型显示出肝脏和脂肪组织中脂质代谢的失调,这可能与VEGF-A的调节作用相关[59]。巨噬细胞的极化状态与炎症反应密切相关,M1型巨噬细胞释放促炎性细胞因子,而M2型巨噬细胞通过分泌抗炎介质抵抗炎症反应,促进组织修复。VEGF-A可能通过影响巨噬细胞的极化状态,进而调节炎症反应和脂质代谢[60]。
VEGF-A在调节脂质代谢和炎症反应中的作用,这为理解激素性股骨头坏死的多因素病理机制提供了新的视角。这些发现无疑在提醒,VEGF-A可能通过影响脂质代谢,间接影响骨细胞的功能和骨组织的健康状况,这可能为开发针对脂质代谢异常相关骨疾病的新疗法提供了线索。
2.5 VEGF-A靶向治疗的临床应用前景 VEGF-A的靶向治疗在激素性股骨头坏死中具有潜在的应用前景。通过提高局部VEGF-A的表达或利用VEGF-A蛋白递送系统,可能促进股骨头的血管再生和骨组织修复。见表2。
2.5.1 基因治疗与组织工程 基因转染技术的最新研究表明,通过慢病毒介导的内皮细胞转染可以成功建立高表达VEGF-A的细胞系[61],这种技术不仅能够用于体外评估VEGF-A对再内皮化和支架内再狭窄的影响,还显示出VEGF-A过表达促进细胞增殖、迁移和血管内皮样管形成的能力。在血管再生治疗中,强调局部集中和持续地使用生长因子,而不是单次快速静脉注射,并且许多天然、合成和复合材料被用作血管生长因子的释放载体[33],例如聚乳酸-羟基乙酸共聚物微粒可以实现VEGF-A的缓释,改善血管生成和组织重塑。 组织工程化骨的骨化过程是一个多细胞因子作用下的复杂过程,需要进一步研究各因子的最佳作用浓度、时间和先后顺序。最新研究表明,多种生长因子的浓缩物能够上调骨膜来源细胞的成血管相关因子及蛋白的表达,单一生长因子的使用不足以创造稳定的血管结构,因为许多生长因子是协同作用的,例如VEGF-A和成纤维细胞生长因子2联合促进骨髓基质细胞驱动骨再生的研究中,证实在促进新血管形成上双因子明显优于单因子,显示了多因子联合促血管化作用的重要性[62],为组织工程领域早期快速血管化问题的解决提供了新思路。近期研究进展表明,细胞-支架或细胞因子-支架策略在组织工程骨的快速血管化方面取得了重要成就,调节各种细胞或细胞因子以满足自然骨发育中骨形成和血管生成的严格空间模式和时间模式,模拟自然骨的生理状态,是创造快速血管化组织工程骨值得探索的方向[63]。
2.5.2 VEGF-A蛋白递送系统的开发 最新的研究进展显示,通过将VEGF-A mRNA封装在可电离脂质介导的纳米颗粒中,如脂质纳米粒,可以有效递送到体内以表达所需的VEGF-A蛋白,从而加速糖尿病伤口的愈合[64]。这种递送系统通过微流体方法制备,得到的纳米颗粒具有规则的球形形态,平均粒径为101.17 nm,窄多分散性为0.17,负Zeta电位为-3.05 mV。通过细胞增殖、迁移和管形成测定,针对人脐静脉内皮细胞评估了纳米颗粒制剂的生物活性,发现脂质纳米粒/VEGF-A mRNA纳米粒可促进内皮细胞增殖,并在体内外表现出成功的mRNA递送和高VEGF-A蛋白表达。中国科学院化学工程学院的研究团队与北京朝阳医院、澳大利亚昆士兰大学合作,基于调节性T细胞来源的外泌体巧妙负载了VEGF抗体,通过新的递送模式以及新的拮抗机制,显著抑制了眼底新生血管性疾病的进展[65]。这种基于外泌体的递送系统提供了一种新的VEGF-A递送策略,可以提高药物疗效并减少不良反应。VEGF-A蛋白的稳定性和生物活性是其递送系统开发的关键。研究表明,通过蛋白质工程策略,可以提高VEGF-A结合分子的热稳定性和改善其生物分布。例如,通过PROSS算法和定向进化方法,可以对构成二聚体的亲和体单体进行工程改造,从而提高其热稳定性和VEGFR2的结合亲和力[66]。
2.5.3 细胞外囊泡 VEGF-A不仅仅以游离形式存在,它可以通过细胞外囊泡的形式被细胞分泌。细胞外囊泡能够将VEGF-A从其产生的细胞运输到周围组织,甚至远端细胞,从而扩大VEGF-A的作用范围[67]。这一过程中,VEGF-A在内质网内被剪切和修饰,并在高尔基体内进行糖基化,随后与细胞膜成分一起脱落释放,以细胞外囊泡的形式存在[68]。细胞外囊泡携带的VEGF-A可能增加了其在组织和循环中的稳定性,保护VEGF-A不被快速降解,从而延长其生物活性,这种稳定性的提升对于VEGF-A在血管生成和炎症反应中的长期效应至关重要。富含VEGF-A的细胞外囊泡可以靶向性地作用于内皮细胞,有效地促进血管生长和增加血管通透性。
这些递送系统的研究和开发是实现VEGF-A治疗激素性股骨头坏死临床应用的关键,它们能够提高其稳定性和生物利用度,从而提高治疗效果。随着纳米技术和生物材料科学的进步,未来可能会开发出更多创新的VEGF-A递送系统,以实现更精准和有效的治疗。
2.5.4 VEGF-A与其他治疗方法的联合应用 一项随机双盲研究显示,抗凝和扩血管药物的联合应用可以降低激素性股骨头坏死的发生率和塌陷率[69]。在这项研究中,预防组患者接受抗凝和扩血管治疗,与对照组相比,预防组的股骨头坏死发生率和股骨头生存率有显著改善,这表明VEGF-A与抗凝及扩血管药物的联合应用可能通过改善股骨头的血液供应,减少坏死区域,从而在治疗激素性股骨头坏死中发挥作用。一项研究发现,与自体骨髓间充质干细胞共植入的掺锶聚磷酸钙可以增强VEGF的表达,促进成骨,并在不削弱力学强度的情况下促进血管生成[70]。这种联合应用提供了一种新的治疗策略,通过促进血管生成和骨修复来治疗股骨头坏死。
在肿瘤治疗领域,双特异性抗体的研究取得了显著进展。例如,PM8002/BNT327作为一种创新的双特异性抗体药物,将抗PD-L1单域抗体与VEGF-A IgG1抗体融合,用于治疗EGFR-TKI耐药的非小细胞肺癌患者[71]。这种双特异性抗体的设计为VEGF-A与其他治疗分子的联合应用提供了新思路,可能在股骨头坏死的治疗中也具有潜在的应用价值。
