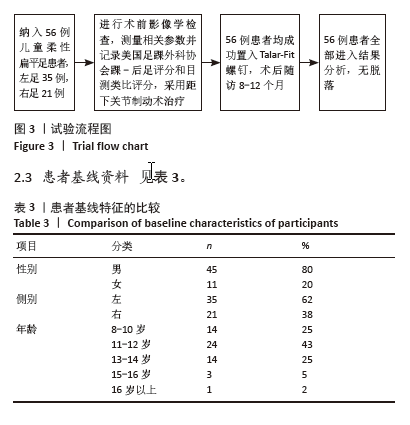
[1] BOBIŃSKI A, TOMCZYK Ł, REICHERT P, et al. Short-term and medium-term radiological and clinical assessment of patients with symptomatic flexible flatfoot following subtalar arthroereisis with Spherus screw. J Clin Med. 2023;12(15):5038.
[2] UEKI Y, SAKUMA E, WADA I. Pathology and management of flexible flat foot in children. J Orthop Sci. 2019;24(1):9-13.
[3] YAMASHITA T, SATO M, ATA S, et al. Predictors of flatfoot in 11-12-year olds: a longitudinal cohort study. Biomed Eng Online. 2024;23(1):83.
[4] PAVONE V, TESTA G, VESCIO A, et al. Diagnosis and treatment of flexible flatfoot: results of 2019 flexible flatfoot survey from the European Paediatric Orthopedic Society. Journal of Pediatric Orthopaedics Part B. 2021;30(5):450-457.
[5] LI B, HE W, YU G, et al. Treatment for flexible flatfoot in children with subtalar arthroereisis and soft tissue procedures. Front Pediatr. 2021;9:656178.
[6] SMITH C, ZAIDI R, BHAMRA J, et al. Subtalar arthroereisis for the treatment of the symptomatic paediatric flexible pes planus: a systematic review. EFORT Open Rev. 2021;6(2):118-129.
[7] HEGAZY FA, ABOELNASR EA, SALEM Y, et al. Validity and diagnostic accuracy of foot posture index-6 using radiographic findings as the gold standard to determine paediatric flexible flatfoot between ages of 6-18 years: a cross-sectional study. Musculoskelet Sci Pract. 2020;46:102107.
[8] 邓明明,孙广超,杜瑞,等.两种术式治疗儿童柔韧性平足合并痛性副舟骨疗效比较[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2023,37(10):1225-1229.
[9] 潘旭月,魏芳远,陈卫衡.青少年柔韧性扁平足距下关节制动术长期疗效与韧带松弛程度的相关性[J].中华骨与关节外科杂志, 2024,17(4):347-353.
[10] METCALFE SA, BOWLING FL, REEVES ND. Subtalar joint arthroereisis in the management of pediatric flexible flatfoot: a critical review of the literature. Foot Ankle Int. 2011;32(12):1127-1139.
[11] SHI C, LI M, ZENG Q, et al. Subtalar arthroereisis combined with medial soft tissue reconstruction in treating pediatric flexible flatfoot with accessory navicular. J Orthop Surg Res. 2023;18(1):55.
[12] SOLTANOLKOTABI M, MALLORY C, ALLEN H, et al. Postoperative findings of common foot and ankle surgeries: an imaging review. Diagnostics (Basel). 2022; 12(5):1090.
[13] 严广斌.AOFAS踝-后足评分系统[J].中华关节外科杂志(电子版), 2014,8(4):557.
[14] 万丽,赵晴,陈军,等.疼痛评估量表应用的中国专家共识(2020版)[J]. 中华疼痛学杂志,2020,16(3):177-187.
[15] MURLEY GS, MENZ HB, LANDORF KB. A protocol for classifying normal- and flat-arched foot posture for research studies using clinical and radiographic measurements. J Foot Ankle Res. 2009;2:22.
[16] DAGNEAUX L, MORONEY P, MAESTRO M. Reliability of hindfoot alignment measurements from standard radiographs using the methods of Meary and Saltzman. Foot Ankle Surg. 2019;25(2):237-241.
[17] GIANNINI S, CADOSSI M, MAZZOTTI A, et al. Bioabsorbable Calcaneo-Stop implant for the treatment of flexible flatfoot: a retrospective cohort study at a minimum follow-up of 4 years. J Foot Ankle Surg. 2017;56(4):776-782.
[18] NEEDLEMAN RL. Current topic review: subtalar arthroereisis for the correction of flexible flatfoot. Foot Ankle Int. 2005;26(4):336-346.
[19] LI B, HE W, YU G, et al. Treatment for flexible flatfoot in children with subtalar arthroereisis and soft tissue procedures. Front Pediatr. 2021;9:656178.
[20] WONG DW, WANG Y, NIU W, et al. Finite element analysis of subtalar joint arthroereisis on adult-acquired flexible flatfoot deformity using customised sinus tarsi implant. J Orthop Translat. 2020;27:139-145.