综上所述,通过精确控制VEGF-A与其他药物的联合应用,可能实现对激素性股骨头坏死更全面的治疗效果,尤其是在改善股骨头血供和促进骨组织修复方面。

| [1] 内蒙古医科大学第二附属医院. 糖皮质激素诱导缺氧状态及程序性细胞死亡在股骨头坏死中调控机制[Z]. 2023 [2] 张煦坚, 赵振群, 刘万林. 激素性股骨头缺血坏死发病机制中的内质网应激[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2021,25(11):1759-1765. [3] 赵千增, 赵振群, 刘万林. 激素性股骨头缺血坏死过程中内质网应激调控自噬与凋亡的作用[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2021,25(29):4685-4690. [4] 刘万林, 郝廷, 冯卫, 等. 家兔激素性股骨头缺血坏死血管壁中差异表达基因的研究[J]. 中华创伤骨科杂志,2008,10(11):1058-1061. [5] YANG H S, YAU W W, CARLYLE B C, et al. Plasma VEGFA and PGF impact longitudinal tau and cognition in preclinical Alzheimer’s disease. Brain. 2024;147(6):2158-2168. [6] 冯卫, 刘万林, 苏秀兰, 等. 激素性股骨头缺血坏死与血管壁中主要促血管生长因子生理活性关系的实验研究[J]. 中华创伤骨科杂志,2008, 10(10):960-964. [7] 郝廷, 刘万林, 苏秀兰. 血管内皮生长因子与激素性股骨头坏死关系的研究进展[J]. 临床医学工程,2009,16(1):85-87. [8] ZHOU Y, ZHU X, CUI H, et al. The Role of the VEGF Family in Coronary Heart Disease. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2021;8:738325. [9] APTE RS, CHEN DS, FERRARA N. VEGF in Signaling and Disease: Beyond Discovery and Development. Cell. 2019;176(6):1248-1264. [10] RIBATTI D. The contribution of Harold F. Dvorak to the study of tumor angiogenesis and stroma generation mechanisms. Endothelium. 2007; 14(3):131-135. [11] PANIGRAHY D, SINGER S, SHEN LQ, et al. PPARgamma ligands inhibit primary tumor growth and metastasis by inhibiting angiogenesis. J Clin Invest. 2002;110(7):923-932. [12] RAHBAR R, VARGAS SO, FOLKMAN J, et al. Role of vascular endothelial growth factor-A in recurrent respiratory papillomatosis. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 2005;114(4):289-295. [13] SAHAY G, QUERBES W, ALABI C, et al. Efficiency of siRNA delivery by lipid nanoparticles is limited by endocytic recycling. Nat Biotechnol.2013;131(7): 653-658. [14] SA-NGUANRAKSA D, O-CHAROENRAT P. The role of vascular endothelial growth factor a polymorphisms in breast cancer. Int J Mol Sci. 2012;13(11):14845-14864. [15] UEMURA A, FRUTTIGER M, D’AMORE PA, et al. VEGFR1 signaling in retinal angiogenesis and microinflammation. Prog Retin Eye Res. 2021;84: 100954. [16] ZHAO Y, GUO S, DENG J, et al. VEGF/VEGFR-Targeted Therapy and Immunotherapy in Non-small Cell Lung Cancer: Targeting the Tumor Microenvironment. Int J Biol Sci. 2022;18(9): 3845-3858. [17] WANG HJ, RAN HF, YIN Y, et al. Catalpol improves impaired neurovascular unit in ischemic stroke rats via enhancing VEGF-PI3K/AKT and VEGF-MEK1/2/ERK1/2 signaling. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2022;43(7): 1670-1685. [18] LIANG N, LI Y, CHUNG HY. Two natural eudesmane-type sesquiterpenes from Laggera alata inhibit angiogenesis and suppress breast cancer cell migration through VEGF- and Angiopoietin 2-mediated signaling pathways. Int J Oncol. 2017; 51(1):213-222. [19] CHATTERJEE S, PATRA D, GHOSH P, et al. Activity of ROCKII not ROCKI promotes pulmonary metastasis of melanoma cells via modulating Smad2/3-MMP9 and FAK-Src-VEGF signalling. Cell Signal. 2022;97: 110389. [20] LEUNG DW, CACHIANES G, KUANG WJ, et al. Vascular endothelial growth factor is a secreted angiogenic mitogen. Science. 1989;246(4935): 1306-1309. [21] WATARI K, SHIBATA T, FUJITA H, et al. NDRG1 activates VEGF-A-induced angiogenesis through PLCγ1/ERK signaling in mouse vascular endothelial cells. Commun Biol. 2020;3(1):107. [22] FARZANEH BEHELGARDI M, ZAHRI S, GHOLAMI SHAHVIR Z, et al. Targeting signaling pathways of VEGFR1 and VEGFR2 as a potential target in the treatment of breast cancer. Mol Biol Rep. 2020;47(3):2061-2071. [23] FEARNLEY GW, BRUNS AF, WHEATCROFT SB, et al. VEGF-A isoform-specific regulation of calcium ion flux, transcriptional activation and endothelial cell migration. Biol Open. 2015;4(6):731-742. [24] WANG XY, MA TL, CHEN KN, et al. Accumulation of LDL/ox-LDL in the necrotic region participates in osteonecrosis of the femoral head: a pathological and in vitro study. Lipids Health Dis. 2021;20(1): 167. [25] 鱼铁羲. 血栓形成倾向在非创伤性股骨头坏死发生中的研究进展[J]. 临床骨科杂志,2021, 24(5):756-760. [26] MA L, FENG X, WANG K, et al. Dexamethasone promotes mesenchymal stem cell apoptosis and inhibits osteogenesis by disrupting mitochondrial dynamics. FEBS Open Bio. 2020;10(2):211-220. [27] TAO SC, YUAN T, RUI BY, et al. Exosomes derived from human platelet-rich plasma prevent apoptosis induced by glucocorticoid-associated endoplasmic reticulum stress in rat osteonecrosis of the femoral head via the Akt/Bad/Bcl-2 signal pathway. Theranostics. 2017;7(3):733-750. [28] DUAN P, WANG H, YI X, et al. C/EBPα regulates the fate of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and steroid-induced avascular necrosis of the femoral head by targeting the PPARγ signalling pathway. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2022;13(1):342. [29] JING J, ZHONG X, LIU BC, et al. [Research progress of vascular endothelial growth factor-A and its isoforms in kidney disease]. Sheng li xue bao. 2022;74(1):59-66. [30] 贾岩波, 刘万林, 任逸众. 