[21] DE PELLEGRIN M, MOHARAMZADEH D. Subtalar arthroereisis for surgical treatment of flexible flatfoot. Foot Ankle Clin. 2021;26(4):765-805.
[22] BERNASCONI A, ARGYROPOULOS M, PATEL S, et al. Subtalar arthroereisis as an adjunct procedure improves forefoot abduction in stage IIb adult-acquired flatfoot deformity. Foot Ankle Spec. 2022; 15(3):209-220.
[23] XIE HG, CHEN L, GENG X, et al. Mid-term assessment of subtalar arthroereisis with Talar-Fit implant in pediatric patients with flexible flatfoot and comparing the difference between different sizes and exploring the position of the inserted implant. Front Pediatr. 2023;11:1258835.
[24] HAGEN L, KOSTAKEV M, PAPE JP, et al. Are there benefits of a 2D gait analysis in the evaluation of the subtalar extra-articular screw arthroereisis? Short-term investigation in children. Clin Biomechanics (Bristol, Avon). 2019;63:73-78.
[25] GRAHAM ME, JAWRANI NT, CHIKKA A. Extraosseous talotarsal stabilization using HyProCure® in adults: a 5-year retrospective follow-up. J Foot Ankle Surg. 2012;51(1):23-29.
[26] DE PELLEGRIN M, MOHARAMZADEH D, STROBL WM, et al. Subtalar extra-articular screw arthroereisis (SESA) for the treatment of flexible flatfoot in children. J Child Orthop. 2014;8(6):479-487.
[27] 曹洪,赵飞,Sauro Angelici,等.经跗骨窦HyProCure螺钉治疗儿童柔韧性平足症[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2017,25(11):
1038-1041.
[28] HERDEA A, NECULAI AG, ULICI A. The role of arthroereisis in improving sports performance, foot aesthetics and quality of life in children and adolescents with flexible flatfoot. Children (Basel). 2022;9(7):973.
[29] 刘冠杰,韩煜,赵康成,等.距下关节制动术治疗柔韧性扁平足的历史与现状[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2018,26(1):52-55.
[30] SINHA S, SONG HR, KIM HJ, et al. Medial arch orthosis for paediatric flatfoot. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery (Hong Kong). 2013;21(1): 37-43.
[31] NILSSON MK, FRIIS R, MICHAELSEN MS, et al. Classification of the height and flexibility of the medial longitudinal arch of the foot. J Foot Ankle Res. 2012;5:3.
[32] SU Y, CHEN W, ZHANG T, et al. Bohler’s angle’s role in assessing the injury severity and functional outcome of internal fixation for displaced intra-articular calcaneal fractures: a retrospective study. BMC Surg. 2013;13:40.
[33] 黄立本,林小永,叶琳,等.跗骨窦螺钉联合软组织手术治疗儿童柔韧性平足症12例[J].中国中医骨伤科杂志,2022,30(7):70-74.
[34] 赵廷虎,陈汉鑫,郑挺渠,等.距下关节制动术治疗成人柔性平足症28例[J].中国中医骨伤科杂志,2023,31(2):70-74.
[35] 徐军奎,赵炼,屈福锋,等.距下关节稳定器治疗儿童柔韧性平足的中期疗效分析[J].中华骨与关节外科杂志,2018,11(2): 106-110+114.
[36] 丰波,邹英财,王永军,等.HyProcure距下关节稳定器治疗儿童柔韧性平足症的中期疗效[J].足踝外科电子杂志,2020,7(2):9-14.
[37] 李兵,俞光荣,杨云峰,等. 距下关节制动联合软组织手术治疗大龄儿童柔性平足症[J]. 中华小儿外科杂志,2020,41(4):356-360.
[38] XIE HG, CHEN L, GENG X, et al. Mid-term assessment of subtalar arthroereisis with Talar-Fit implant in pediatric patients with flexible flatfoot and comparing the difference between different sizes and exploring the position of the inserted implant. Front Pediatr. 2023;11:1258835.
[39] DE CESAR NETTO C, SHAKOOR D, ROBERTS L, et al. Hindfoot alignment of adult acquired flatfoot deformity: a comparison of clinical assessment and weightbearing cone beam CT examinations. Foot Ankle Surg. 2019;25(6):790-797.
[40] MCKEON PO, HERTEL J, BRAMBLE D, et al. The foot core system: a new paradigm for understanding intrinsic foot muscle function. Br J Sports Med. 2015;49(5):290.
[41] BUDIMAN-MAK E, CONRAD KJ, MAZZA J, et al. A review of the foot function index and the foot function index - revised. J Foot Ankle Res. 2013;6(1):5.
[42] VARNI JW, SEID M, RODE CA. The PedsQL: measurement model for the pediatric quality of life inventory. Med Care. 1999;37(2):126-139. |