激素性股骨头坏死发病机制中细胞凋亡的研究进展[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2012,16(13):2444-2450. [31] 赵振群, 张志峰, 刘万林, 等. 激素性股骨头坏死过程中低氧诱导因子1α与骨细胞凋亡[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2015,19(51):8201-8207. [32] MA J, REN Y, WANG B, et al. [Progress of developmental mechanism of subtype H vessels in osteonecrosis of the femoral head]. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2021;35(11): 1486-1491. [33] 特列克·坎扎勒, 叶尔扎提·哈加合曼, 金格勒. 组织工程骨血管化研究进展[J]. 中国科技论文在线精品论文,2017,10(11):1189-1195. [34] 白志刚, 刘万林, 苏秀兰, 等. VEGFmRNA与BMP-2在非创伤性股骨头坏死中表达的研究[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志,2009, 17(3):224-227. [35] FENG W, TU X. All-trans retinoic acid and vascular endothelial growth factor induced the directional osteogenic differentiation of mouse embryonic fibroblasts. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2020;34(2):246-255. [36] MONTI F, PERAZZA F, LEONI L, et al. RANK-RANKL-OPG Axis in MASLD: Current Evidence Linking Bone and Liver Diseases and Future Perspectives. Int J Mol Sci. 2024;25(17):9193. [37] STUANI AS, SILVANO P, ARNEZ MFM, et al. VEGF and FGF-2 Released In Palatal Suture after Rapid Maxillary Expansion (RME). Braz Dent J. 2021;32(1):98-103. [38] WU J, CAI P, LU Z, et al. Identification of potential specific biomarkers and key signaling pathways between osteogenic and adipogenic differentiation of hBMSCs for osteoporosis therapy. J Orthop Surg Res. 2020;15(1):437. [39] KUSUYAMA J, BANDOW K, SHAMOTO M, et al. Low intensity pulsed ultrasound (LIPUS) influences the multilineage differentiation of mesenchymal stem and progenitor cell lines through ROCK-Cot/Tpl2-MEK-ERK signaling pathway. J Biol Chem. 2014;289(15):10330-10344. [40] ZHAO SJ, KONG FQ, JIE J, et al. Macrophage MSR1 promotes BMSC osteogenic differentiation and M2-like polarization by activating PI3K/AKT/GSK3β/β-catenin pathway. Theranostics. 2020; 10(1):17-35. [41] SONG S, ZHANG G, CHEN X, et al. HIF-1α increases the osteogenic capacity of ADSCs by coupling angiogenesis and osteogenesis via the HIF-1α/VEGF/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway. J Nanobiotechnology. 2023;21(1):257. [42] XU Y, JIANG Y, WANG Y, et al. LINC00473 rescues human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells from apoptosis induced by dexamethasone through the PEBP1mediated Akt/Bad/Bcl2 signaling pathway. Int J Mol Med. 2021;47(1): 171-182. [43] BURGER MG, GROSSO A, BRIQUEZ PS, et al. Robust coupling of angiogenesis and osteogenesis by VEGF-decorated matrices for bone regeneration. Acta Biomater. 2022;149:111-125. [44] LIN M, YANG J, YAN W, et al. [Research progress of tissue engineering technology in promoting revascularization of necrotic femoral bone tissue]. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2021; 35(11):1479-1485. [45] HUANG C, SHI S, QIN M, et al. A Composite Hydrogel Functionalized by Borosilicate Bioactive Glasses and VEGF for Critical-Size Bone Regeneration. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2024;11(26): e2400349. [46] 贾月欣, 杨光路. 血管内皮生长因子(VEGF)与神经系统疾病相关性研究进展[J]. 世界最新医学信息文摘(连续型电子期刊),2020,20(32): 130-131. [47] XU L, XIANG W, YANG J, et al. PHB2 promotes SHIP2 ubiquitination via the E3 ligase NEDD4 to regulate AKT signaling in gastric cancer. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2024;43(1):17. [48] THAPA N, CHEN M, HORN HT, et al. Phosphatidylinositol-3-OH kinase signalling is spatially organized at endosomal compartments by microtubule-associated protein 4. Nat Cell Biol. 2020;22(11):1357-1370. [49] HANG X, ZHAO L, WU B, et al. BCL-2 isoform β promotes angiogenesis by TRiC-mediated upregulation of VEGF-A in lymphoma. Oncogene. 2022;41(28):3655-3663. [50] LUO X, ZHAO M, LIU S, et al. Effect of Oroxylum indicum on hepatocellular carcinoma via the P53 and VEGF pathways based on microfluidic chips. BMC Complement Med Ther. 2023;23(1):400. [51] LI J, MA A, LAN W, et al. Platycodon D-induced A549 Cell Apoptosis through RRM1-Regulated p53/VEGF/ MMP2 Pathway. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2022;22(13):2458-2467. [52] TANG H, ZHANG S, HUANG C, et al. MiR-448-5p/VEGFA Axis Protects Cardiomyocytes from Hypoxia Through Regulating the FAS/FAS-L Signaling Pathway. Int Heart J. 2021;62(3): 647-657. [53] YANG HB, KIM HY, KIM SH, et al. Suppressive role of vascular endothelial growth factor on intestinal apoptosis in induced necrotizing enterocolitis in rats. Ann Surg Treat Res. 2023;105(3):157-164. [54] YANG Z, MO X, GONG Q, et al. Critical effect of VEGF in the process of endothelial cell apoptosis induced by high glucose. Apoptosis. 2008;13(11): 1331-1343. [55] 龚瑜林, 李云隆, 刘万林, 等. mTOR短发卡RNA靶向调控血管内皮细胞自噬在激素性股骨头坏死中作用机制[J]. 中华实验外科杂志, 2021,38(7):1234-1237. [56] ZHOU Y, ZHU X, WANG H, et al. The Role of VEGF Family in Lipid Metabolism. Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2023;24(2):253-265. [57] DONG J, LI M, PENG R, et al. ACACA reduces lipid accumulation through dual regulation of lipid metabolism and mitochondrial function via AMPK- PPARα- CPT1A axis. J Transl Med. 2024; 22(1):196. [58] LU Y, WEI X, CHEN M, et al. Non-ceruloplasmin-bound copper and copper speciation in serum with extraction using functionalized dendritic silica spheres followed by ICP-MS detection. Anal Chim Acta. 2023;1251:340993. [59] CUSI K, ALKHOURI N, HARRISON SA, et al. Efficacy and safety of PXL770, a direct AMP kinase activator, for the treatment of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (STAMP-NAFLD): a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 2a study. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2021;6(11): 889-902. [60] ZHOU W, LIU K, ZENG L, et al. Targeting VEGF-A/VEGFR2 Y949 Signaling-Mediated Vascular Permeability Alleviates Hypoxic Pulmonary Hypertension. Circulation. 2022;146(24): 1855-1881. [61] WU X, ZHAO Y, TANG C, et al. Re-Endothelialization Study on Endovascular Stents Seeded by Endothelial Cells through Up- or Downregulation of VEGF. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2016;8(11): 7578-7589. [62] STONE OA, CARTER JG, LIN PC, et al. Differential regulation of blood flow-induced neovascularization and mural cell recruitment by vascular endothelial growth factor and angiopoietin signalling. J Physiol. 2017;595(5): 1575-1591. [63] LV N, ZHOU Z, HOU M, et al. Research progress of vascularization strategies of tissue-engineered bone. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2023;11: 1291969. [64] ZHA W, WANG J, GUO Z, et al. Efficient delivery of VEGF-A mRNA for promoting diabetic wound healing via ionizable lipid nanoparticles. Int J Pharm. 2023;632:122565. [65] TIAN Y, ZHANG F, QIU Y, et al. Reduction of choroidal neovascularization via cleavable VEGF antibodies conjugated to exosomes derived from regulatory T cells. Nat Biomed Eng. 2021;5(9): 968-982. [66] SAWAMIPHAK S, SEIDEL S, ESSMANN CL, et al. Ephrin-B2 regulates VEGFR2 function in developmental and tumour angiogenesis. Nature. 2010;465(7297):487-491. [67] CHINNICI CM, IANNOLO G, CITTADINI E, et al. Extracellular Vesicle-Derived microRNAs of Human Wharton’s Jelly Mesenchymal Stromal Cells May Activate Endogenous VEGF-A to Promote Angiogenesis. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(4):2045. [68] TREPS L, PERRET R, EDMOND S, et al. Glioblastoma stem-like cells secrete the pro-angiogenic VEGF-A factor in extracellular vesicles. J Extracell Vesicles. 2017;6(1):1359479. [69] 刘保一, 杨磊, 王本杰, 等. 激素性股骨头坏死的预防与内科治疗的长期临床随访观察[J]. 中华医学杂志,2017,97(41):3213-3218. [70] MONT MA, SALEM HS, PIUZZI NS, et al. Nontraumatic Osteonecrosis of the Femoral Head: Where Do We Stand Today? A 5-Year Update. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2020;102(12):1084-1099. [71] ZHAO Y, CHEN G, CHEN J, et al. AK112, a novel PD-1/VEGF bispecific antibody, in combination with chemotherapy in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC): an open-label, multicenter, phase II trial. E Clin Med. 2023; 62:102106. |
| [1] | 王正业, 刘万林, 赵振群. miRNA在激素诱导股骨头坏死机制中的研究进展[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(5): 1207-1214. |
| [2] | 杨 肖, 白月辉, 赵甜甜, 王东昊, 赵 琛, 袁 硕. 颞下颌关节骨关节炎软骨退变:机制及再生的挑战[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(4): 926-935. |
| [3] | 杨 虎, 郑 宇, 贾承明, 王 通, 张广飞, 纪垚垚. 免疫微环境调节骨再生[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(3): 701-710. |
| [4] | 卢永恒, 朱 双, 赵飞艳, 艾福军, 刘艳洁, 董阳婷, 官志忠, 魏 娜. 氟暴露对原代神经细胞内质网-线粒体钙转移及细胞凋亡的影响[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(1): 111-119. |
| [5] | 吴芷菁, 李加利, 张佳昕, 王唐蓉, 郑煜洲, 孙梓暄. α-酮戊二酸工程化小细胞外囊泡延缓皮肤衰老[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(1): 120-129. |
| [6] | 徐海超, 罗丽花, 潘乙怀. 牙髓干细胞及衍生产物在牙髓再生中的应用与进展[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(1): 153-162. |
| [7] | 刘 宇, 龚森怡, 杨丽华, 李伟风, 胡玉雯, 闫钦彪, 郭美锦. 间充质干细胞来源外泌体分离、鉴定技术及应用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(1): 194-203. |
| [8] | 尹 路, 蒋川锋, 陈俊杰, 易 明, 王子赫, 石厚银, 汪国友, 沈骅睿. 沙苑子苷A对关节软骨细胞凋亡的影响[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(8): 1541-1547. |
| [9] | 万玲玲, 吴梦滢, 张宇骄, 罗青清. 炎性因子干扰素γ以焦亡途径影响人血管平滑肌细胞的迁移和凋亡[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(7): 1422-1428. |
| [10] | 李佳林, 张耀东, 娄艳茹, 于 洋, 杨 蕊. 间充质干细胞分泌组发挥作用的分子机制[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(7): 1512-1522. |
| [11] | 贺光辉, 原 杰, 柯燕琴, 丘小婷, 张晓玲. Hemin调控小鼠软骨细胞氧化应激的线粒体途径[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(6): 1183-1191. |
| [12] | 何 波, 陈 文, 马岁录, 何志军, 宋 渊, 李金鹏, 刘 涛, 魏晓涛, 王威威, 谢 婧. 皮瓣缺血再灌注损伤的发病机制及治疗进展[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(6): 1230-1238. |
| [13] | 兰双笠, 向飞帆, 邓光慧, 肖喻琨, 阳运康, 梁 杰. 柚皮苷抑制骨质疏松大鼠骨组织的铁沉积及细胞凋亡[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(5): 888-898. |
| [14] | 张熊劲夫, 陈奕达, 程歆怡, 刘岱珲, 施 勤. 年轻大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞来源外泌体逆转老龄大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞衰老[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(36): 7709-7718. |
| [15] | 周 洋, 刘可鑫, 王得利, 孙 璋. 工程化细胞外囊泡修复骨缺损的再生作用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(36): 7839-7847. |
VEGF-A是一种具有高度特异性的促血管生成活性的生长因子,它通过与血管内皮细胞上的血管内皮生长因子受体
(vascular endothelial growth factor receptors,
VEGFRs)结合,激活下游信号通路,促进血管内皮细胞的增殖、迁移和血管生成[5]。在激素性股骨头坏死中,VEGF-A的表达降低可能导致骨组织内血管数量减少,从而加剧股骨头的缺血状态[6]。
此外,VEGF-A还具有抗凋亡作用,能够减少骨细胞和骨髓细胞的凋亡,保护骨组织。因此,VEGF-A在激素性股骨头坏死的治疗中具有重要的潜在价值[7]。
此次综述旨在总结VEGF-A在激素性股骨头坏死中的作用机制,包括其在促进血管生成、抗凋亡以及调节脂质代谢等方面的研究进展[8]。同时,也将讨论VEGF-A靶向治疗的临床应用前景,包括基因治疗和蛋白递送系统在直接将VEGF-A递送到股骨头以促进局部血管化中的应用。通过这些研究整合及分析,以期能够为激素性股骨头坏死的治疗提供新的视角和策略,改善患者的预后。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:人工关节;骨植入物;脊柱;骨折;内固定;数字化骨科;组织工程
1.1.1 检索人及检索时间 由第一作者在 2024年11月进行检索。
1.1.2 文献检索时限 各数据库建库至2024年11月。
1.1.3 检索数据库 PubMed、中国知网、万方数据库及维普数据库。
1.1.4 检索词 英文检索词为“steroid-
induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head,VEGF-A/VEGF,biomarker,therapeutic
target,apoptosis,endothelial injury,osteocyte apoptosis,osteonecrosis,lipid metabolism,signaling pathway,PI3K/Akt”;中文检索词为“激素性股骨头坏死,股骨头坏死,VEGF-A/VEGF,生物标志物,治疗靶点,凋亡,血管内皮损伤,骨坏死,脂质代谢,信号通路,PI3K/Akt”。
1.1.5 检索文献类型 研究原著及综述。
1.1.6 手工检索情况 手工查阅相关书籍《激素性股骨头坏死的病因及诊疗》。
1.1.7 检索策略 以中国知网与PubMed数据库检索策略为例,见图1。
1.1.8 检索文献量 初步检索得到文献
1 911篇,包括英文文献 1 121篇、中文文献790篇,其中PubMed 数据库1 021篇、中国知网203篇、万方数据库384篇、维普数据库303篇。
1.2 入组标准
1.2.1 纳入标准 ①选择与miRNA在激素诱导的股骨头坏死中的作用机制、生物标志物和治疗有关的文章;②文献质量、相关性、可靠性高,或创新性较为突出的文献;③优先选择最近10年内发表的文献。
1.2.2 排除标准 ①与研究主题无关的文献;②重复性文献;③观点陈旧或存在争议的文献。
1.3 文献质量评价和筛选 共检索到1 911篇文献,初筛剔除重复文献后,通过泛读对剩余文献的标题、摘要进行筛选,无法判别时精读全文,选取与主题更为相符的文献,最终纳入符合要求的文献71篇,包括英文文献57篇、中文文献 14篇。文献筛选流程详见图2。
1.4 数据的提取 研究文献由相互独立的3人提取并通过小组多次讨论解决分歧。信息记录侧重于VEGF-A靶向调控血管化治疗激素性股骨头坏死的机制方面的最新研究进展。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:人工关节;骨植入物;脊柱;骨折;内固定;数字化骨科;组织工程
文题释义:
激素诱导的股骨头坏死:其特征是股骨头血供中断和软骨下骨坏死,导致关节功能障碍。长期使用糖皮质激素是其主要诱因,病理机制涉及多个因素,包括血管内凝血和骨细胞凋亡等。血管内皮生长因子A:是一种具有高度特异性促血管生成活性的生长因子,它通过与血管内皮细胞上的血管内皮生长因子受体结合,激活下游信号通路,诱导内皮细胞迁移及增殖,以促进血管的生成。#br# #br#
这篇关于VEGF-A在激素性股骨头坏死治疗中作用机制的文章,具有以下几个显著特点和重要意义。首先,文章从多角度深入分析了VEGF-A在促进血管生成、抗凋亡、调节脂质代谢以及促进骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化中的作用,这种全面性为理解VEGF-A在激素性股骨头坏死中的复杂作用机制提供了坚实的基础。其次,文章通过系统性综述,整合了来自多个数据库的文献资源,为读者提供了一个全面的VEGF-A研究视角,这不仅对基础科研人员有所启发,也对临床医生在制定治疗方案时具有指导价值。文章的创新之处在于,它不仅讨论了VEGF-A的传统作用,还介绍了VEGF-A蛋白递送系统的新进展,包括脂质纳米粒和基于外泌体的递送系统,这些新型递送系统的开发为VEGF-A的临床应用提供了新的可能性。此外,文章提出的VEGF-A与其他治疗策略联合应用的潜力,可能为提高激素性股骨头坏死的治疗效果提供新的途径。总体而言,这篇文章在VEGF-A与激素性股骨头坏死的研究领域提供了新的见解,随着对VEGF-A作用机制的进一步阐明和递送技术的不断进步,期待这些研究成果能够转化为改善激素性股骨头坏死患者预后的临床应用,这不仅对科研领域有重要贡献,也对临床治疗具有深远影响。#br#
#br#
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:人工关节;骨植入物;脊柱;骨折;内固定;数字化骨科;组织工程#br#
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||